Abstract
Aim
The aim of this survey was to compare Chinese natives and foreign inhabitants in Chengdu, China, with respect to: (1) attitudes towards dental appearance, (2) subjective orthodontic treatment need, and (3) the main factors influencing orthodontic treatment need.
Methodology
A total of 522 subjects, including 227 foreign inhabitants and 295 Chinese natives in Chengdu participated in the survey. A simple random sampling method was adopted and a face‐to‐face interview was conducted at some public sites using a questionnaire. Data was entered by two persons synchronously using Epidata 3.0, and SPSS 13.0 was used to analyze these data.
Results
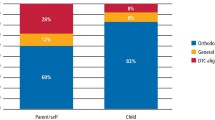
89.0% of foreign inhabitants were satisfied with their teeth compared to only 46.8% of Chinese natives. Females were more dissatisfied with their teeth than males. Chinese natives put improving appearance as the top priority (55.9%) for seeking orthodontic treatment; however, in foreign inhabitants, the main reason for seeking treatment was to improve masticatory function (44.1%), followed by ”to be pretty“ (35.2%). The importance of well‐aligned teeth and self‐perception of psycho‐social impact of malocclusion were the same two main factors influencing subjective orthodontic treatment need (P<0.05) in foreign inhabitants and Chinese natives. Subjective orthodontic treatment need between the two target groups was significantly different (P<0.05).
Conclusion
(1) It was very common that Chinese natives were dissatisfied with their dental appearance, and their subjective orthodontic treatment needs were high. (2) There were some differences in orthodontic treatment motives between the two target groups. (3) There were differences in subjective orthodontic treatment needs between foreign inhabitants and Chinese natives. However, the prominent influential factors were almost the same. There may be benefit to understanding subjective orthodontic needs of different races.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Tang, Y., Huang, X. et al. Factors Influencing Subjective Orthodontic Treatment Need and Culture‐related Differences among Chinese Natives and Foreign Inhabitants. Int J Oral Sci 2, 149–157 (2010). https://doi.org/10.4248/IJOS10050
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4248/IJOS10050