Abstract
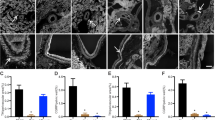
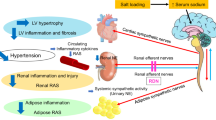
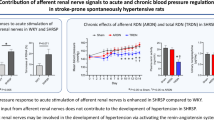
The incidence of hypertension and hypertensive renal disease is increasing worldwide, and new strategies to prevent these diseases need to be investigated. The aims of this study were 1) to examine if transient exposure to an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) during an early period in hypertension development confers protection against subsequent worsening of hypertension and renal injury induced by the NO synthase inhibitor NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME), and 2) conversely, to examine the effects of transient exposure to angiotensin II (Ang II) during the same period. First, spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) were treated transiently from age 3 to 10 weeks with an ARB (candesartan cilexetil), a calcium channel antagonist or a vasodilator, then taken off treatment for 2 months. Administration of L-NAME at age 18 weeks caused severe hypertension and renal injury. However, the rats that had been exposed to the ARB not only had a lower blood pressure, but also failed to show signs of renal injury or increase of oxidative stress. Furthermore, the elevation of components of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system was also suppressed in these rats. In the second study, Wistar-Kyoto rats (WKY) and SHR were exposed to Ang II from age 4 to 8 weeks. The follow-up showed that the blood pressures in the WKY remained elevated compared to controls, while the SHR had heightened increases in blood pressure, renal renin mRNA, and urinary 8-hyroxydeoxyguanosine after L-NAME administration. Together, these experiments demonstrate that transient treatment of rats during an early phase in the development of hypertension with an ARB suppresses the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and confers long-term protection against subsequent L-NAME–induced renal injury and increases in renal oxidative stress. Conversely, developmental exposure to Ang II during this “critical” period had the opposite effect, predisposing rats to higher blood pressure, renal injury, and oxidative stress after L-NAME administration.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
References
Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J : Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. Lancet 2005; 365: 217–223.
de Champlain J, Wu R, Girouard H, et al: Oxidative stress in hypertension. Clin Exp Hypertens 2004; 26: 593–601.
Escobales N, Crespo MJ : Oxidative-nitrosative stress in hypertension. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 2005; 3: 231–246.
Nakaya H, Sasamura H, Hayashi M, Saruta T : Temporary treatment of prepubescent rats with angiotensin inhibitors suppresses the development of hypertensive nephrosclerosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 2001; 12: 659–666.
Nakaya H, Sasamura H, Mifune M, et al: Prepubertal treatment with angiotensin receptor blocker causes partial attenuation of hypertension and renal damage in adult Dahl salt-sensitive rats. Nephron 2002; 91: 710–718.
Nakaya H, Sasamura H, Kitamura Y, et al: Effects of angiotensin inhibitors on renal injury and angiotensin receptor expression in early hypertensive nephrosclerosis. Hypertens Res 1999; 22: 303–312.
Naito Y, Tsujino T, Fujioka Y, Ohyanagi M, Iwasaki T : Augmented diurnal variations of the cardiac renin-angiotensin system in hypertensive rats. Hypertension 2002; 40: 827–833.
Yagi K : Simple procedure for specific assay of lipid hydroperoxides in serum or plasma. Methods Mol Biol 1998; 108: 107–110.
Toba H, Nakagawa Y, Miki S, et al: Calcium channel blockades exhibit anti-inflammatory and antioxidative effects by augmentation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase and the inhibition of angiotensin converting enzyme in the NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester–induced hypertensive rat aorta: vasoprotective effects beyond the blood pressure–lowering effects of amlodipine and manidipine. Hypertens Res 2005; 28: 689–700.
Jover B, Mimran A : Nitric oxide inhibition and renal alterations. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 2001; 38 ( Suppl 2): S65–S70.
Harrap SB, Van der Merwe WM, Griffin SA, Macpherson F, Lever AF : Brief angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor treatment in young spontaneously hypertensive rats reduces blood pressure long-term. Hypertension 1990; 16: 603–614.
Wu JN, Berecek KH : Prevention of genetic hypertension by early treatment of spontaneously hypertensive rats with the angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor captopril. Hypertension 1993; 22: 139–146.
Adams MA, Bobik A, Korner PI : Enalapril can prevent vascular amplifier development in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertension 1990; 16: 252–260.
Nagai Y, Yao L, Kobori H, et al: Temporary angiotensin II blockade at the prediabetic stage attenuates the development of renal injury in type 2 diabetic rats. J Am Soc Nephrol 2005; 16: 703–711.
Julius S, Nesbitt SD, Egan BM, et al: Feasibility of treating prehypertension with an angiotensin-receptor blocker. N Engl J Med 2006; 354: 1685–1697.
Zanchi A, Schaad NC, Osterheld MC, et al: Effects of chronic NO synthase inhibition in rats on renin-angiotensin system and sympathetic nervous system. Am J Physiol 1995; 268: H2267–H2273.
Lin Y, Tsuchihashi T, Kagiyama S, Matsumura K, Abe I : The influence of chronic antihypertensive treatment on the central pressor response in SHR. Hypertens Res 2001; 24: 173–178.
Cuzzocrea S, Mazzon E, Dugo L, Di Paola R, Caputi AP, Salvemini D : Superoxide: a key player in hypertension. FASEB J 2004; 18: 94–101.
Evans JL, Youngren JF, Goldfine ID : Effective treatments for insulin resistance: trim the fat and douse the fire. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2004; 15: 425–431.
Scheuer H, Gwinner W, Hohbach J, et al: Oxidant stress in hyperlipidemia-induced renal damage. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2000; 278: F63–F74.
Kouyama R, Suganami T, Nishida J, et al: Attenuation of diet-induced weight gain and adiposity through increased energy expenditure in mice lacking angiotensin II type 1a receptor. Endocrinology 2005; 146: 3481–3489.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishiguro, K., Sasamura, H., Sakamaki, Y. et al. Developmental Activity of the Renin-Angiotensin System during the “Critical Period” Modulates Later L-NAME–Induced Hypertension and Renal Injury. Hypertens Res 30, 63–75 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.30.63
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.30.63
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Hypotensive and antihypertensive effects of an aqueous extract from Guinep fruit (Melicoccus bijugatus Jacq) in rats
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Pre-emptive medicine for hypertension and its prospects
Hypertension Research (2019)
-
Chrysin Pretreatment Improves Angiotensin System, cGMP Concentration in L-NAME Induced Hypertensive Rats
Indian Journal of Clinical Biochemistry (2019)
-
Clinical significance of ‘cardiometabolic memory’: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials
Hypertension Research (2017)
-
Time course of cardiac inflammation during nitric oxide synthase inhibition in SHR: impact of prior transient ACE inhibition
Hypertension Research (2016)