Abstract
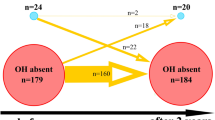
Orthostatic hypotension (OH) is a potent predictor of cardiovascular frailty. Although OH is determined by changes in brachial blood pressure (BP), it has been reported that there are significant differences between central BP and peripheral BP. The prevalence of OH has been reported to be higher in subjects with isolated systolic hypertension. Since an early returning of the reflection pressure wave due to advanced arterial stiffness is one of the underlying mechanisms of systolic hypertension, a significant association between alterations of the reflection pressure wave and OH has been hypothesized. To explore this hypothesis, the orthostatic changes in carotid BP and arterial waveform were evaluated. The study subjects were 155 community residents (69±7 years old). Carotid and brachial BP were measured simultaneously in the supine position and 1 min after standing using a cuff-oscillometric and tonometric method. The carotid augmentation index (AIx) was obtained from the pressure waveform. The orthostatic decline of BP was more prominent in the carotid artery than the brachial artery. Nine subjects were diagnosed with orthostatic systolic hypotension (OSH) from brachial BP, while 21 subjects were diagnosed from carotid BP (p<0.001). The orthostatic change in carotid systolic BP was significantly associated with that in carotid AIx (r=0.361, p<0.001). The decline of the reflection component of carotid pulse pressure (-4.0±8.4 mmHg) was more prominent than that of the incident component (-1.2±9.9 mmHg, p=0.002). These results indicate that evaluation of brachial BP may not represent the orthostatic changes in central BP. Alteration of the reflection pressure wave could be one of the underlying mechanisms of OSH in the central artery.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
References
Boddaert J, Tamim H, Verny M, Belmin J : Arterial stiffness is associated with orthostatic hypotension in elderly subjects with history of falls. J Am Geriatr Soc 2004; 52: 568–572.
Ooi WL, Hossain M, Lipsitz LA : The association between orthostatic hypotension and recurrent falls in nursing home residents. Am J Med 2000; 108: 106–111.
Matsubayashi K, Okumiya K, Wada T, et al: Postural dysregulation in systolic blood pressure is associated with worsened scoring on neurobehavioral function tests and leukoaraiosis in the older elderly living in a community. Stroke 1997; 28: 2169–2173.
Viramo P, Luukinen H, Koski K, Laippala P, Sulkava R, Kivela SL : Orthostatic hypotension and cognitive decline in older people. J Am Geriatr Soc 1999; 47: 600–604.
Rose KM, Tyroler HA, Nardo CJ, et al: Orthostatic hypotension and the incidence of coronary heart disease: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study. Am J Hypertens 2000; 13: 571–578.
Eigenbrodt ML, Rose KM, Couper DJ, Arnett DK, Smith R, Jones D : Orthostatic hypotension as a risk factor for stroke: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study, 1987–1996. Stroke 2000; 31: 2307–2313.
Eguchi K, Kario K, Hoshide S, et al: Greater change of orthostatic blood pressure is related to silent cerebral infarct and cardiac overload in hypertensive subjects. Hypertens Res 2004; 27: 235–241.
Masaki KH, Schatz IJ, Burchfiel CM, et al: Orthostatic hypotension predicts mortality in elderly men: the Honolulu Heart Program. Circulation 1998; 98: 2290–2295.
Tilvis RS, Hakala SM, Valvanne J, Erkinjuntti T : Postural hypotension and dizziness in a general aged population: a four-year follow-up of the Helsinki Aging Study. J Am Geriatr Soc 1996; 44: 809–814.
The Consensus Committee of the American Autonomic Society and the American Academy of Neurology : Consensus statement on the definition of orthostatic hypotension, pure autonomic failure, and multiple system atrophy. Neurology 1996; 46: 1470.
Nichols WW, O'Rourke MF ( eds): McDonald's Blood Flow in Arteries. Theoretical, Experimental and Clinical Principles, 4th ed. London, Arnold, 1998.
Mahmud A, Feely J : Effect of smoking on arterial stiffness and pulse pressure amplification. Hypertension 2003; 41: 183–187.
Mahmud A, Feely J : Acute effect of caffeine on arterial stiffness and aortic pressure waveform. Hypertension 2001; 38: 227–231.
Mahmud A, Feely J : Divergent effect of acute and chronic alcohol on arterial stiffness. Am J Hypertens 2002; 15: 240–243.
Murakami T : Squatting: the hemodynamic change is induced by enhanced aortic wave reflection. Am J Hypertens 2002; 15: 986–988.
Murgo JP, Westerhof N, Giolma JP, Altobelli SA : Aortic impedance in normal man: relationship to pressure waveforms. Circulation 1980; 62: 105–116.
Dart AM, Kingwell BA : Pulse pressure—a review of mechanisms and clinical relevance. J Am Coll Cardiol 2001; 37: 975–984.
Applegate WB, Davis BR, Black HR, Smith WM, Miller ST, Burlando AJ : Prevalence of postural hypotension at baseline in the Systolic Hypertension in the Elderly Program (SHEP) cohort. J Am Geriatr Soc 1991; 39: 1057–1064.
Kohara K, Tabara Y, Tachibana R, Nakura J, Miki T : Microalbuminuria and arterial stiffness in a general population: the Shimanami Health Promoting Program (J-SHIPP) study. Hypertens Res 2004; 27: 471–477.
Yamashina A, Tomiyama H, Takeda K, et al: Validity, reproducibility, and clinical significance of noninvasive brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity measurement. Hypertens Res 2002; 25: 359–364.
Cortez-Cooper MY, Supak JA, Tanaka H : A new device for automatic measurements of arterial stiffness and ankle-brachial index. Am J Cardiol 2003; 91: 1519–1522.
Safar ME, Blacher J, Pannier B, et al: Central pulse pressure and mortality in end-stage renal disease. Hypertension 2002; 39: 735–738.
Nurnberger J, Keflioglu-Scheiber A, Opazo Saez AM, Wenzel RR, Philipp T, Schafers RF : Augmentation index is associated with cardiovascular risk. J Hypertens 2002; 20: 2407–2414.
Weber T, Auer J, O'Rourke MF, et al: Arterial stiffness, wave reflections, and the risk of coronary artery disease. Circulation 2004; 109: 184–189.
Boddaert J, Tamim H, Verny M, Belmin J : Arterial stiffness is associated with orthostatic hypotension in elderly subjects with history of falls. J Am Geriatr Soc 2004; 52: 568–572.
Kohara K, Tabara Y, Yamamoto Y, Miki T : Orthostatic hypertension: another orthostatic disorder to be aware of. J Am Geriatr Soc 2000; 48: 1538–1539.
Van Bortel LM, Struijker-Boudier HA, Safar ME : Pulse pressure, arterial stiffness, and drug treatment of hypertension. Hypertension 2001; 38: 914–921.
Gatzka CD, Cameron JD, Dart AM, et al: Correction of carotid augmentation index for heart rate in elderly essential hypertensives. ANBP2 Investigators. Australian comparative outcome trial of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor- and diuretic-based treatment of hypertension in the elderly. Am J Hypertens 2001; 14: 573–577.
Wilkinson IB, Mohammad NH, Tyrrell S, et al: Heart rate dependency of pulse pressure amplification and arterial stiffness. Am J Hypertens 2002; 15: 24–30.
Smit AA, Halliwill JR, Low PA, Wieling W : Pathophysiological basis of orthostatic hypotension in autonomic failure. J Physiol 1999; 519: 1–10.
Lenard Z, Studinger P, Kovats Z, Reneman R, Kollai M : Comparison of aortic arch and carotid sinus distensibility in humans—relation to baroreflex sensitivity. Auton Neurosci 2001; 92: 92–99.
Asmar RG, London GM, O'Rourke ME, Safar ME, REASON Project Coordinators and Investigators : Improvement in blood pressure, arterial stiffness and wave reflections with a very-low-dose perindopril/indapamide combination in hypertensive patient. A comparison with atenolol. Hypertension 2001; 38: 922–926.
Maurer M, Rivadeneira H, Bloomfield D : Should orthostatic changes in blood pressure be measured after one or three minutes in elderly subjects? Am J Geriatr Cardiol 1998; 7: 29–33.
Ward C, Kenny RA : Reproducibility of orthostatic hypotension in symptomatic elderly. Am J Med 1996; 100: 418–422.
Tabara Y, Kohara K, Ohnishi M, et al: Effect of elapsed time after standing up on orthostatic blood pressure change in the elderly. Nippon Ronen Igakkai Zasshi 2002; 39: 193–196 ( in Japanese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tabara, Y., Nakura, J., Kondo, I. et al. Orthostatic Systolic Hypotension and the Reflection Pressure Wave. Hypertens Res 28, 537–543 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.28.537
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.28.537
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Indexes of cerebral autoregulation do not reflect impairment in syncope: insights from head-up tilt test of vasovagal and autonomic failure subjects
European Journal of Applied Physiology (2017)
-
Wave reflections, arterial stiffness, heart rate variability and orthostatic hypotension
Hypertension Research (2014)
-
Clinical usefulness of the second peak of radial systolic blood pressure for estimation of aortic systolic blood pressure
Journal of Human Hypertension (2009)