Abstract
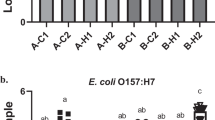
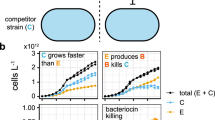
It is well established that host-associated microbial communities can interfere with the colonization and establishment of microbes of foreign origins, a phenomenon often referred to as bacterial interference or colonization resistance. However, due to the complexity of the indigenous microbiota, it has been extremely difficult to elucidate the community colonization resistance mechanisms and identify the bacterial species involved. In a recent study, we have established an in vitro mice oral microbial community (O-mix) and demonstrated its colonization resistance against an Escherichia coli strain of mice gut origin. In this study, we further analyzed the community structure of the O-mix by using a dilution/regrowth approach and identified the bacterial species involved in colonization resistance against E. coli. Our results revealed that, within the O-mix there were three different types of bacterial species forming unique social structure. They act as ‘Sensor’, ‘Mediator’ and ‘Killer’, respectively, and have coordinated roles in initiating the antagonistic action and preventing the integration of E. coli. The functional role of each identified bacterial species was further confirmed by E. coli-specific responsiveness of the synthetic communities composed of different combination of the identified players. The study reveals for the first time the sophisticated structural and functional organization of a colonization resistance pathway within a microbial community. Furthermore, our results emphasize the importance of ‘Facilitation’ or positive interactions in the development of community-level functions, such as colonization resistance.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Adlerberth I, Cerquetti M, Poliane I, Wold A, Collignon A . (2000). Mechanisms of colonisation and colonisation resistance of the digestive tract part 1: bacteria/host interactions. Microb Ecol Health Dis 12: 223–239.
Alain LS . (2004). Antagonistic activities of lactobacilli and bifidobacteria against microbial pathogens. FEMS Microbiol Rev 28: 405–440.
Backhed F, Ding H, Wang T, Hooper LV, Koh GY, Nagy A et al (2004). The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc Nati Acad Sci USA 101: 15718–15723.
Bernet-Camard MF, Lievin V, Brassart D, Neeser JR, Servin AL, Hudault S . (1997). The human Lactobacillus acidophilus strain LA1 secretes a nonbacteriocin antibacterial substance(s) active in vitro and in vivo. Appl Environ Microbiol 63: 2747–2753.
Brook I . (1999). Bacterial interference. Crit Rev Microbiol 25: 155–172.
Bruno JF, Stachowicz JJ, Bertness MD . (2003). Inclusion of facilitation into ecological theory. Trends Ecol Evol 18: 119–125.
Burmolle M, Webb JS, Rao D, Hansen LH, Sorensen SJ, Kjelleberg S . (2006). Enhanced biofilm formation and increased resistance to antimicrobial agents and bacterial invasion are caused by synergistic interactions in multispecies biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 72: 3916–3923.
Case TJ . (1990). Invasion resistance arises in strongly interacting species-rich model competition communities. Proc Nati Acad Sci USA 87: 9610–9614.
Chan RC, Reid G, Irvin RT, Bruce AW, Costerton JW . (1985). Competitive exclusion of uropathogens from human uroepithelial cells by Lactobacillus whole cells and cell wall fragments. Infect Immun 47: 84–89.
Chun J, Kim K, Lee JH, Choi Y . (2010). The analysis of oral microbial communities of wild-type and toll-like receptor 2-deficient mice using a 454 GS FLX Titanium pyrosequencer. BMC Microbiol 10: 101.
Cook KL, Garland JL, Layton AC, Dionisi HM, Levine LH, Sayler GS . (2006). Effect of microbial species richness on community stability and community function in a model plant-based wastewater processing system. Microb Ecol 52: 725–737.
Corthesy B, Gaskins HR, Mercenier A . (2007). Cross-talk between probiotic bacteria and the host immune system. J Nutr 137: 781S–790S.
Dillon RJ, Vennard CT, Buckling A, Charnley AK . (2005). Diversity of locust gut bacteria protects against pathogen invasion. Ecol Lett 8: 1291–1298.
Falagas ME, Rafailidis PI, Makris GC . (2008). Bacterial interference for the prevention and treatment of infections. Int J Antimicrob Agents 31: 518–522.
Fons M, Gomez A, Karjalainen T . (2000). Mechanisms of colonisation and colonisation resistance of the digestive tract part 2: bacteria/bacteria interactions. Microb Ecol Health Dis 12: 240–246.
Franklin R, Mills A . (2006). Structural and functional responses of a sewage microbial community to dilution-induced reductions in diversity. Microb Ecol 52: 280–288.
Franklin RB, Garland JL, Bolster CH, Mills AL . (2001). Impact of dilution on microbial community structure and functional potential: comparison of numerical simulations and batch culture experiments. Appl Environ Microbiol 67: 702–712.
Freter R . (1956). Experimental enteric Shigella and Vibrio infections in mice and guinea pigs. J Exp Med 104: 411–418.
Guarner F, Malagelada JR . (2003). Gut flora in health and disease. Lancet 361: 512–519.
He X, Hu W, Kaplan C, Guo L, Shi W, Lux R . (2012). Adherence to streptococci facilitates fusobacterium nucleatum integration into an oral microbial community. Microb Ecol 63: 532–542.
He X, Tian Y, Guo L, Ano T, Lux R, Zusman D et al (2010a). In vitro communities derived from oral and gut microbial floras inhibit the growth of bacteria of foreign origins. Microb Ecol 60: 665–676.
He X, Tian Y, Guo L, Ano T, Lux R, Zusman D et al (2010b). Oral-derived bacterial flora defends its domain by recognizing and killing intruders—A molecular analysis using Escherichia coli as a model intestinal bacterium. Microb Ecol 60: 655–664.
Hodgson DJ, Rainey PB, Buckling A . (2002). Mechanisms linking diversity, productivity and invasibility in experimental bacterial communities. Proc R Soc Lond. Series B: Biological Sciences 269: 2277–2283.
Hongoh Y, Ohkuma M, Kudo T . (2003). Molecular analysis of bacterial microbiota in the gut of the termite Reticulitermes speratus (Isoptera; Rhinotermitidae). FEMS Microbiol Ecol 44: 231–242.
Kuramitsu HK, He X, Lux R, Anderson MH, Shi W . (2007). Interspecies interactions within oral microbial communities. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 71: 653.
Leslie M . (2012). Gut microbes keep rare immune cells in Line. Science 335: 1428.
Ley RE, Hamady M, Lozupone C, Turnbaugh PJ, Ramey RR, Bircher JS et al (2008a). Evolution of mammals and their gut microbes. Science 320: 1647–1651.
Ley RE, Lozupone CA, Hamady M, Knight R, Gordon JI . (2008b). Worlds within worlds: evolution of the vertebrate gut microbiota. Nat Rev Micro 6: 776–788.
Lloyd AB, Cumming RB, Kent RD . (1977). Prevention of Salmonella typhihurium infection in poultry by pretreatment of chickens and poults with intestinal extracts. Aust Vet J 53: 82–87.
McGrady-Steed J, Harris PM, Morin PJ . (1997). Biodiversity regulates ecosystem predictability. Nature 390: 162–165.
Parsek MR, Greenberg EP . (2005). Sociomicrobiology: the connections between quorum sensing and biofilms. Trends Microbiol 13: 27–33.
Reid G, Howard J, Gan BS . (2001). Can bacterial interference prevent infection? Trends Microbiol 9: 424–428.
Reid G, Jass J, Sebulsky MT, McCormick JK . (2003). Potential uses of probiotics in clinical practice. Clin Microbiol Rev 16: 658–672.
Robinson C, Schloss P, Ramos Y, Raffa K, Handelsman J . (2010a). Robustness of the bacterial community in the cabbage white butterfly larval midgut. Microb Ecol 59: 199–211.
Robinson C, Bohannan BJM, Yong VB . (2010b). From structure to function: the ecology of host-associated microbial communities. Microbiol Mole Biol Rev 74: 453–476.
Rolfe RD . (1997). Colonization resistance. In: Mackie RI, White BA, Isaacson RE (eds). Gastrointestinal Microbiology. Chapman and Hall: New York, NY, pp 501–535.
Sheffield VC, Cox DR, Lerman LS, Myers RM . (1989). Attachment of a 40-base-pair G+C-rich sequence (GC-clamp) to genomic DNA fragments by the polymerase chain reaction results in improved detection of single-base changes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 232–236.
Stachowicz JJ, Whitlatch RB, Osman RW . (1999). Species diversity and invasion resistance in a marine ecosystem. Science 286: 1577–1579.
Thomsen MA, D'antonio CM, Suttle KB, Sousa WP . (2006). Ecological resistance, seed density and their interactions determine patterns of invasion in a California coastal grassland. Ecol Lett 9: 160–170.
Van Der Waaij D, Van Der Waaij BD . (1990). The colonization resistance of the digestive tract in different animal species and in man; a comparative study. Epidemiol Infect 105: 237–243.
Vandenbergh PA . (1993). Lactic acid bacteria, their metabolic products and interference with microbial growth. FEMS Microbiol Rev 12: 221–237.
Veivers PC, O'Brien RW, Slaytor M . (1982). Role of bacteria in maintaining the redox potential in the hindgut of termites and preventing entry of foreign bacteria. J Insect Physiol 28: 947–951.
Wang R, Kaplan A, Guo L, Shi W, Lux R, He X . (2012). The influence of iron availability on human salivary microbial community composition. Microb Ecol 64: 152–161.
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by US National Institutes of Health (NIH) Grants (DE020102 and DE021108) and International Science and Technology Cooperation Program of China (2011DFA30940).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, X., McLean, J., Guo, L. et al. The social structure of microbial community involved in colonization resistance. ISME J 8, 564–574 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2013.172
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2013.172
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Capturing the environment of the Clostridioides difficile infection cycle
Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology (2022)
-
Engineering complex communities by directed evolution
Nature Ecology & Evolution (2021)
-
The effects of a multispecies synbiotic on microbiome-related side effects of long-term proton pump inhibitor use: A pilot study
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
FBA Ecological Guild: Trio of Firmicutes-Bacteroidetes Alliance against Actinobacteria in Human Oral Microbiome
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Bioadhesion in the oral cavity and approaches for biofilm management by surface modifications
Clinical Oral Investigations (2020)