Abstract
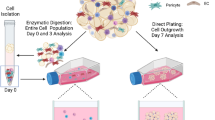
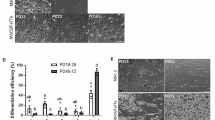
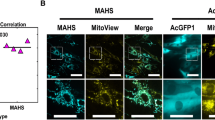
When adipose‐derived stem cells (ASCs) are retrieved from the stromal vascular portion of adipose tissue, a large amount of mature adipocytes are often discarded. However, by modified ceiling culture technique based on their buoyancy, mature adipocytes can be easily isolated from the adipose cell suspension and dedifferentiated into lipid‐free fibroblast‐like cells, named dedifferentiated fat (DFAT) cells. DFAT cells re‐establish active proliferation ability and undertake multipotent capacities. Compared with ASCs and other adult stem cells, DFAT cells showed unique advantages in their abundance, isolation and homogeneity. In this concise review, the establishment and culture methods of DFAT cells are introduced and the current profiles of their cellular nature are summarized. Under proper induction culture in vitro or environment in vivo, DFAT cells could demonstrate adipogenic, osteogenic, chondrogenic and myogenic potentials. In angiogenic conditions, DFAT cells could exhibit perivascular characteristics and elicit neovascularization. Our preliminary findings also suggested the pericyte phenotype underlying such cell lineage, which supported a novel interpretation about the common origin of mesenchymal stem cells and tissue‐specific stem cells within blood vessel walls. Current research on DFAT cells indicated that this alternative source of adult multipotent cells has great potential in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, J., Sugawara, A., Yamashita, J. et al. Dedifferentiated fat cells: an alternative source of adult multipotent cells from the adipose tissues. Int J Oral Sci 3, 117–124 (2011). https://doi.org/10.4248/IJOS11044
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4248/IJOS11044
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Hypertonicity induces mitochondrial extracellular vesicles (MEVs) that activate TNF-α and β-catenin signaling to promote adipocyte dedifferentiation
Stem Cell Research & Therapy (2023)
-
Integrins and extracellular matrix proteins modulate adipocyte thermogenic capacity
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Towards an Insulin Resistant Adipose Model on a Chip
Cellular and Molecular Bioengineering (2021)
-
The neovascularization effect of dedifferentiated fat cells
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Focus on dedifferentiated adipocytes: characteristics, mechanisms, and possible applications
Cell and Tissue Research (2019)