Abstract
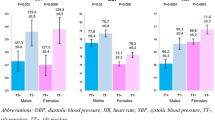
The relation between changes in blood pressure and changes in autonomic activity over a very short period of time has not been reported thus far. To examine this relation, we here introduced a new method of power spectrum analysis with wavelet transformation, which has very fine time resolution and is able to assess changes in autonomic activity quantitatively even during movement. Our subjects were 15 hypertensive and 17 normotensive subjects. A head-up tilt test was performed in all subjects, and during the test, electrocardiogram and blood pressure were recorded continuously. The power spectrums for both parameters were calculated simultaneously every 5 s using wavelet transformation. The high frequency of the RR interval of the electrocardiogram (RR-HF) and low frequency of systolic blood pressure (SBP-LF) were defined and calculated as markers of parasympathetic and α-1 receptor blocker, bunazosin-sensitive sympathetic activity, respectively. Focusing on the changes for 2 min immediately after head-up tilting, it was found that the changes in SBP-LF and RR-HF were significantly delayed, by at least 40 s, in hypertensives compared with normotensives and also in elderly compared with non-elderly subjects. Multiple regression analysis demonstrated that the instantaneous change in RR-HF was the most important confounding factor for a fall in blood pressure immediately after head-up tilting. In conclusion, real-time changes in autonomic activity calculated by wavelet transformation may provide sensitive and useful information about acute changes in cardiovascular regulation, such as delayed reaction of the autonomic regulation after head-up tilting, that may be major causes of the blood pressure fall in hypertensive and elderly subjects.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
References
Masuo K, Mikami H, Ogihara T, Tuck ML : Changes in frequency of orthostatic hypotension in elderly hypertensive patients under medications. Am J Hypertens 1996; 9: 263–268.
James MA, Potter JF : Orthostatic blood pressure changes and arterial baroreflex sensitivity in elderly subjects. Age Ageing 1999; 28: 522–530.
Ewing DJ, Hume L, Campbell IW, Murray A, Neilson JM, Clarke BF : Autonomic mechanisms in the initial heart rate response to standing. J Appl Physiol 1980; 49: 809–814.
Wieling W, Borst C, van Brederode JF, et al: Testing for autonomic neuropathy: heart rate changes after orthostatic manoeuvres and static muscle contractions. Clin Sci (Lond) 1983; 64: 581–586.
Nakao M, Nomura K, Karita K, Nishikitani M, Yano E : Relationship between brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity and heart rate variability in young Japanese men. Hypertens Res 2004; 27: 925–931.
Walther T, Wessel N, Baumert M, Stepan H, Voss A, Faber R : Longitudinal analysis of heart rate variability in chronic hypertensive pregnancy. Hypertens Res 2005; 28: 113–118.
Hilton MF, Bates RA, Godfrey KR, Chappell MJ, Cayton RM : Evaluation of frequency and time-frequency spectral analysis of heart rate variability as a diagnostic marker of the sleep apnoea syndrome. Med Biol Eng Comput 1999; 37: 760–769.
Houtveen JH, Molenaar PC : Comparison between the Fourier and Wavelet methods of spectral analysis applied to stationary and nonstationary heart period data. Psychophysiology 2001; 38: 729–735.
Toledo E, Gurevitz O, Hod H, Eldar M, Akselrod S : Wavelet analysis of instantaneous heart rate: a study of autonomic control during thrombolysis. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2003; 284: R1079–R1091.
Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology : Heart rate variability. Standards of measurement, physiological interpretation, and clinical use. Eur Heart J 1996; 17: 354–381.
Japundzic N, Grichois ML, Zitoun P, Laude D, Elghozi JL : Spectral analysis of blood pressure and heart rate in conscious rats: effects of autonomic blockers. J Auton Nerv Syst 1990; 30: 91–100.
Malliani A, Pagani M, Lombardi F, Cerutti S : Cardiovascular neural regulation explored in the frequency domain. Circulation 1991; 84: 482–492.
Persson PB, Stauss H, Chung O, Wittmann U, Unger T : Spectrum analysis of sympathetic nerve activity and blood pressure in conscious rats. Am J Physiol 1992; 263: H1348–H1355.
Brown DR, Brown LV, Patwardhan A, Randall DC : Sympathetic activity and blood pressure are tightly coupled at 0.4 Hz in conscious rats. Am J Physiol 1994; 267: R1378–R1384.
Nagai R, Nagata S, Fukuya F, Higaki J, Rakugi H, Ogihara T : Changes in autonomic activity and baroreflex sensitivity with the hypertension process and age in rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 2003; 30: 419–425.
Malliani A, Lombardi F, Pagani M : Power spectrum analysis of heart rate variability: a tool to explore neural regulatory mechanisms. Br Heart J 1994; 71: 1–2.
Montano N, Ruscone TG, Porta A, Lombardi F, Pagani M, Malliani A : Power spectrum analysis of heart rate variability to assess the changes in sympathovagal balance during graded orthostatic tilt. Circulation 1994; 90: 1826–1831.
Morillo CA, Eckberg DL, Ellenbogen KA, et al: Vagal and sympathetic mechanisms in patients with orthostatic vasovagal syncope. Circulation 1997; 96: 2509–2513.
Mosqueda-Garcia R, Furlan R, Fernandez-Violante R, et al: Sympathetic and baroreceptor reflex function in neurally mediated syncope evoked by tilt. J Clin Invest 1997; 99: 2736–2744.
Hayano J, Taylor JA, Yamada A, et al: Continuous assessment of hemodynamic control by complex demodulation of cardiovascular variability. Am J Physiol 1993; 264: H1229–H1238.
Lipsitz LA, Hayano J, Sakata S, Okada A, Morin RJ : Complex demodulation of cardiorespiratory dynamics preceding vasovagal syncope. Circulation 1998; 98: 977–983.
Jasson S, Medigue C, Maison Blanche P, et al: Instant power spectrum analysis of heart rate variability during orthostatic tilt using a time-/frequency-domain method. Circulation 1997; 96: 3521–3526.
Pereira de Souza Neto E, Custaud MA, Frutoso J, Somody L, Gharib C, Fortrat JO : Smoothed pseudo Wigner-Ville distribution as an alternative to Fourier transform in rats. Auton Neurosci 2001; 87: 258–267.
Crowe JA, Gibson NM, Woolfson MS, Somekh MG : Wavelet transform as a potential tool for ECG analysis and compression. J Biomed Eng 1992; 14: 268–272.
Chan HL, Huang HH, Lin JL : Time-frequency analysis of heart rate variability during transient segments. Ann Biomed Eng 2001; 29: 983–996.
Mainardi LT, Bianchi AM, Cerutti S : Time-frequency and time-varying analysis for assessing the dynamic responses of cardiovascular control. Crit Rev Biomed Eng 2002; 30: 175–217.
Tabara Y, Nakura J, Kondo I, Miki T, Kohara K : Orthostatic systolic hypotension and the reflection pressure wave. Hypertens Res 2005; 28: 537–543.
James MA, Robinson TG, Panerai RB, Potter JF : Arterial baroreceptor-cardiac reflex sensitivity in the elderly. Hypertension 1996; 28: 953–960.
Steptoe A, Vogele C : Cardiac baroreflex function during postural change assessed using non-invasive spontaneous sequence analysis in young men. Cardiovasc Res 1990; 24: 627–632.
Hughson RL, Maillet A, Gharib C, et al: Reduced spontaneous baroreflex response slope during lower body negative pressure after 28 days of head-down bed rest. J Appl Physiol 1994; 77: 69–77.
Kardos A, Rudas L, Simon J, Gingl Z, Csanady M : Effect of postural changes on arterial baroreflex sensitivity assessed by the spontaneous sequence method and Valsalva manoeuvre in healthy subjects. Clin Auton Res 1997; 7: 143–148.
O'Leary DD, Kimmerly DS, Cechetto AD, Shoemaker JK : Differential effect of head-up tilt on cardiovagal and sympathetic baroreflex sensitivity in humans. Exp Physiol 2003; 88: 769–774.
O'Leary DD, Lin DC, Hughson RL : Determination of baroreflex gain using auto-regressive moving-average analysis during spontaneous breathing. Clin Physiol 1999; 19: 369–377.
Eguchi K, Kario K, Hoshide S, et al: Greater change of orthostatic blood pressure is related to silent cerebral infarct and cardiac overload in hypertensive subjects. Hypertens Res 2004; 27: 235–241.
Lampert R, Ickovics JR, Viscoli CJ, Horwitz RI, Lee FA : Effects of propranolol on recovery of heart rate variability following acute myocardial infarction and relation to outcome in the Beta-Blocker Heart Attack Trial. Am J Cardiol 2003; 91: 137–142.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moriguchi, K., Rakugi, H., Nagata, S. et al. Impairment of Instantaneous Autonomic Regulation Relates to Blood Pressure Fall Immediately after Standing in the Elderly and Hypertensives. Hypertens Res 29, 557–566 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.29.557
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.29.557