Abstract
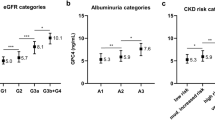
We investigated whether chronic kidney disease (CKD) was associated with carotid intima-media thickening in 1,351 male individuals undergoing general health screening. Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) was estimated by the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease equations using 0.881 as a coefficient for Japanese, and low estimated GFR (eGFR) was defined as an eGFR value of <60 mL/min/1.73 m2. Albuminuria was defined as a urine albumin–to−urine creatinine ratio of ≥30 mg/g, and CKD was defined when low eGFR and/or albuminuria was present. After adjusting for age, CKD was associated with carotid intima-media thickening with an odds ratio of 1.47 (95% confidence interval [CI] 1.05–2.06, p=0.0024). After adjusting for age, fasting plasma glucose, and smoking status, both albuminuria and low eGFR were significantly associated with intima-media thickening in individuals with hypertension with an odds ratio of 1.85 (95% CI 1.13–3.03, p=0.015) and 1.79 (95% CI 1.09–2.94, p=0.022), respectively. On the other hand, neither of them was associated with carotid intima-media thickening in individuals without hypertension. Similarly, after adjusting for age, systolic blood pressure, and smoking status, both albuminuria and low eGFR were significantly associated with intima-media thickening in individuals with high fasting glucose (defined as fasting plasma glucose levels of ≥110 mg/dL or current use of anti-diabetic medication), but not in those without. Our data indicate that CKD or its components (low eGFR and albuminuria) may be associated with early carotid atherosclerosis in low-risk individuals, such as those undergoing general health screening, who have hypertension and/or impaired glucose metabolism.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
References
Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY : Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med 2004; 351: 1296–1305.
Briet M, Bozec E, Laurent S, et al: Arterial stiffness and enlargement in mild-to-moderate chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 2006; 69: 350–357.
Iino Y, Hayashi M, Kawamura T, et al: Renoprotective effect of losartan in comparison to amlodipine in patients with chronic kidney disease and hypertension—a report of the Japanese Losartan Therapy Intended for the Global Renal Protection in Hypertensive Patients (JLIGHT) study. Hypertens Res 2004; 27: 21–30.
Munakata M, Nunokawa T, Yoshinaga K, Toyota T : Brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity is an independent risk factor for microalbuminuria in patients with essential hypertension—a Japanese Trial on the Prognostic Implication of Pulse Wave Velocity (J-TOPP). Hypertens Res 2006; 29: 515–521.
K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease : evaluation, classification, and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis 2002; 39: S1–S266.
Ishizaka N, Ishizaka Y, Toda E, Hashimoto H, Nagai R, Yamakado M : Association between cigarette smoking, metabolic syndrome, and carotid arteriosclerosis in Japanese individuals. Atherosclerosis 2005; 181: 381–388.
Manjunath G, Sarnak MJ, Levey AS : Prediction equations to estimate glomerular filtration rate: an update. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 2001; 10: 785–792.
Imai E, Horio M : Epidemiology of chronic kidney disease: the difference between Japan and Western countries. J Blood Press 2007; 13: 359–363 ( in Japanese).
Ishizaka N, Ishizaka Y, Toda E, Nagai R, Yamakado M : Association between serum uric acid, metabolic syndrome, and carotid atherosclerosis in Japanese individuals. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2005; 25: 1038–1044.
Handa N, Matsumoto M, Maeda H, Hougaku H, Kamada T : Ischemic stroke events and carotid atherosclerosis. Results of the Osaka Follow-Up Study for Ultrasonographic Assessment of Carotid Atherosclerosis (the OSACA Study). Stroke 1995; 26: 1781–1786.
Ninomiya T, Kiyohara Y, Kubo M, et al: Metabolic syndrome and CKD in a general Japanese population: the Hisayama Study. Am J Kidney Dis 2006; 48: 383–391.
Nakamura K, Okamura T, Hayakawa T, et al: Chronic kidney disease is a risk factor for cardiovascular death in a community-based population in Japan: NIPPON DATA90. Circ J 2006; 70: 954–959.
Tanaka H, Shiohira Y, Uezu Y, Higa A, Iseki K : Metabolic syndrome and chronic kidney disease in Okinawa, Japan. Kidney Int 2006; 69: 369–374.
Konta T, Hao Z, Abiko H, et al: Prevalence and risk factor analysis of microalbuminuria in Japanese general population: the Takahata study. Kidney Int 2006; 70: 751–756.
Stehouwer CD, Nauta JJ, Zeldenrust GC, Hackeng WH, Donker AJ, den Ottolander GJ : Urinary albumin excretion, cardiovascular disease, and endothelial dysfunction in non–insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Lancet 1992; 340: 319–323.
Tillin T, Forouhi N, McKeigue P, Chaturvedi N : Microalbuminuria and coronary heart disease risk in an ethnically diverse UK population: a prospective cohort study. J Am Soc Nephrol 2005; 16: 3702–3710.
Willey KA, Kidd JF, Harris JP, Xu ZR, Yue DK : Albuminuria is an independent predictor of carotid intima-media thickness and atherosclerosis in NIDDM patients. Diabetes Care 1995; 18: 1502–1503.
Jorgensen L, Jenssen T, Johnsen SH, et al: Albuminuria as risk factor for initiation and progression of carotid atherosclerosis in non-diabetic persons: the Tromso Study. Eur Heart J 2007; 28: 363–369.
Preston E, Ellis MR, Kulinskaya E, Davies AH, Brown EA : Association between carotid artery intima-media thickness and cardiovascular risk factors in CKD. Am J Kidney Dis 2005; 46: 856–862.
Taniwaki H, Nishizawa Y, Kawagishi T, et al: Decrease in glomerular filtration rate in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes is linked to atherosclerosis. Diabetes Care 1998; 21: 1848–1855.
Rodondi N, Yerly P, Gabriel A, et al: Microalbuminuria, but not cystatin C, is associated with carotid atherosclerosis in middle-aged adults. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2007; 22: 1107–1114.
Shulman NB, Ford CE, Hall WD, et al: Prognostic value of serum creatinine and effect of treatment of hypertension on renal function. Results from the hypertension detection and follow-up program. The Hypertension Detection and Follow-up Program Cooperative Group. Hypertension 1989; 13: I80–I93.
Segura J, Campo C, Gil P, et al: Development of chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular prognosis in essential hypertensive patients. J Am Soc Nephrol 2004; 15: 1616–1622.
Lorber D, Reddan D : Clinical characteristics of chronic kidney disease patients with and without diabetes: a subanalysis of the PAERI study. Clin Nephrol 2006; 66: 11–16.
Segura J, Campo C, Ruilope LM : Effect of proteinuria and glomerular filtration rate on cardiovascular risk in essential hypertension. Kidney Int Suppl 2004; ( 92): S45–S49.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishizaka, N., Ishizaka, Y., Toda, Ei. et al. Association between Chronic Kidney Disease and Carotid Intima-Media Thickening in Individuals with Hypertension and Impaired Glucose Metabolism. Hypertens Res 30, 1035–1041 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.30.1035
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.30.1035
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Renal size and cardiovascular risk in prepubertal children
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Impact of kidney function and urinary protein excretion on intima–media thickness in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes
Clinical and Experimental Nephrology (2015)
-
Impact of kidney function and urinary protein excretion on pulmonary function in Japanese patients with chronic kidney disease
Clinical and Experimental Nephrology (2014)
-
Association between microalbuminuria and subclinical atherosclerosis evaluated by carotid artery intima-media in elderly patients with normal renal function
BMC Nephrology (2012)
-
The relationship between intracranial arterial stenosis and glomerular filtration rate
Journal of Thrombosis and Thrombolysis (2012)