Abstract
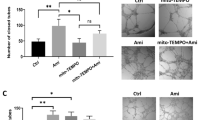
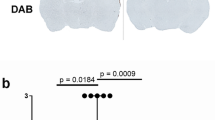
We investigated whether an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor could inhibit matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) activities in cerebral infarct lesions after middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) in rats. After placebo or trandolapril (5 mg/kg per day) was administered orally for 7 days, we permanently occluded the right middle cerebral artery. ACE activity in extracts from the infarct side of placebo-treated rats was significantly higher than that in extracts from the non-infarct side from 5 days after MCAO, though they did not differ at 1 day. ACE activities in extracts from both hemispheric segments in the trandolapril-treated group were significantly decreased compared with those in the placebo-treated group before MCAO, and this significant reduction persisted even at 7 days after MCAO. In the placebo-treated group, MMP-9 and MMP-2 activities in the infarct side were significantly increased at 12 h and at 1 day after MCAO, respectively. Trandolapril treatment significantly reduced MMP-9 and MMP-2 activities to 68.5% and 53.2%, respectively. Seven days after MCAO, the ratios of infarct areas to the hemispheric sectional areas in placebo- and trandolapril-treated rats were 55.4±2.1% and 30.9±2.9%, respectively, and this difference was significant. Neurological severity scores were significantly improved from 1 to 7 days after MCAO in trandolapril-treated rats. Cumulative survival in trandolapril-treated rats was significantly increased compared with that in placebo-treated rats. Thus, the inhibition of MMP-9 by trandolapril might be part of the mechanism that prevents cerebral damage after cerebral ischemia.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
References
Fukuhara M, Geary RL, Diz DI, et al: Angiotensin-converting enzyme expression in human carotid artery atherosclerosis. Hypertension 2000; 35: 353–359.
Sadoshima J : Cytokine actions of angiotensin II. Circ Res 2000; 86: 1187–1189.
Kim S, Iwao H : Molecular and cellular mechanisms of angiotensin II–mediated cardiovascular and renal diseases. Pharmacol Rev 2000; 52: 11–34.
Mabuchi T, Kitagawa K, Ohtsuki T, et al: Contribution of microglia/macrophages to expansion of infarction and response of oligodendrocytes after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke 2000; 31: 1735–1743.
Ganten D, Lang RE, Lehmann E, Unger T : Brain angiotensin: on the way to becoming a well-studied neuropeptide system. Biochem Pharmacol 1984; 33: 3523–3528.
Okamoto K, Takai S, Sasaki S, Miyazaki M : Trandolapril reduces infarction area after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Hypertens Res 2002; 25: 583–588.
Yurchenco PD, Schittny JC : Molecular architecture of basement membranes. FASEB J 1990; 4: 1577–1590.
Galis ZS, Sukhova GK, Lark MW, Libby P : Increased expression of matrix metalloproteinases and matrix degrading activity in vulnerable regions of human atherosclerotic plaques. J Clin Invest 1994; 94: 2493–2503.
Goetzl EJ, Banda MJ, Leppert D : Matrix metalloproteinases in immunity. J Immunol 1996; 156: 1–4.
Risau W, Wolburg H : Development of the blood-brain barrier. Trends Neurosci 1990; 13: 174–178.
Rosenberg GA : Matrix metalloproteinases in brain injury. J Neurotrauma 1995; 12: 833–842.
Romanic AM, White RF, Arleth AJ, Ohlstein EH, Barone FC : Matrix metalloproteinase expression increases after cerebral focal ischemia in rats: inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-9 reduces infarct size. Stroke 1998; 29: 1020–1030.
Hamann GF, Okada Y, Fitridge R, del Zoppo GJ : Microvascular basal lamina antigens disappear during cerebral ischemia and reperfusion. Stroke 1995; 26: 2120–2126.
Sorbi D, Fadly M, Hicks R, Alexander S, Arbeit L : Captopril inhibits the 72 kDa and 92 kDa matrix metalloproteinases. Kidney Int 1993; 44: 1266–1272.
Reinhardt D, Sigusch HH, Hensse J, Tyagi SC, Korfer R, Figulla HR : Cardiac remodelling in end stage heart failure: upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) irrespective of the underlying disease, and evidence for a direct inhibitory effect of ACE inhibitors on MMP. Heart 2002; 88: 525–530.
Ikeda N, Nonoguchi N, Zhao MZ, et al: Bone marrow stromal cells that enhanced fibroblast growth factor-2 secretion by herpes simplex virus vector improve neurological outcome after transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke 2005; 36: 2725–2730.
Takai S, Jin D, Sakaguchi M, Miyazaki M : Significant target organs for hypertension and cardiac hypertrophy by angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Hypertens Res 2004; 27: 213–219.
Kishi K, Muramatsu M, Jin D, et al: The effects of chymase on the matrix metalloproteainase-2 activation of neointimal hyperplasia after balloon injury in dogs. Hypertens Res 2007; 30: 77–83.
Arenas IA, Xu Y, Lopez-Jaramillo P, Davidge ST : Angiotensin II–induced MMP-2 release from endothelial cells is mediated by TNF-α. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2004; 286: C779–C784.
Rouet-Benzineb P, Gontero B, Dreyfus P, Lafuma C : Angiotensin II induces nuclear factor-κB activation in cultured neonatal rat cardiomyocytes through protein kinase C signaling pathway. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2000; 32: 1767–1778.
Miyazaki M, Kawamoto T, Okunishi H : Vascular affinity of trandolapril. Am J Hypertens 1995; 8: 63S–67S.
Gohlke P, Urbach H, Scholkens B, Unger T : Inhibition of converting enzyme in the cerebrospinal fluid of rats after oral treatment with converting enzyme inhibitors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1989; 249: 609–616.
Moursi MG, Ganten D, Lang RE, Unger T : Antihypertensive action and inhibition of tissue converting enzyme (CE) by three prodrug CE inhibitors, enalapril, ramipril and perindopril in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Hypertens 1986; 4 ( Suppl 3): S495–S498.
Takai S, Song K, Tanaka T, Okunishi H, Miyazaki M : Antinociceptive effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and an angiotensin II receptor antagonist in mice. Life Sci 1996; 59: PL331–PL336.
Hamai M, Iwai M, Ide A, et al: Comparison of inhibitory action of candesartan and enalapril on brain ischemia through inhibition of oxidative stress. Neuropharmacology 2006; 51: 822–828.
Lou M, Blume A, Zhao Y, et al: Sustained blockade of brain AT1 receptors before and after focal cerebral ischemia alleviates neurologic deficits and reduces neuronal injury, apoptosis, and inflammatory responses in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2004; 24: 536–547.
Lu Q, Zhu YZ, Wong PT : Neuroprotective effects of candesartan against cerebral ischemia in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Neuroreport 2005; 16: 1963–1967.
Kagiyama T, Kagiyama S, Phillips MI : Expression of angiotensin type 1 and 2 receptors in brain after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Regul Pept 2003; 110: 241–247.
Iwai M, Liu HW, Chen R, et al: Possible inhibition of focal cerebral ischemia by angiotensin II type 2 receptor stimulation. Circulation 2004; 110: 843–848.
Copin JC, Goodyear MC, Gidday JM, et al: Role of matrix metalloproteinases in apoptosis after transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats and mice. Eur J Neurosci 2005; 22: 1597–1608.
Koistinaho M, Malm TM, Kettunen MI, et al: Minocycline protects against permanent cerebral ischemia in wild type but not in matrix metalloprotease-9−deficient mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2005; 25: 460–467.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanaka, H., Takai, S., Jin, D. et al. Inhibition of Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Activity by Trandolapril after Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion in Rats. Hypertens Res 30, 469–475 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.30.469
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.30.469
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Matrix metalloproteinases and ADAMs in stroke
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2019)