Abstract
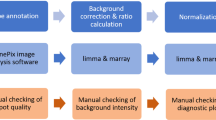
The plant pathogenic Betaproteobacterium Ralstonia solanacearum is a complex species in that most of the strains share the common characteristic of being naturally transformable. In this study, we used a new approach based on comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) on microarrays to investigate the extent of horizontal gene transfers (HGTs) between different strains of R. solanacearum. Recipient strains from phylotypes I, II and III were naturally transformed in vitro by genomic DNA from the GMI1000 reference strain (phylotype I) and the resulting DNAs were hybridized on a microarray representative of the 5120 predicted genes from the GMI1000 strain. In addition to transfer of the antibiotic resistance marker, in 8 of the 16 tested transformants, CGH on microarrays detected other transferred GMI1000 genes and revealed their number, category, function and localization along the genome. We showed that DNA blocks up to 30 kb and 33 genes could be integrated during a single event. Most of these blocks flanked the marker gene DNA but, interestingly, multiple DNA acquisitions along the genome also occurred in a single recombinant clone in one transformation experiment. The results were confirmed by PCR amplification, cloning and sequencing and Southern blot hybridization. This represents the first comprehensive identification of gene acquisitions and losses along the genome of the recipient bacterial strain during natural transformation experiments. In future studies, this strategy should help to answer many questions related to HGT mechanisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Accession codes
References
Allen C, Prior P, Hayward AC . (2005). Bacterial Wilt Disease and the Ralstonia solanacearum Species complex. APS Press: St Paul, MN, USA.
Araki HD, Goss TEM, Jakob K, Halldorsdottir SS, Kreitman M, Bergelson J . (2006). Presence/absence polymorphism for alternative pathogenicity islands in Pseudomonas viridiflava, a pathogen of Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 5887–5892.
Bertolla F, Frostegård A, Brito B, Nesme X, Simonet P . (1999). During infection of its hosts, the plant pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum naturally develops a state of competence and exchanges genetic material. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 12: 467–472.
Bertolla F, Van Gijsegem F, Nesme X, Simonet P . (1997). Conditions for natural transformation of Ralstonia solanacearum. Appl Environ Microbiol 63: 4965–4968.
Boucher C, Martinel A, Barberis P, Alloing G, Zischek C . (1985). Virulence genes are carried by a megaplasmid of the plant pathogen Pseudomonas solanacearum. Mol Gen Genet 205: 270–275.
Coenye T, Vandamme P . (2005). Displacement of ɛ-proteobacterial core genes by horizontally transferred homologous genes. Res Microbiol 156: 738–747.
Comas I, Moya A, Azad RK, Lawrence JG, Gonzalez-Candelas F . (2006). The evolutionary origin of Xanthomonadales genomes and the nature of the horizontal gene transfer process. Mol Biol Evol 23: 2049–2057.
Coupat B, Chaumeille-Dole F, Fall S, Prior P, Simonet P, Nesme X et al. (2008). Natural transformation in the Ralstonia solanacearum species complex: number and size of DNA that can be transferred. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 66: 14–24.
Cunnac S, Occhialini A, Barberis P, Boucher C, Genin S . (2004). Inventory and functional analysis of the large Hrp regulon in Ralstonia solanacearum: identification of novel effector proteins translocated to plant host cells through the type III secretion system. Mol Microbiol 53: 115–128.
Daubin V, Lerat E, Perriere G . (2003). The source of laterally transferred genes in bacterial genomes. Genome Biol 4: R57.
Daubin V, Ochman H . (2004). Bacterial genomes as new gene homes: the genealogy of ORFans in E. coli. Genome Res 14: 1036–1042.
Davison J . (1999). Genetic exchange between bacteria in the environment. Plasmid 42: 73–91.
de Vries J, Wackernagel W . (2002). Integration of foreign DNA during natural transformation of Acinetobacter sp. by homology-facilitated illegitimate recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99: 2094–2099.
Fall S, Mercier A, Bertolla F, Calteau A, Gueguen L, Perrière G et al. (2007). Horizontal gene transfer regulation in bacteria as a ‘spandrel’ of DNA repair mechanisms. PLoS One 2: e1055.
Fegan M, Prior P . (2005). How complex is the ‘Ralstonia solanacearum species complex’. In: Allen C, Prior P, Hayward C (ed). Bacterial Wilt: the Disease and the Ralstonia solanacearum Species Complex. APS Press: St Paul, MN, USA, pp 449–462.
Gogarten JP, Townsend JP . (2005). Horizontal gene transfer, genome innovation and evolution. Nat Rev Microbiol 3: 679–687.
Guidot A, Prior P, Schoenfeld J, Carrère S, Genin S, Boucher C . (2007). Genomic structure and phylogeny of the plant pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum inferred from gene distribution analysis. J Bacteriol 189: 377–387.
Hacker J, Kaper JB . (2000). Pathogenicity islands and the evolution of microbes. Annu Rev Microbiol 54: 641–679.
Hudson RE, Bergthorsson U, Roth JR, Ochman H . (2002). Effect of chromosome location on bacterial mutation rates. Mol Biol Evol 19: 85–92.
Hueck CJ . (1998). Type III protein secretion systems in bacterial pathogens of animals and plants. Mol Biol Rev 62: 379–433.
Kirill SL, Shor BM, Tran HT, Taylor W, Keen JD, Resnick MA et al. (1998). Factors affecting inverted repeat stimulation of recombination and deletion in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 148: 1507–1524.
Kobayashi I . (2001). Behavior of restriction-modification systems as selfish mobile elements and their impact on genome evolution. Nucleic Acids Res 29: 3742–3756.
Koonin EV, Wolf YI . (2008). Genomics of bacteria and archaea: the emerging dynamic view of the prokaryotic world. Nucleic Acids Res 36: 6688–6719.
Loria R, Kers J, Joshi M . (2006). Evolution of plant pathogenicity in Streptomyces. Annu Rev Phytopathol 44: 469–487.
Ma W, Dong FFT, Stavrinides J, Guttman DS . (2006). Type III effector diversification via both pathoadaptation and horizontal transfer in response to a coevolutionary arms race. PLoS Genet 2: 2131–2142.
Majewski J, Cohan FM . (1999). DNA sequence similarity requirements for interspecific recombination in Bacillus. Genetics 153: 1525–1533.
Majewski J, Zawadzki P, Pickerill P, Cohan FM, Dowson CG . (2000). Barriers to genetic exchange between bacterial species: Streptococcus pneumoniae transformation. J Bacteriol 182: 1016–1023.
Matic I . (1995). Interspecies gene exchange in bacteria: the role of SOS and mismatch repair system in evolution of species. Cell 80: 507–515.
Meier P, Wackernagel W . (2005). Impact of mutS inactivation on foreign DNA acquisition by natural transformation in Pseudomonas stutzeri. J Bacteriol 187: 143–154.
Mercier A, Bertolla F, Passelègue-Robe E, Simonet P . (2007). Natural transformation based foreign DNA acquisition in a Ralstonia solanacearum mutS mutant. Res Microbiol 158: 537–544.
Nakamura Y, Itoh T, Matsuda H, Gojobori T . (2004). Biased biological functions of horizontally transferred genes in prokaryotic genomes. Nat Genet 36: 760–766.
Nester EW, Stocker AD . (1963). Biosynthetic latency in early stages of deoxyribonucleic acid transformation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 86: 785–796.
Ochman H, Lawrence JG, Groisman EA . (2000). Lateral gene transfer and the nature of bacterial innovation. Nature 405: 299–304.
Occhialini A, Cunnac S, Reymond N, Genin S, Boucher C . (2005). Genome-wide analysis of gene expression in Ralstonia solanacearum reveals that the hrpB gene acts as a regulatory switch controlling multiple virulence pathways. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 18: 938–949.
Ochman H, Moran NA . (2001). Genes lost and genes found: evolution of bacterial pathogenesis and symbiosis. Science 292: 1096–1099.
Raymond J, Zhaxybayeva O, Gogarten JP, Gerdes SY, Blankenship RE . (2002). Whole-genome analysis of photosynthetic prokaryotes. Science 298: 1616–1620.
Rayssiguier C, Thaler DS, Radman M . (1989). The barrier to recombination between Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium is disrupted in mismatch-repair mutants. Nature 342: 396–401.
Ruzin A, Lindsay J, Novick RP . (2001). Molecular genetics of SaPI1—a mobile pathogenicity island in Staphylococcus aureus. Mol Microbiol 41: 365–377.
Salanoubat M, Genin S, Artiguenave F, Gouzy J, Mangenot S, Arlat M et al. (2002). Genome sequence of the plant pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum. Nature 415: 497–502.
Sarkar SF, Gordon JS, Martin GB, Guttman DS . (2006). Comparative genomics of host-specific virulence in Pseudomonas syringae. Genetics 174: 1041–1056.
Takahata S, Ida T, Senju N, Sanbongi Y, Miyata A, Maebashi K et al. (2007). Horizontal gene transfer of ftsI, encoding penicillin-binding protein 3, in Haemophilus influenzae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 51: 1589–1595.
Thomas CM, Nielsen KM . (2005). Mechanisms of, and barriers to, horizontal gene transfer between bacteria. Nat Rev Microbiol 3: 711–721.
Valls M, Genin S, Boucher C . (2006). Integrated regulation of the type III secretion system and other virulence determinants in Ralstonia solanacearum. PloS Pathogens 2: 798–807.
Wicker E, Grassart L, Coranson-Beaudu R, Mian D, Guilbaud C, Fegan M et al. (2007). Ralstonia solanacearum strains from Martinique (French West Indies) exhibiting a new pathogenic potential. Appl Environ Microbiol 73: 6790–6801.
Acknowledgements
The microarray experiments were conducted in the LIPM (INRA-CNRS) laboratory in Toulouse (France) with Christian Boucher and Stéphane Genin. We acknowledge them for their kind welcome and help. We are grateful to D Bernillon for technical assistance in the Southern blot hybridizations. This study was supported by the Regional Council of La Réunion, the European Community (FEOGA) and CIRAD under Research Grant 3P118. Bénédicte Coupat is financially supported by a grant from MENESER.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guidot, A., Coupat, B., Fall, S. et al. Horizontal gene transfer between Ralstonia solanacearum strains detected by comparative genomic hybridization on microarrays. ISME J 3, 549–562 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2009.14
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2009.14
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
High genomic variability in the plant pathogenic bacterium Pectobacterium parmentieri deciphered from de novo assembled complete genomes
BMC Genomics (2018)
-
Comparative genomic analysis of Ralstonia solanacearum reveals candidate genes for host specificity
BMC Genomics (2015)
-
Contrasting recombination patterns and demographic histories of the plant pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum inferred from MLSA
The ISME Journal (2012)
-
Genomes of three tomato pathogens within the Ralstonia solanacearum species complex reveal significant evolutionary divergence
BMC Genomics (2010)
-
In planta gene expression analysis of Xanthomonas oryzae pathovar oryzae, African strain MAI1
BMC Microbiology (2010)