Abstract
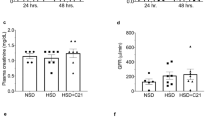
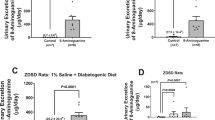
The metabolic syndrome is a risk factor for the development of chronic kidney disease. Angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockers (ARBs) and thiazolidinediones (TZDs) provide renovascular protection, probably in the metabolic syndrome. However, the effect of both agents administered together in patients with metabolic syndrome remains to be determined. The aim of this study was to assess the effects of ARB plus TZD combination therapy in Zucker obese rats fed a high-protein diet, an animal model of metabolic syndrome and renal injury. Zucker obese rats were fed a high-protein diet (OHP; n=6), a high-protein diet containing candesartan, an ARB (OHP+C; n=6), or a high-protein diet containing both candesartan and pioglitazone (OHP+CP; n=6) for 12 weeks. Systolic blood pressure and urinary protein excretion were measured throughout the study, and renal histology and immunohistochemistry were assessed at 12 weeks. OHP rats developed hypertension (157±4 mmHg) and proteinuria (178±44 mg/d), and these conditions were significantly ameliorated by candesartan (to 143±3 mmHg and 84±25 mg/d, respectively). Pioglitazone enhanced the antihypertensive and anti-proteinuric effects of candesartan (121±3 mmHg, 16±8 mg/d, respectively). Histologically, candesartan ameliorated glomerulosclerosis, podocyte injury, interstitial fibrosis and monocyte/macrophage infiltration into the tubulointerstitium in the kidneys of OHP rats. Pioglitazone abrogated residual interstitial fibrosis in the kidneys of OHP+C rats. Our results suggested that pioglitazone augmented the antihypertensive, anti-proteinuric and possibly renal anti-fibrotic actions of candesartan in Zucker obese rats fed a high-protein diet. The combination therapy of ARB and TZD may protect against renal injury in patients with metabolic syndrome.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
References
Lakka HM, Laaksonen DE, Lakka TA, et al: The metabolic syndrome and total and cardiovascular disease mortality in middle-aged men. JAMA 2002; 288: 2709–2716.
Isomaa B, Almgren P, Tuomi T, et al: Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality associated with the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Care 2001; 24: 683–689.
Chen J, Muntner P, Hamm LL, et al: The metabolic syndrome and chronic kidney disease in U.S. adults. Ann Intern Med 2004; 140: 167–174.
Kurella M, Lo JC, Chertow GM : Metabolic syndrome and the risk for chronic kidney disease among nondiabetic adults. J Am Soc Nephrol 2005; 16: 2134–2140.
Tanaka H, Shiohira Y, Uezu Y, Higa A, Iseki K : Metabolic syndrome and chronic kidney disease in Okinawa, Japan. Kidney Int 2006; 69: 369–374.
Ruster C, Wolf G : Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and progression of renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 2006; 17: 2985–2991.
Karalliedde J, Viberti G : Evidence for renoprotection by blockade of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in hypertension and diabetes. J Hum Hypertens 2006; 20: 239–253.
Derosa G, Cicero AF, Dangelo A, et al: Thiazolidinedione effects on blood pressure in diabetic patients with metabolic syndrome treated with glimepiride. Hypertens Res 2005; 28: 917–924.
Sarafidis PA, Bakris GL : Protection of the kidney by thiazolidinediones: an assessment from bench to bedside. Kidney Int 2006; 70: 1223–1233.
Kiberd B : The chronic kidney disease epidemic: stepping back and looking forward. J Am Soc Nephrol 2006; 17: 2967–2973.
Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY : Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med 2004; 351: 1296–1305.
Zucker LM : Hereditary obesity in the rat associated with hyperlipemia. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1965; 131: 447–458.
Kasiske BL, O'Donnell MP, Keane WF : The Zucker rat model of obesity, insulin resistance, hyperlipidemia, and renal injury. Hypertension 1992; 19 ( Suppl 1): I110–I115.
Kasiske BL, Cleary MP, O'Donnell MP, Keane WF : Effects of genetic obesity on renal structure and function in the Zucker rat. J Lab Clin Med 1985; 106: 598–604.
Alavi FK, Zawada ET, Simmons JL : Renal hemodynamic and histological consequences of diets high in unsaturated fat, protein or sucrose in obese Zucker rats. Clin Nephrol 1995; 43: 122–130.
Mizuno M, Sada T, Kato M, Koike H : Renoprotective effects of blockade of angiotensin II AT1 receptors in an animal model of type 2 diabetes. Hypertens Res 2002; 25: 271–278.
Schmitz PG, O'Donnell MP, Kasiske BL, Katz SA, Keane WF : Renal injury in obese Zucker rats: glomerular hemodynamic alterations and effects of enalapril. Am J Physiol 1992; 263: F496–F502.
Yoshimoto T, Naruse M, Nishikawa M, et al: Antihypertensive and vasculo- and renoprotective effects of pioglitazone in genetically obese diabetic rats. Am J Physiol 1997; 272: E989–E996.
Buckingham RE, Al-Barazanji KA, Toseland CD, et al: Peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor-γ agonist, rosiglitazone, protects against nephropathy and pancreatic islet abnormalities in Zucker fatty rats. Diabetes 1998; 47: 1326–1334.
Baylis C, Atzpodien EA, Freshour G, Engels K : Peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor γ agonist provides superior renal protection versus angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition in a rat model of type 2 diabetes with obesity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2003; 307: 854–860.
Tomita N, Higaki J, Kaneda Y, et al: Hypertensive rats produced by in vivo introduction of the human renin gene. Circ Res 1993; 73: 898–905.
Namikoshi T, Tomita N, Fujimoto S, et al: Isohumulones derived from hops ameliorate renal injury via an anti-oxidative effect in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. Hypertens Res 2007; 30: 175–184.
Coimbra TM, Janssen U, Grone HJ, et al: Early events leading to renal injury in obese Zucker (fatty) rats with type II diabetes. Kidney Int 2000; 57: 167–182.
Palmer BF : Disturbances in renal autoregulation and the susceptibility to hypertension-induced chronic kidney disease. Am J Med Sci 2004; 328: 330–343.
Dubey RK, Zhang HY, Reddy SR, Boegehold MA, Kotchen TA : Pioglitazone attenuates hypertension and inhibits growth of renal arteriolar smooth muscle in rats. Am J Physiol 1993; 265: R726–R732.
Hayashi K, Kanda T, Homma K, et al: Altered renal microvascular response in Zucker obese rats. Metabolism 2002; 51: 1553–1561.
Rodriguez WE, Tyagi N, Joshua IG, et al: Pioglitazone mitigates renal glomerular vascular changes in high-fat, high-calorie–induced type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2006; 291: F694–F701.
Zhang HY, Reddy SR, Kotchen TA : Antihypertensive effect of pioglitazone is not invariably associated with increased insulin sensitivity. Hypertension 1994; 24: 106–110.
Iida KT, Kawakami Y, Suzuki M, et al: Effect of thiazolidinediones and metformin on LDL oxidation and aortic endothelium relaxation in diabetic GK rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2003; 284: E1125–E1130.
Dobrian AD, Schriver SD, Khraibi AA, Prewitt RL : Pioglitazone prevents hypertension and reduces oxidative stress in diet-induced obesity. Hypertension 2004; 43: 48–56.
Calnek DS, Mazzella L, Roser S, Roman J, Hart CM : Peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor γ ligands increase release of nitric oxide from endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2003; 23: 52–57.
Cho DH, Choi YJ, Jo SA, Jo I : Nitric oxide production and regulation of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase phosphorylation by prolonged treatment with troglitazone: evidence for involvement of peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor (PPAR) γ–dependent and PPARγ-independent signaling pathways. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 2499–2506.
Wakino S, Hayashi K, Tatematsu S, et al: Pioglitazone lowers systemic asymmetric dimethylarginine by inducing dimethylarginine dimethylamino-hydrolase in rats. Hypertens Res 2005; 28: 255–262.
Arima S, Kohagura K, Takeuchi K, et al: Biphasic vasodilator action of troglitazone on the renal microcirculation. J Am Soc Nephrol 2002; 13: 342–349.
Xu ZG, Lanting L, Vaziri ND, et al: Upregulation of angiotensin II type 1 receptor, inflammatory mediators, and enzymes of arachidonate metabolism in obese Zucker rat kidney: reversal by angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockade. Circulation 2005; 111: 1962–1969.
Diep QN, El Mabrouk M, Cohn JS, et al: Structure, endothelial function, cell growth, and inflammation in blood vessels of angiotensin II–infused rats: role of peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor-γ. Circulation 2002; 105: 2296–2302.
Wolf G, Chen S, Ziyadeh FN : From the periphery of the glomerular capillary wall toward the center of disease: podocyte injury comes of age in diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 2005; 54: 1626–1634.
Benigni A, Zoja C, Tomasoni S, et al: Transcriptional regulation of nephrin gene by peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor-γ agonist: molecular mechanism of the antiproteinuric effect of pioglitazone. J Am Soc Nephrol 2006; 17: 1624–1632.
Abbate M, Zoja C, Remuzzi G : How does proteinuria cause progressive renal damage? J Am Soc Nephrol 2006; 17: 2974–2984.
Ma LJ, Marcantoni C, Linton MF, Fazio S, Fogo AB : Peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor-γ agonist troglitazone protects against nondiabetic glomerulosclerosis in rats. Kidney Int 2001; 59: 1899–1910.
Zafiriou S, Stanners SR, Saad S, Polhill TS, Poronnik P, Pollock CA : Pioglitazone inhibits cell growth and reduces matrix production in human kidney fibroblasts. J Am Soc Nephrol 2005; 16: 638–645.
Li Y, Wen X, Spataro BC, Hu K, Dai C, Liu Y : Hepatocyte growth factor is a downstream effector that mediates the antifibrotic action of peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor-γ agonists. J Am Soc Nephrol 2006; 17: 54–65.
Pasceri V, Wu HD, Willerson JT, Yeh ET : Modulation of vascular inflammation in vitro and in vivo by peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor-γ activators. Circulation 2000; 101: 235–238.
Ishibashi M, Egashira K, Hiasa K, et al: Antiinflammatory and antiarteriosclerotic effects of pioglitazone. Hypertension 2002; 40: 687–693.
Namikoshi T, Satoh M, Tomita N, et al: Pioglitazone ameliorates endothelial dysfunction in obese rats with nephropathy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2007; 361: 835–840.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Namikoshi, T., Tomita, N., Satoh, M. et al. Pioglitazone Enhances the Antihypertensive and Renoprotective Effects of Candesartan in Zucker Obese Rats Fed a High-Protein Diet. Hypertens Res 31, 745–755 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.31.745
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.31.745
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Interplay between the renin-angiotensin system, the canonical WNT/β-catenin pathway and PPARγ in hypertension
Current Hypertension Reports (2018)
-
Azelnidipine attenuates glomerular damage in Dahl salt-sensitive rats by suppressing sympathetic nerve activity
Hypertension Research (2012)
-
Endothelial dysfunction as an underlying pathophysiological condition of chronic kidney disease
Clinical and Experimental Nephrology (2012)
-
Thiazolidinediones in the treatment of patients with Post-Transplant-Hyperglycemia or new-onset diabetes mellitus after renal transplantation (NODAT) – A new therapeutic option?
Wiener klinische Wochenschrift (2010)
-
Renoprotective effects of an angiotensin II receptor blocker in experimental model rats with hypertension and metabolic disorders
Hypertension Research (2009)