Abstract
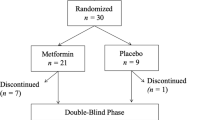
The aim of our study was to investigate the metabolic effect of telmisartan and irbesartan in subjects treated with rosiglitazone, a well-known insulin-sensitizing drug, in order to clarify the direct metabolic effects of the two former drugs. Patients were enrolled, evaluated, and followed at 3 Italian centers. We evaluated 188 type 2 diabetic patients with metabolic syndrome (94 males and 94 females in total; 49 males and 46 females, aged 56±5, treated with telmisartan; and 45 males and 48 females, aged 55±4, treated with irbesartan). All had been diabetic for at least 6 months, and glycemic control by the maximum tolerated dietary changes and maximum tolerated dose of oral hypoglycemic agents had been attempted and failed in all cases. All patients took a fixed dose of rosiglitazone, 4 mg/day. We administered telmisartan (40 mg/day) or irbesartan (150 mg/day) in a randomized, controlled, double-blind clinical manner. We evaluated body mass index (BMI), glycemic control (HbA1c, fasting plasma glucose and insulin levels [FPG, and FPI, respectively], and homeostasis model assessment [HOMA] index), lipid profile (total cholesterol [TC], low density lipoprotein-cholesterol [LDL-C], high density lipoprotein-cholesterol [HDL-C], and triglycerides [TG]), systolic and diastolic blood pressure (SBP and DBP), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and leptin during the 12 months of this treatment. No BMI change was observed after 6 or 12 months in either group. Significant decreases in HbA1c and FPG were observed after 6 months in the telmisartan group, and after 12 months in both groups. The decrease in HbA1c and FPG at 12 months was statistically significant only in the telmisartan group. A significant decrease in FPI was observed at 12 months in both groups, and this decrease was significantly greater in the telmisartan group. Significant decreases in the HOMA index were observed at 6 and 12 months in both groups, and the decrease in the HOMA index after 12 months was significantly greater in the telmisartan group than in the irbesartan group. Significant changes in SBP, DBP, TC, and LDL-C were observed after 6 and 12 months in both groups. Significant decreases in TNF-α and leptin levels were observed after 6 months in the telmisartan group, and after 12 months in both groups. In conclusion, in this study of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome, telmisartan seemed to result in a greater improvement in glycemic and lipid control and metabolic parameters related to metabolic syndrome compared to irbesartan. These observed metabolic effects of different angiotensin type 1 receptor blockers could be relevant when choosing a therapy to correct metabolic derangement of patients affected by metabolic syndrome and diabetes.
Similar content being viewed by others

Article PDF
References
American Diabetes Association : Hypertension management in adults with diabetes. Diabetes Care 2004; 27 ( Suppl 1): 65–67.
Adler AI : Treating high blood pressure in diabetes: the evidence. Semin Vasc Med 2002; 2: 127–137.
Ruilope LM, Rosei EA, Bakris GL, et al: Angiotensin receptor blockers: therapeutic targets and cardiovascular protection. Blood Press 2005; 14: 196–209.
Gradman AH : AT1-receptor blockers: differences that matter. J Hum Hypertens 2002; 16 ( Suppl 3): S90–S16.
Pylypchuk GB : ACE inhibitor— versus angiotensin II blocker—induced cough and angioedema. Ann Pharmacother 1998; 32: 1060–1066.
Sica DA, Bakris GL : Type 2 diabetes: RENAAL and IDNT—the emergence of new treatment options. J Clin Hypertens 2002; 4: 52–57.
American Diabetes Association, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases : Prevention or delay of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2004; 27 ( Suppl 1): 47–54.
Schupp M, Clemenz M, Gineste R, et al: Molecular characterization of new selective peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor γ modulators with angiotensin receptor blocking activity. Diabetes 2005; 54: 3442–3452.
American Diabetes Association : Screening for diabetes (Position Statement). Diabetes Care 2001; 24 ( Suppl): S21–S24.
Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults: Executive Summary of the Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA 2001; 285: 2486–2497.
Guidelines Subcommittee : 1999 World Health Organization–International Society of Hypertension Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension. J Hypertens 1999; 17: 151–183.
World Health Organization: Obesity: Preventing and Managing the Global Epidemic, Report of WHO Consultation on Obesity. Geneva, WHO, 1997.
American Diabetes Association : Nutrition recommendations and principles for people with diabetes mellitus (Position Statement). Diabetes Care 2001; 24 ( Suppl): S44–S47.
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC : Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985; 28: 412–419.
Bunn HF, Gabbay KH, Gallop PM : The glycosylation of haemoglobin. Relevance to diabetes mellitus. Science 1978; 200: 21–27.
European Diabetes Policy Group 1999: A desktop guide to type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med 1999; 16: 716–730.
Heding LG : Determination of total serum insulin (IRI) in insulin-treated diabetic patients. Diabetologia 1972; 8: 260–266.
Klose S, Borner K : Enzymatische Bestimmung des Gesamtcholesterins mit dem (Enzymatic dosage of total cholesterolemia by Greiner Selective Analyzer [GSA II]). J Clin Chem Clin Biochem 1978; 15: 121–130.
Wahlefeld AW : Triglycerides determination after enzymatic hydrolysis, in Bergmeyer HU ( ed): Methods of Enzymatic Analysis, 2nd English ed. New York, Academic Press, 1974, pp 18–31.
Havel RJ, Eder HA, Bragdon JH : The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest 1955; 34: 1345–1353.
Friedewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS : Estimation of the concentration of low density lipoprotein in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem 1972; 18: 499–502.
Zhang M, Tracey K : The Cytokine Handbook, 3rd ed. San Diego, Academic Press, 1988.
Misra A, Garg A : Leptin: its receptor and obesity. J Invest Med 1996; 44: 540–548.
Winer BJ : Statistical Principles in Experimental Design, 2nd ed. New York, McGraw-Hill, 1971.
Skrha J, Ambos A : Can the atherosclerosis prevention targets be achieved in type 2 diabetes? Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2005; 68 ( Suppl 1): S48–S51.
Barnett AH : Preventing renal complications in diabetic patients: the Diabetics Exposed to Telmisartan and Enalapril (DETAIL) study. Acta Diabetol 2005; 42 ( Suppl 1): S42–S49.
Miura Y, Yamamoto N, Tsunekawa S, et al: Replacement of valsartan and candesartan by telmisartan in hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetes: metabolic and antiatherogenic consequences. Diabetes Care 2005; 28: 757–758.
Bramlage P, Pittrow D, Kirch W : The effect of irbesartan in reducing cardiovascular risk in hypertensive type 2 diabetic patients: an observational study in 16,600 patients in primary care. Curr Med Res Opin 2004; 20: 1625–1631.
Ravera M, Ratto E, Vettoretti S, Parodi D, Deferrari G : Prevention and treatment of diabetic nephropathy: the program for irbesartan mortality and morbidity evaluation. J Am Soc Nephrol 2005; 16 ( Suppl 1): S48–S52.
Derosa G, Cicero AF, Gaddi A, Mugellini A, Ciccarelli L, Fogari R : Effects of doxazosin and irbesartan on blood pressure and metabolic control in patients with type 2 diabetes and hypertension. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 2005; 45: 599–604.
Derosa G, Ragonesi PD, Mugellini A, Ciccarelli L, Fogari R : Effects of telmisartan compared with eprosartan on blood pressure control, glucose metabolism and lipid profile in hypertensive, type 2 diabetic patients: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled 12-month study. Hypertens Res 2004; 27: 457–464.
Derosa G, Cicero AFG, Bertone G, et al: Comparison of the effects of telmisartan and nifedipine gastrointestinal therapeutic system on blood pressure control, glucose metabolism, and the lipid profile in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and a 12-month, randomized, double-blind study. Clin Ther 2004; 26: 1228–1236.
Derosa G, Cicero AFG, Gaddi A, et al: Metabolic effects of pioglitazone and rosiglitazone in patients with diabetes and metabolic syndrome treated with glimepiride: a twelve-month, multicenter, double-blind, randomized, controlled, parallel-group trial. Clin Ther 2004; 26: 744–754.
Derosa G, Cicero AFG, Gaddi AV, et al: Long-term effects of glimepiride or rosiglitazone in combination with metformin on blood pressure control in type 2 diabetic patients affected by the metabolic syndrome: a 12-month, double-blind, randomized clinical trial. Clin Ther 2005; 27: 1383–1391.
Clasen R, Schupp M, Foryst-Ludwig A, et al: PPARgamma-activating angiotensin type-1 receptor blockers induce adiponectin. Hypertension 2005; 46: 137–143.
Tsuchida A, Yamauchi T, Takekawa S, et al: Peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor (PPAR) α activation increases adiponectin receptors and reduces obesity-related inflammation in adipose tissue: comparison of activation of PPARα, PPARγ, and their combination. Diabetes 2005; 54: 3358–3370.
Berger JP, Petro AE, Macnaul KL, et al: Distinct properties and advantages of a novel peroxisome proliferators–activated protein (gamma) selective modulator. Mol Endocrinol 2003; 17: 662–676.
Wang M, Tafuri S : Modulation of PPARgamma activity with pharmaceutical agents: treatment of insulin resistance and atherosclerosis. J Cell Biochem 2003; 89: 38–47.
Guan HP, Ishizuka T, Chui PC, Lehrke M, Lazar MA : Corepressors selectively control the transcriptional activity of PPARgamma in adipocytes. Gene Dev 2005; 19: 453–461.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Derosa, G., Cicero, A., D'angelo, A. et al. Telmisartan and Irbesartan Therapy in Type 2 Diabetic Patients Treated with Rosiglitazone: Effects on Insulin-Resistance, Leptin and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α. Hypertens Res 29, 849–856 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.29.849
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.29.849
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Effects of two different angiotensin receptor blockers on blood glucose level and HbA1c in type-2 diabetes mellitus patients with hypertension
The Egyptian Journal of Internal Medicine (2023)
-
Chapter 5. Treatment with antihypertensive drugs
Hypertension Research (2014)
-
Effects of telmisartan therapy on interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha levels: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Hypertension Research (2013)
-
Relationship between Telmisartan Dose and Glycaemic Control in Japanese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Hypertension
Clinical Drug Investigation (2012)
-
Differential effects of candesartan and olmesartan on adipose tissue activity biomarkers in type II diabetic hypertensive patients
Hypertension Research (2010)