Abstract
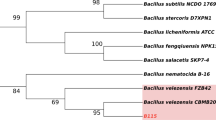
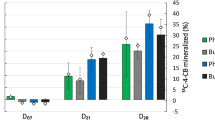
Bacteria and functional genes associated with biphenyl (BP) degradation in the root zone of an Austrian pine (Pinus nigra L.) growing naturally in polychlorinated-BP (PCB)-contaminated soil were identified using stable isotope probing (SIP) integrated with comprehensive functional gene analyses. SIP revealed 75 different genera that derived carbon from 13C-BP, with Pseudonocardia, Kribella, Nocardiodes and Sphingomonas predominating carbon acquisition. Rhodococcus spp. were not detected with SIP, despite being the most abundant BP utilizers isolated from agar plates. Only one organism, an Arthrobacter spp., was detected as a BP utilizer by both cultivation and SIP methods. Time-course SIP analyses indicated that secondary carbon flow from BP-utilizing bacteria into other soil organisms may have occurred largely between 4 and 14 days incubation. Functional gene contents of the BP-utilizing metagenome (13C-DNA) were explored using the GeoChip, a functional gene array containing 6465 probes targeting aromatic degradative genes. The GeoChip detected 27 genes, including several associated with catabolism of BP, benzoate and a variety of aromatic ring hydroxylating dioygenase (ARHD) subunits. Genes associated with the β-ketoadipate pathway were also detected, suggesting a potential role for this plant aromatic catabolic pathway in PCB degradation. Further ARHD analyses using targeted polymerase chain reaction primers and sequence analyses revealed novel dioxygenase sequences in 13C-DNA, including several sequences that clustered distantly from all known ARHDs and others that resembled known Rhodococcus ARHDs. The findings improve our understanding of BP degradation and carbon flow in soil, reveal the extent of culture bias, and may benefit bioremediation research by facilitating the development of molecular tools to detect, quantify and monitor populations involved in degradative processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Accession codes
Accessions
GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ
References
Abraham WR, Nogales B, Golyshin PN, Pieper DH, Timmis KN . (2002). Polychlorinated biphenyl-degrading microbial communities in soils and sediments. Curr Opin Microbiol 5: 246–253.
Amman RI, Ludwig W, Schleifer KH . (1995). Phylogenetic identification and in situ detection of individual microbial cells without cultivation. Microbiol Rev 59: 143–169.
Bailey RE, Gonsoir SJ, Rhinehart WL . (1983). Biodegradation of the monochlorobiphenyls and biphenyl in river water. Environ Sci Technol 17: 617–621.
Baldwin BR, Nakatsu CH, Nies L . (2003). Detection and enumeration of aromatic oxygenase genes by multiplex and real-time PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 69: 3350–3358.
Bellicanta GS, Pellizari VH . (2004). Development of degenerate primers for detection of distinct aromatic ring-hydroxylating dioxygenases. 10th ISME International Symposium on Microbial Ecology; 2004, Cancun.
Cole JR, Chai B, Farris RJ, Wang Q, Kulam SA, McGarrell DM et al. (2005). The ribosomal database project (RDPII): sequences and tools for high-throughput rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 33 (Database Issue): D294–D296.
Dejonghe W, Berteloot E, Goris J, Boon N, Crul K, Maertens S et al. (2003). Synergistic degradation of linuron by a bacterial consortium and isolation of a single linuron-degrading variovorax strain. Appl Environ Microbiol 69: 1532–1541.
Donnely PK, Hegde RS, Fletcher JS . (1994). Growth of PCB-degrading bacteria on compounds from photosynthetic plants. Chemosphere 28: 981–988.
Ebert S, Rieger PG, Knackmuss HJ . (1999). Function of coenzyme F420 in aerobic catabolism of 2,4, 6-trinitrophenol and 2,4-dinitrophenol by Nocardioides simplex FJ2–1A. J Bacteriol 181: 2669–2674.
Erb RW, Wagner-Dobler I . (1993). Detection of polychlorinated biphenyl degradation genes in polluted sediments by direct DNA extraction and polymerase chain reaction. Appl Environ Microbiol 59: 4065–4073.
Ferraroni M, Seifert J, Travkin VM, Thiel M, Kaschabek S, Scozzafava A et al. (2005). Crystal structure of the hydroxyquinol 1,2-dioxygenase from Nocardioides simplex 3E, a key enzyme involved in polychlorinated aromatics biodegradation. J Biol Chem 280: 21144–21154.
Flagan SF, Leadbetter JR . (2006). Utilization of capsaicin and vanillylamine as growth substrates by Capsicum (hot pepper)-associated bacteria. Environ Microbiol 8: 560–565.
Friedrich MW . (2006). Stable-isotope probing of DNA: insights into the function of uncultivated microorganisms from isotopically labeled metagenomes. Curr Opin Biotechnol 17: 59–66.
Gallagher E, McGuinness L, Phelps C, Youg LY, Kerkhof LJ . (2005). 13C-carrier DNA shortens the incubation time needed to detect benzoate-utilizing denitrifying bacteria by stable-isotope probing. Appl Environ Microbiol 71: 5192–5196.
Ginard M, Lalucat J, Tummler B, Romling U . (1997). Genome organization of Pseudomonas stutzeri and resulting taxonomic and evolutionary considerations. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47: 132–143.
Griffiths RI, Whiteley AS, O'Donnell AG, Bailey MJ . (2000). Rapid method for coextraction of DNA and RNA from natural environments for analysis of ribosomal DNA- and RNA-based microbial community composition. Appl Environ Microbiol 66: 5488–5491.
Grund E, Kutzner HJ . (1998). Utilization of quinate and p-hydroxybenzoate by actinomycetes: key enzymes and taxonomic relevance. J Basic Microbiol 38: 241–255.
Hammann R, Kutzner HJ . (1998). Key enzymes for the degradation of benzoate, m- and p-hydroxybenzoate by some members of the order Actinomycetales. J Basic Microbiol 38: 207–220.
Harwood CS, Parales RE . (1996). The beta-ketoadipate pathway and the biology of self-identity. Annu Rev Microbiol 50: 553–590.
He Z, Gentry T, Schadt CW, Wu L, Liebich J, Chong SC et al. (2007). GeoChip: a comprehensive microarray for investigating biogeochemical and ecological environmental processes. ISME J 1: 67–77.
Jeon CO, Park W, Ghiorse WC, Madsen EL . (2004). Polaromonas naphthalenivorans sp. nov., a naphthalene-degrading bacterium from naphthalene-contaminated sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54: 93–97.
Johnson JL . (1994). Similarity analyses of rRNAs. In: Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Wood WA, Krieg NR (eds). Methods for General and Molecular Bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC, pp 683–700.
Juteau P, Larocque R, Rho D, LeDuy A . (1999). Analysis of the relative abundance of different types of bacteria capable of toluene degradation in a compost biofilter. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 52: 863–868.
Kamagata Y, Fulthorpe RR, Tamura K, Takami H, Forney LJ, Tiedje JM . (1997). Pristine environments harbor a new group of oligotrophic 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid-degrading bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 63: 2266–2272.
Kampfer P, Kroppenstedt RM . (2004). Pseudonocardia benzenivorans sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54: 749–751.
Leigh MB, Fletcher JS, Nagle DP, Mackova M, Macek T . (2001). Vegetation and fungi at Czech PCB-contaminated sites as bioremediation candidates. In: Leeson A, Foote EA, Banks MK, Magar V (eds). Phytoremediation, Wetlands and Sediments: Sixth International In Situ and On-site Bioremediation Symposium; June 4–7, 2001; San Diego, CA. Battelle Press: Columbus, OH, pp 61–68.
Leigh MB, Prouzova P, Mackova M, Macek T, Nagle DP, Fletcher JS . (2006). Polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB)-degrading bacteria associated with trees in a PCB-contaminated site. Appl Environ Microbiol 72: 2331–2342.
Lueders T, Kindler R, Miltner A, Friedrich MW, Kaestner M . (2006). Identification of bacterial micropredators distinctively active in a soil microbial food web. Appl Environ Microbiol 72: 5342–5348.
Madsen EL . (2006). The use of stable isotope probing techniques in bioreactor and field studies on bioremediation. Curr Opin Biotechnol 17: 92–97.
Manefield M, Whiteley AS, Griffiths RI, Bailey MJ . (2002). RNA stable isotope probing, a novel means of linking microbial community function to phylogeny. Appl Environ Microbiol 68: 5367–5373.
Padmanabhan P, Padmanabhan S, DeRito C, Gray A, Gannon D, Snape JR et al. (2003). Respiration of 13C-labeled substrates added to soil in the field and subsequent 16S rRNA gene analysis of 13C-labeled soil DNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 69: 1614–1622.
Pieper DH . (2005). Aerobic degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67: 170–191.
Ringelberg DB, Talley JW, Perkins EJ, Tucker SG, Luthy RG, Bouwer EJ et al. (2001). Successon of phenotypic, genotypic and metabolic community characteristics during in vitro bioslurry treatment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-contaminated sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 67: 1542–1550.
Saito A, Iwabuchi T, Harayama S . (2000). A novel phenanthrene dioxygenase from Nocardioides sp Strain KP7:expression in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 182: 2134–2141.
Singer AC, Thompson IP, Bailey MJ . (2004). The tritrophic trinity: a source of pollutant-degrading enzymes and its implications for phytoremediation. Curr Opin Microbiol 7: 239–244.
Swofford DL . (2000). PAUP*: Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (and other methods), version 40. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA.
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ . (1994). CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22: 4673–4680.
Thompson JR, Marcelino LA, Polz MF . (2002). Heteroduplexes in mixed-template amplifications: formation, consequence and elimination by ‘reconditioning PCR’. Nucleic Acids Res 30: 2083–2088.
Tillmann S, Strompl C, Timmis KN, Abraham WR . (2005). Stable isotope probing reveals the dominant role of Burkholderia species in aerobic degradation of PCBs. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 52: 207–217.
Whiteley AS, Manefield M, Lueders T . (2006). Unlocking the ‘microbial black box’ using RNA-based stable isotope probing technologies. Curr Opin Biotechnol 17: 67–71.
Wilmotte A, Van der Auwera F, de Wachter R . (1993). Structure of the 16S ribosomal RNA of the thermophilic cyanobacterium Chlorogloeopsis HTF (Mastigoclaudus laminosus HTF) strain PCC7518, and phylogenetic analysis. FEBS Lett 317: 96–100.
Wu L, Liu X, Schadt CW, Zhou J . (2006). Microarray-based analysis of subnanogram quantities of microbial community DNAs by using whole-community genome amplification. Appl Environ Microbiol 72: 4931–4941.
Yu Y, Breitbart M, McNairnie P, Rohwer F . (2006). FastGroupII: a web-based bioinformatics platform for analyses of large 16S rDNA libraries. BMC Bioinformatics 7: 57.
Zhou J, Bruns MA, Tiedje JM . (1996). DNA recovery from soils of diverse composition. Appl Environ Microbiol 62: 316–322.
Acknowledgements
This work benefited from the technical assistance of Anthony Gaca, Cleopatra Mwansa and Najibah Rehman. Thanks to Mike Manefield and Mark J Bailey for training in SIP techniques. We thank Liyou Wu for providing GeoChips, Gene Wickham for training in hybridization methods and Ye Deng and Dan Cardin for bioinformatic support. T-RF prediction and Rieske center HMM analyses were performed by Benli Chai. SIP incubation methods were developed by Joonhong Park, Debora Rodrigues provided real-time PCR protocols and Stephan Gantner contributed to soil DNA extraction method development. Field site access was provided generously by Colorlak, logistical support provided by Vítek Matĕjů, Martina Macková and Tomáš Macek and Nathan Stewart assisted with field work. This work was supported by David L Boren (NSEP) Graduate International Fellowships and an NSF Postdoctoral Fellowship to MBL, NIEHS grant 2P42ES04911 under the Superfund Basic Science Program, and The Center for Microbial Ecology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leigh, M., Pellizari, V., Uhlík, O. et al. Biphenyl-utilizing bacteria and their functional genes in a pine root zone contaminated with polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). ISME J 1, 134–148 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2007.26
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2007.26
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Pot experimental trial for assessing the role of different composts on decontamination and reclamation of a polluted soil from an illegal dump site in Southern Italy using Brassica juncea and Sorghum bicolor
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2023)
-
Identification of bovine respiratory disease through the nasal microbiome
Animal Microbiome (2022)
-
Metabolic flexibility of aerobic methanotrophs under anoxic conditions in Arctic lake sediments
The ISME Journal (2022)
-
DNA stable isotope probing on soil treated by plant biostimulation and flooding revealed the bacterial communities involved in PCB degradation
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Novel clades of soil biphenyl degraders revealed by integrating isotope probing, multi-omics, and single-cell analyses
The ISME Journal (2021)