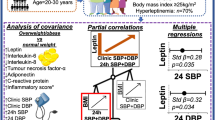
Abstract
Hypertension contributes to the occurrence and progression of cardiovascular diseases. The angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker telmisartan is reported to activate the peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor γ and improve insulin sensitivity. We investigated the effects of telmisartan treatment on visceral fat, serum adiponectin and vascular inflammation markers in Japanese hypertensive patients. This was an open-label, non-controlled study. Twenty-eight essential hypertensive patients (22 men and 6 women; age 60.6±1.9 years; body mass index [BMI] 25.5±0.6 kg/m2) participated. Fat area was assessed with computerized tomography. All the subjects were started on telmisartan 40 mg/day, which was increased to 80 mg/day to achieve the blood pressure target of less than 130/80 mmHg. We assessed the visceral and subcutaneous fat areas, serum adiponectin levels, and vascular inflammation markers at baseline and 24 weeks of telmisartan treatment. There were significant reductions in visceral fat area (from 103.1±7.9 to 93.3±8.4 cm2, p<0.01) and pulse wave velocity (from 1,706±52 to 1,587±51 cm/s, p<0.01) at 24 weeks. In contrast, significant increases in serum high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (from 5.06±0.15 to 5.32±0.13 mmol/L, p<0.05) and adiponectin levels (from 8.27±0.76 to 9.13±0.81 μg/mL, p<0.05) were observed. Also, there were reductions in the interleukin-6 level (from 2.26±0.27 to 1.60±0.14 pg/mL, p<0.01). We also conducted these investigations in male subjects alone and similar findings were obtained for all of these parameters. In conclusion, telmisartan treatment was associated with an improvement of vascular inflammation, reductions in visceral fat and increases in serum adiponectin.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
References
Defronzo RA, Ferrannini E : Insulin resistance: a multifaced syndrome responsible for cardiovascular disease. Diabetes Care 1991; 14: 173–194.
Agata J, Miyazaki Y, Takada M, et al: Association of insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia with disturbed lipid metabolism in patients with essential hypertension. Hypertens Res 1998; 21: 57–62.
Hirose H, Saito I, Kawabe H, Saruta T : Insulin resistance and hypertension: seven-year follow-up study in middle-aged Japanese men (the KEIO study). Hypertens Res 2003; 26: 795–800.
Jarrett RJ, Keen H, McCartney M, et al: Glucose tolerance and blood pressure in two population samples: their relation to diabetes mellitus and hypertension. Int J Epidemiol 1978; 7: 15–24.
Modan M, Halkin H, Almog S, et al: Hyperinsulinemia: a link between hypertension obesity and glucose intolerance. J Clin Invest 1985; 75: 809–817.
Benson SC, Pershadsingh HA, Ho CI, et al: Identification of telmisartan as a unique angiotensin II receptor antagonist with selective PPARgamma-modulating activity. Hypertension 2004; 43: 993–1002.
Schupp M, Janke J, Clasen R, Unger T, Kintscher U : Angiotensin type 1 receptor blockers induce peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor-gamma activity. Circulation 2004; 109: 2054–2057.
Fujimoto M, Masuzaki H, Tanaka T, et al: An angiotensin II AT1 receptor antagonist, telmisartan augments glucose uptake and GLUT4 protein expression in 3 T3–L1 adipocytes. FEBS Lett 2004; 576: 492–497.
Schupp M, Clemenz M, Gineste R, et al: Molecular characterization of new selective peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor gamma modulators with angiotensin receptor blocking activity. Diabetes 2004; 54: 3442–3452.
Sugimoto K, Qi NR, Kazdova L, Pravenec M, Ogihara T, Kurtz TW : Telmisartan but not valsartan increases caloric expenditure and protects against weight gain and hepatic steatosis. Hypertension 2006; 47: 1003–1009.
Araki K, Masaki T, Katsuragi I, Tanaka K, Kakuma T, Yoshimatsu H : Telmisartan prevents obesity and increases the expression of uncoupling protein 1 in diet-induced obese mice. Hypertension 2006; 48: 51–57.
Pollare T, Lithell H, Berne C : A comparison of the effects of hydrochlorothiazide and captopril on glucose and lipid metabolism in patients with hypertension. N Engl J Med 1989; 321: 868–873.
Iimura O, Shimamoto K, Matsuda K, et al: Effects of angiotensin receptor antagonist and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor on insulin sensitivity in fructose-fed hypertensive rats and essential hypertensives. Am J Hypertens 1995; 8: 353–357.
Honjo S, Nichi Y, Wada Y, Hamamoto Y, Koshiyama H : Possible beneficial effect of telmisartan on glycemic control in diabetic subjects. Diabetes Care 2005; 28: 498.
Erbe DV, Gartrell K, Zhang YL, et al: Molecular activation of PPARgamma by angiotensin II type 1−receptor antagonists. Vascul Pharmacol 2006; 45: 154–162.
Vitale C, Mercuro G, Castiglioni C, et al: Metabolic effect of telmisartan and losartan in hypertensive patients with metabolic syndrome. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2005; 4: 6.
Miura Y, Yamamoto N, Tsunekawa S, et al: Replacement of valsartan and candesartan by telmisartan in hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetes: metabolic and antiatherogenic consequences. Diabetes Care 2005; 28: 757–758.
Pershadsingh HA, Kurtz TW : Insulin-sensitizing effects of telmisartan: implications for treating insulin-resistant hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Diabetes Care 2004; 27: 1015.
Shimabukuro M, Tanaka H, Shimabukuro T : Effects of telmisartan on fat distribution in individuals with the metabolic syndrome. J Hypertens 2007; 25: 841–848.
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA : Homeostasis model assesment: insulin resistance and beta-cell faunction from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985; 28: 412–419.
Yoshizumi T, Nakamura T, Yamane M, Islam AHMW, Menju M, Yamasaki K : Abdominal fat: standardized technique for measurement at CT. Radiology 1999; 211: 283–286.
Mertens I, Ballaux D, Funahashi T, et al: Inverse relationship between plasminogen activator inhibitor-I activity and adiponectin in overweight and obese women. Interrelationship with visceral adipose tissue, insulin resistance, HDL-chol and inflammation. Thromb Haemost 2005; 94: 1190–1195.
Milan G, Granzotto M, Scarda A, et al: Resistin and adiponectin expression in visceral fat of obese rats: effect of weight loss. Obes Res 2002; 10: 1095–1103.
Addy CL, Gavrila A, Tsiodras S, Brodovicz K, Karchmer AW, Mantzoros CS : Hypoadiponectinemia is associated with insulin resistance, hypertriglyceridemia, and fat redistribution in human immunodeficiency virus–infected patients treated with highly active antiretroviral therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003; 88: 627–636.
Usui I, Fujisaka S, Yamazaki K, et al: Telmisartan reduced blood pressure and HOMA-IR with increasing plasma leptin level in hypertensive and type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2007; 77: 210–214.
Yoshida T, Yamagishi S, Nakamura K, et al: Telmisartan inhibits AGE-induced C-reactive protein production through downregulation of the receptor for AGE via peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor-gamma activation. Diabetologia 2006; 49: 3094–3099.
Kobayashi J, Murase Y, Asano A, et al: Effect of walking with a pedometer on serum lipid and adiponectin levels in Japanese middle-aged men. J Atheroscler Thromb 2006; 13: 197–201.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chujo, D., Yagi, K., Asano, A. et al. Telmisartan Treatment Decreases Visceral Fat Accumulation and Improves Serum Levels of Adiponectin and Vascular Inflammation Markers in Japanese Hypertensive Patients. Hypertens Res 30, 1205–1210 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.30.1205
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.30.1205
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Adjunctive telmisartan treatment on body metabolism in clozapine or olanzapine treated patients with schizophrenia: a randomized, double blind, placebo controlled trial
Psychopharmacology (2019)
-
Utilization of antihypertensive drugs in obesity-related hypertension: a retrospective observational study in a cohort of patients from Southern Italy
BMC Pharmacology and Toxicology (2016)
-
The Different Therapeutic Choices with ARBs. Which One to Give? When? Why?
American Journal of Cardiovascular Drugs (2016)
-
Visceral fat area is associated with HbA1c but not dialysate-related glucose load in nondiabetic PD patients
Scientific Reports (2015)
-
Adipose Tissue Immune Response: Novel Triggers and Consequences for Chronic Inflammatory Conditions
Inflammation (2014)