Abstract
Aim
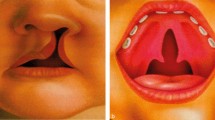
Malonyl‐CoA is regarded as a key signaling molecule in mammalian cells. It is converted to acetyl‐CoA, and to a lesser extent, to malonyl acid and malonylcarnitine (C3DC). Availability of carnitine has been reported to be essential for the developing fetus. The objectives of the present study were to analyze associations of malonylcarnitine, acetylcarnitine (C2), and free carnitine (C0) in subjects with orofacial clefts.
Methodology
We performed a retrospective analysis of carnitine concentration obtained from a newborn screening program carried out in our institution. Concentrations of whole blood malonylcarnitine, acetylcarnitine, and free carnitine were measured using tandem mass spectrometry. The study group consisted of 51 children with non‐syndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate. In total, 106 healthy children without congenital anomalies served as controls. Cut‐off points were established using likelihood ratio values.
Results
The mean concentration of malonylcarnitine in the cleft group was lower than that of the control group, 0.048 μmol·L−1 vs. 0.058 μmol·L−1, respectively (P=0.009). In patients with orofacial cleft, low malonylcarnitine levels (≤0.047 μmol·L−1) were 1.7 times more predominant than in healthy individuals (P=0.03). The mean concentration of acetylcarnitine was also lower in affected newborns in comparison to controls, 33.8 μmol·L−1 vs. 37.8 μmol·L−1, respectively (P=0.026). After analysis of acetylcarnitine and free carnitine concentrations, the likelihood ratio test did not indicate valuable cut‐off points.
Conclusion
The study provides initial data indicating a potential association between decreased malonylcarnitine and abnormal palatogenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hozyasz, K., Oltarzewski, M. & Dudkiewicz, Z. Malonylcarnitine in Newborns with Non‐syndromic Cleft Lip with or without Cleft Palate. Int J Oral Sci 2, 136–141 (2010). https://doi.org/10.4248/IJOS10047
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4248/IJOS10047