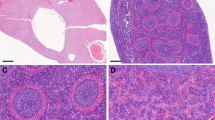
Abstract
At least 12 species in the genus Bartonella are zoonotic pathogens that may be transmitted among mammalian hosts by fleas or other arthropods. Apparent host specificity by some Bartonella species to mammalian hosts has been observed, and the detection of multiple Bartonella species in mammalian fleas suggests that fleas take bloodmeals from a variety of host species. However, many flea species are observed to parasitize a narrow host range. Therefore, we suspect that fleas may acquire Bartonella by a mechanism other than ingesting infectious blood. We found that detection of multiple Bartonella genotypes and species is apparently common in fleas and that the majority of fleas tested (5/9) carried Bartonella species atypical of their hosts. We also detected Bartonella DNA in flea reproductive tissues, suggesting that vertical transmission of this organism in vectors is possible, potentially leading to the accumulation of Bartonella diversity over time within fleas.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Abbot P, Aviles AE, Eller L, Durden LA . (2007). Mixed infections, cryptic diversity, and vector-borne pathogens: evidence from Polygenis fleas and Bartonella species. Appl Environ Microbiol 73: 6045–6052.
Bai Y, Kosoy M, Cully JF, Bala T, Ray C, Collinge SK . (2007). Acquisition of non-specific Bartonella strains by the northern grasshopper mouse (Onychomys leucogaster). FEMS Microbial Ecol 61: 438–448.
Bai Y, Kosoy M, Martin A, Ray C, Sheff K, Chalcraft L et al. (2008). Characterization of Bartonella strains isolated from black-tailed prairie dogs (Cynomys ludovicianus). Vector-Borne Zoonot 8: 1–5.
Bown KJ, Bennet M, Begon M . (2004). Flea-borne Bartonella grahamii and Bartonella taylorii in bank voles. Emerg Infect Dis 10: 684–687.
Brinkerhoff RJ . (2008). Mammal and Flea Occurrence in Association with Black-Tailed Prairie Dog (Cynomys Ludovicianus) Colonies: Implications for Interspecific Plague Transmission Ph.D. Dissertation University of Colorado, Boulder, Colorado, USA.
Brinkerhoff RJ, Collinge SK, Bai Y, Ray C . (2009). Are carnivores universally good sentinels of plague? Vector-Borne Zoonot 9: 491–497.
Brinkerhoff RJ, Ray C, Thiagarajan B, Cully JF, Collinge SK, Holmes B et al. (2008). Prairie dog presence affects disease vector occurrence on small rodents. Ecography 31: 654–662.
Castle KT, Kosoy M, Lerdthusnee K, Phelan L, Bai Y, Gage KL et al. (2004). Prevalence and diversity of Bartonella in rodents of northern Thailand: a comparison with Bartonella in rodents from southern China. Am J Trop Med Hyg 70: 429–433.
Chomel BB, Boulouis HJ, Breitschwerdt EB, Kasten RW, Vayssier-Taussat M, Birtles RJ et al. (2009). Ecological fitness and strategies of adaptation of Bartonella species to their hosts and vectors. Vet Res 40. ARTN 29.
Chomel BB, Boulouis HJ, Maruyama S, Breitschwerdt EB . (2006). Bartonella spp. in pets and effect on human health. Emerg Infect Dis 12: 389–394.
Chomel BB, Kasten RW, Floyd-Hawkins K, Chi B, Yamamoto K, Roberts-Wilson J et al. (1996). Experimental transmission of Bartonella henselae by the cat flea. J Clin Microbiol 34: 1952–1956.
Finkelstein JL, Brown TP, O’Reilly KL, Wedincamp J, Foil LD . (2002). Studies on the growth of Bartonella henselae in the cat flea (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae). J Med Entomol 39: 915–919.
Gabriel MW, Henn J, Foley FE, Brown RN, Kasten RW, Foley P et al. (2009). Zoonotic Bartonella in fleas collected on gray foxes (Urocyon cinereoargentteus). Vector-Borne Zoonot 9: 597–602.
Halos L, Jamal T, Maillard R, Girard B, Guillot J, Chomel B et al. (2004). Role of Hippoboscidae flies as potential vectors of Bartonella spp. infecting wild and domestic ruminants. Appl Environ Microbiol 70: 6302–6305.
Inoue K, Maruyama S, Kabeya H, Yamada N, Ohashi N, Sato Y et al. (2008). Prevalence and genetic diversity of Bartonella species isolated from wild rodents in Japan. Appl Environ Microbiol 74: 5086–5092.
Jardine C, Appleyard G, Kosoy MY, McColl D, Chirino-Trejo M, Wobeser G et al. (2005). Rodent-associated Bartonella in Saskatchewan, Canada. Vector-Borne Zoonot 5: 402–409.
Kosoy M, Morway C, Sheff KW, Bai Y, Colborn J, Chalcraft JL et al. (2008). Bartonella tamiae sp nov., a newly recognized pathogen isolated from three human patients from Thailand. J Clin Microbiol 46: 772–775.
Norman AF, Regnery R, Jameson P, Greene C, Krause DC . (1995). Differentiation of Bartonella-like isolates at the species level by PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism in the citrate synthase gene. J Clin Microbiol 33: 1797–1803.
Raoult D, Roux V . (1999). The body louse as a vector of reemerging human disease. Clin Infect Dis 29: 888–911.
Salkeld DJ, Stapp P . (2008). No evidence for deer mouse involvement in plague (Yersinia pestis) epizootics in prairie dogs. Vector-Borne Zoonot 8: 331–337.
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S . (2007). MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA4) Software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24: 1596–1599.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brinkerhoff, R., Kabeya, H., Inoue, K. et al. Detection of multiple Bartonella species in digestive and reproductive tissues of fleas collected from sympatric mammals. ISME J 4, 955–958 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2010.22
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2010.22
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Cattle Farming and Plantation Forest are Associated with Bartonella Occurrence in Wild Rodents
EcoHealth (2024)
-
Rats as potential reservoirs for neglected zoonotic Bartonella species in Flanders, Belgium
Parasites & Vectors (2020)
-
Vector-Borne Pathogens in Ectoparasites Collected from High-Elevation Pika Populations
EcoHealth (2020)
-
Bartonella, Rodents, Fleas and Ticks: a Molecular Field Study on Host-Vector-Pathogen Associations in Saxony, Eastern Germany
Microbial Ecology (2016)
-
The effect of ecological and temporal factors on the composition of Bartonella infection in rodents and their fleas
The ISME Journal (2014)