Abstract
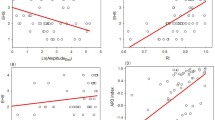
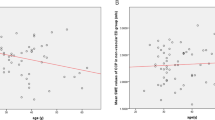
Knowledge of the time course of penile erection is very important to understanding erection physiology. The changes in the intracavernosal pressure (ICP) and the different phases of an erection are pivotal to the ability to produce and maintain a rigid penile erection. This study investigated an objective and low-invasiveness method for identifying different erection phases based on an innovative ICP analysis technique. Blood infuses into the corpora cavernosa and causes the ICP to increase. The ICP usually exhibits tiny oscillations at the frequency of the heartbeat when it increases from diastole to systole. The characteristic oscillation amplitudes corresponding to the period when the full and rigid erection phases begin can be extracted by power spectral density analysis. The reliability and accuracy of the proposed method was verified by the Bland–Altman graphs indicating a good agreement with the existing method that compares the ICP with the arterial pressure. Moreover, all of the intraclass correlation coefficient values were close to 1.00, with the lower limit of the 95% confidence interval exceeding 0.75. The described novel objective and low-invasiveness method can therefore be used for identifying the full and rigid erection phases of the penis in urological investigations during different erection phases.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dean RC, Lue TF . Physiology of penile erection and pathophysiology of erectile dysfunction. Urol Clin North Am 2005; 32: 379–395.
Lue TF . The mechanism of penile erection in the monkey. Semin Urol 1986; 4: 217–224.
Becker AJ, Uckert S, Stief CG, Truss MC, Machtens S, Scheller F et al. Cavernous and systemic testosterone levels in different phases of human penile erection. Urology 2000; 56: 125–129.
Chen KK, Chan JY, Chang LS, Chen MT, Chan SH . Intracavernous pressure as an experimental index in a rat model for the evaluation of penile erection. J Urol 1992; 147: 1124–1128.
Giuliano F, Bernabe J, Jardin A, Rousseau JP . Antierectile role of the sympathetic nervous system in rats. J Urol 1993; 150 (2 Pt 1): 519–524.
Mulcahy JJ . Male Sexual Function: A Guide to Clinical Management. 2nd edn. Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, 2006.
Smith DR . Smith's General Urology. 16th edn. Lange Medical Books/McGraw-Hill: New York, 2004.
Wespes E, Delcour C, Rondeux C, Struyven J, Schulman CC . The erectile angle: Objective criterion to evaluate the papaverine test in impotence. J Urol 1987; 138: 1171–1173.
Suzuki N, Sato Y, Hisasue S, Kato R, Suzuki K, Tsukamoto T . Effect of testosterone on intracavernous pressure elicited with electrical stimulation of the medial preoptic area and cavernous nerve in male rats. J Androl 2007; 28: 218–222.
Lee RP, Wang D, Lin NT, Chou YW, Chen HI . A modified technique for tail cuff pressure measurement in unrestrained conscious rats. J Biomed Sci 2002; 9: 424–427.
Matsuura S, Obara T, Tsuchiya N, Suzuki Y, Habuchi T . Cavernous nerve regeneration by biodegradable alginate gel sponge sheet placement without sutures. Urology 2006; 68: 1366–1371.
Tian L, Xin ZC, Liu WJ, Yang YM, Liu G, Chen L et al. Effects of icariin on the erectile function and expression of nitrogen oxide synthase isoforms in corpus cavernosum of arterigenic erectile dysfunction rat model. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2004; 84: 954–957.
Brock G, Tu LM, Linet OI . Return of spontaneous erection during long-term intracavernosal alprostadil (Caverject) treatment. Urology 2001; 57: 536–541.
Mills TM, Lewis RW, Stopper VS . Androgenic maintenance of inflow and veno-occlusion during erection in the rat. Biol Reprod 1998; 59: 1413–1418.
El-Sakka AI, Lue TF . Physiology of penile erection. ScientificWorldJournal 2004; 4 (Suppl 1): 128–134.
Geddes LA, Voelz M, Combs C, Reiner D, Babbs CF . Characterization of the oscillometric method for measuring indirect blood pressure. Ann Biomed Eng 1982; 10: 271–280.
Mauck GW, Smith CR, Geddes LA, Bourland JD . The meaning of the point of maximum oscillations in cuff pressure in the indirect measurement of blood pressure—part ii. J Biomech Eng 1980; 102: 28–33.
Rehman J, Christ G, Melman A, Fleischmann J . Intracavernous pressure responses to physical and electrical stimulation of the cavernous nerve in rats. Urology 1998; 51: 640–644.
Brown DR, Randall DC, Knapp CF, Lee KC, Yingling JD . Stability of the heart rate power spectrum over time in the conscious dog. FASEB J 1989; 3: 1644–1650.
Harris FJ . On the use of windows for harmonic analysis with the discrete Fourier transform. Proc IEEE 1989; 66: 51–83.
Kuo TB, Chan SH . Continuous, on-line, real-time spectral analysis of systemic arterial pressure signals. Am J Physiol 1993; 264 (6 Pt 2): H2208–H2213.
Rienzo MD . Blood Pressure and Heart Rate Variability: Computer Analysis, Methodology and Clinical Applications. IOS Press: Amsterdam, 1993.
Bland JM, Altman DG . Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1986; 1: 307–310.
Bland JM, Altman DG . A note on the use of the intraclass correlation coefficient in the evaluation of agreement between two methods of measurement. Comput Biol Med 1990; 20: 337–340.
Portney LG, Watkins MP . Foundations of Clinical Research: Application to Practice 2nd edn. Prentice Hall Health: New Jersey, 2000.
Lee J, Koh D, Ong CN . Statistical evaluation of agreement between two methods for measuring a quantitative variable. Comput Biol Med 1989; 19: 61–70.
Ding XG, Li SW, Zheng XM, Hu LQ, Hu WL, Luo Y . Effect of platelet rich plasma on the regeneration of cavernous nerve: experiment with rats. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2008; 88: 2578–2580.
Zahran AR, Vachon P, Courtois F, Carrier S . Increases in intracavernous penile pressure following injections of excitatory amino acid receptor agonists in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus of anesthetized rats. J Urol 2000; 164: 1793–1797.
Giuliano FI, Allard J, Rampin O, Droupy S, Benoit G, Alexandre L et al. Pro-erectile effect of systemic apomorphine: existence of a spinal site of action. J Urol 2002; 167: 402–406.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by grants V95D-008 from the Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan. We are grateful to Lee Hui-Chen for her assistance with statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, WR., Chuang, CY., Li, PC. et al. Intracavernosal pressure characteristics analyzed by power spectral density for identifying the phase of penile erection. Int J Impot Res 21, 336–342 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2009.30
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2009.30