Abstract
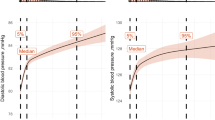
Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS) is associated with increases in cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Vascular changes in individuals with OSAS have not been fully elucidated, however. The possible impact of OSAS on the extent of aortic pressure augmentation (AG), an indicator of cardiovascular risk, was investigated. Forty-five consecutive male patients aged 35 to 78 years (56.0±9.6 years) who were referred to the sleep clinic of Nagoya University Hospital for screening and treatment of OSAS and 71 age-matched healthy men were enrolled in the study. AG was derived from the pressure waveform measured at the radial artery by applanation tonometry. The number of apnea and hypopnea episodes per hour (apnea-hypopnea index [AHI]) was determined by standard polysomnography. AG was significantly greater in OSAS patients than in controls (9.0±4.1 vs. 6.4±3.4 mmHg, p<0.001), and it was significantly reduced in 19 OSAS patients treated with continuous positive airway pressure. AG was also significantly correlated with the AHI (r=0.562, p<0.001) and age (r=0.356, p=0.016) but not with the serum concentrations of low and high density lipoprotein-cholesterol, triglyceride, or glycosylated hemoglobin. Stepwise multiple regression analysis revealed that the AHI was the most significant contributing factor to the increased AG in OSAS patients (β=0.109, r=0.530, p<0.001). OSAS may thus have an adverse effect on vascular function that can be ameliorated by appropriate treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
References
Phillipson EA : Sleep apnea, in Braunwald E, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Longo DL, Jameson JL (eds): Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine, 15th ed. New York, McGraw-Hill, 2001, pp 1520–1523.
Noda A, Nakata S, Koike Y, et al: Continuous positive airway pressure improves daytime baroreflex sensitivity and nitric oxide production in patients with moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Hypertens Res 2007: 30: 669–676.
Peppard PE, Young T, Palta M, Skatrud J : Prospective study of the association between sleep-disordered breathing and hypertension. N Engl J Med 2000; 342: 1378–1384.
Marin JM, Carrizo SJ, Vicente E, Agusti AG : Long-term cardiovascular outcomes in men with obstructive sleep apnoea-hypopnoea with or without treatment with continuous positive airway pressure: an observational study. Lancet 2005; 365: 1046–1053.
Yaggi H, Cancato J, Kernan W, Lichtman JH, Brass LM, Mohsenin V : Obstructive sleep apnea as a risk factor for stroke and death. N Engl J Med 2005; 353: 2034–2041.
Peker Y, Hender J, Norman J, Kraiczi H, Carlson J : Increased incidence of cardiovascular disease in middle-aged men with obstructive sleep apnea. Am J Respir Cir Care Med 2002; 166: 159–165.
Phillips BG, Narkiewicz K, Pesek CA, Haynes WG, Dyken ME, Somers VK : Effects of obstructive sleep apnea on endothelin-1 and blood pressure. J Hypertens 1999; 17: 61–66.
Ohga E, Nagase T, Tomita T, et al: Increased levels of circulating ICAM-1, VCAM-1, and L-selectin in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. J Appl Physiol 1999; 87: 10–14.
Bokinsky G : Spontaneous platelet activation and aggregation during obstructive sleep-apnea and its response to therapy with nasal continuous positive air pressure. Chest 1995; 108: 625–630.
Nichols WW, Singh BW : Augmentation index as a measure of peripheral vascular disease state. Curr Opin Cardiol 2002; 17: 543–551.
O’Rourke MF, Staessen JA, Vlachopoulos C, Duprez D, Plante GE : Clinical applications of arterial stiffness; definitions and reference values. Am J Hypertens 2002; 15: 426–444.
Filipovsky J, Svobodova V, Pecen L : Reproducibility of radial pulse wave analysis in healthy subjects. J Hypertens 2000; 18: 1033–1040.
Weber T, Auer J, O’Rourke MF, et al: Arterial stiffness, wave reflections, and the risk of coronary artery disease. Circulation 2004; 109: 184–189.
Chirinos JA, Zambrano JP, Chakko S, et al: Aortic pressure augmentation predicts adverse cardiovascular events in patients with established coronary artery disease. Hypertension 2005; 45: 980–985.
Suzuki T, Nakano H, Maekawa J, et al: Obstructive sleep apnea and carotid-artery intima media thickness. Sleep 2004; 27: 129–133.
The Report of an American Academy of Sleep Medicine Task Force. Sleep-related breathing disorders in adults : recommendations for syndrome definition and measurement techniques in clinical research. Sleep 1999; 22: 667–689.
Kelly RP, Hayward C, Avolio A, O’Rourke M : Noninvasive determination of age-related changes in human arterial pulse. Circulation 1989; 80: 1652–1659.
Chen CH, Nevo E, Fetics B, et al: Estimation of central aortic pressure waveform by mathematical transformation of radial tonometry pressure validation of generalized transfer function. Circulation 1997; 95: 1827–1836.
Wilkinson IB, Fuchs SA, Jansen IM, et al: Reproducibility of pulse wave velocity and augmentation index measurement by pulse wave analysis. J Hypertens 1998; 16: 2079–2084.
Chambless LE, Heiss G, Folsom AR, et al: Association of coronary heart disease incidence with carotid arterial wall thickness and major risk factors: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. Am J Epidemiol 1997; 146: 483–494.
Peker Y, Heder J, Kraiczi H, Loth S : Respiratory disturbance index. An independent predictor of mortality in coronary artery disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000; 162: 81–86.
Noda A, Okada T, Yasuma F, Sobue T, Nakashima N, Yokota M : Prognosis of the middle-aged and aged patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 1998; 52: 79–85.
Shahar E, Whitney CW, Redline S, et al: Sleep-disordered breathing and cardiovascular disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2001; 163: 19–25.
Brooks D, Homer RL, Kozar LF, Render-Teixeira C, Phillipson EA : Obstructive sleep apnea as a cause of systemic hypertension. Evidence from a canine model. J Clin Invest 1997; 99: 106–109.
Noda A, Okada T, Hayashi H, Yasuma F, Yokota M : 24-Hour ambulatory blood pressure variability in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Chest 1993; 103: 1343–1347.
Noda A, Okada T, Yasuma F, Nakashima N, Yokota M : Cardiac hypertrophy in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Chest 1995; 107: 1538–1544.
Noda A, Yasuma F, Okada T, Yokota M : Circadian rhythm of autonomic activity in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Clin Cardiol 1998; 21: 271–276.
Bradley TD, Floras JS : Sleep apnea and heart failure. Part I: Obstructive sleep apnea. Circulation 2003; 107: 1671–1678.
Narkiewicz K, Somers VK : The sympathetic nervous system and obstructive sleep apnea: implications for hypertension. J Hypertens 1997; 15: 1613–1619.
Kato M, Roberts-Thomson P, Phillips BG, et al: Impaired endothelium-dependent vasodilation of resistance vessels in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Circulation 2000; 102: 2607–2610.
Jelic S, Bartele MN, Mateika JH, Nagai P, DeMeersman RE, Basner RC : Arterial stiffness increases during obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep 2002; 25: 850–855.
Bazzano LA, Khan Z, Reynolds K, He J : Effect of nocturnal nasal continuous positive airway pressure on blood pressure in obstructive sleep apnea. Hypertension 2007; 50: 417–423.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noda, A., Nakata, S., Fukatsu, H. et al. Aortic Pressure Augmentation as a Marker of Cardiovascular Risk in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome. Hypertens Res 31, 1109–1114 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.31.1109
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.31.1109
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Effect of CPAP on arterial stiffness in severely obese patients with obstructive sleep apnoea
Sleep and Breathing (2015)
-
Increased arterial stiffness in obstructive sleep apnea: a systematic review
Hypertension Research (2011)
-
Pulse wave analysis in a pilot randomised controlled trial of auto-adjusting and continuous positive airway pressure for obstructive sleep apnoea
Sleep and Breathing (2011)
-
The incremental effect of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome on right and left ventricular myocardial performance in newly diagnosed essential hypertensive subjects
Hypertension Research (2009)