Abstract
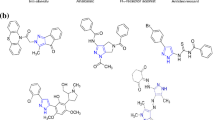
A novel way of chemical modification of the antibiotic olivomycin I at the 2′-keto group of the side chain of the aglycone moiety was developed. Reaction of olivomycin I with the carboxymethoxylamine hemihydrochloride gave the key intermediate, 2′-carboxymethoxime-olivomycin I, which was further reacted with different amines in the presence of benzotriazol-1-yl-oxy-trispyrrolidinophosphonium hexafluorophosphate to give the corresponding amides. The antiproliferative and topoisomerase I (Topo-I)-poisoning activities of the novel derivatives were examined. One of the novel derivatives showed a marked inhibitory activity against Topo-I, a pronounced antitumor activity in in vivo experiments on mice bearing leukemia P-388 and lower toxic side effects compared with the parent olivomycin I.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Lombo, F., Menendez, N., Salas, J. A. & Mendez, C. The aureolic acid family of antitumor compounds: structure, mode of action, biosynthesis, and novel derivatives. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 73, 1–14 (2006).
Chen, K. X., Gresh, N., Hui, X., Pullman, B. & Zakrzewska, K. Modelling basic features of specificity in DNA–aureolic acid-derived antibiotic interactions. FEBS Lett. 245, 145–149 (1989).
Berlin, Y. A. et al. Aureolic acid group of antibiotics. Nature 218, 193–194 (1968).
Gause, G. F. Chromomycin, olivomycin, mithramycin. In Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology (eds Sartorelli, A.C. et al.) 615–622 (Springler-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, 1975).
Remsing, L. L. et al. Mithramycin SK A novel antitumor drug with improved therapeutic index, mithramycin SA, and demycarosyl-mithramycin SK: three new products generated in the mithramycin producer Streptomyces argillaceus through combinatorial biosynthesis. JACS 125, 5745–5753 (2003).
Albertini, V. et al. Novel GC-rich DNA-binding compound produced by a genetically engineered mutant of the mithramycin producer Streptomyces argillaceus exhibits improved transcriptional repressor activity: implications for cancer therapy. Nucleic Acids Res. 34, 1721–1734 (2006).
Menendez, N. et al. Deoxysugar transfer during chromomycin A3 biosynthesis in Streptomyces griseus subsp. griseus: new derivatives with antitumor activity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72, 167–177 (2006).
Remsing, L. L. et al. Ketopremithramycins and ketomithramycins, four new aureolic acid-type compounds obtained upon inactivation of two genes involved in the biosynthesis of the deoxysugar moieties of the antitumor drug mithramycin by Streptomycyes argillaceus, reveal novel insights into post-PSK tailoring steps of the mithramycin biosynthetic pathway. JACS 124, 1601–1614 (2002).
Simonova, VS et al. Olivomycin induces tumor cell apoptosis and suppresses p53-induced transcription. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 139, 455–459 (2005).
Lotito, L., Ferri, F., Russo, A. & Capranico, G. DNA topoisomerase I as a transcription protein and a lethal cellular toxin. Ital. J. Biochem. 56, 122–129 (2007).
Hou, M. N., Lu, W. J., Lin, H. Y. & Yuann, J. M. Studies of sequence-specific DNA binding DNA cleavage, and topoisomerase I inhibition by the dimeric chromomycin a3 complexed with Fe (II). Biochemistry 47, 5493–5502 (2008).
Yoshimura, Y., Koenuma, M., Matsumoto, K., Tori, K. & Terui, Y. NMR studies of chromomycins, olivomycins and their derivatives. J. Antibiot. 41, 53–67 (1988).
Thiem, J. & Meyer, B. Studies on the structure of olivomycin A and mithramycin by 1H and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Tetrahedron 37, 551–558 (1981).
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Russian Fond of Fundamental Research (Grant no. 06-04-08127 for 2006-2007), a grant of the President of Russian Federation for the support of young Russian scientists (AN Tevyashova, MK-5422.2007.4) and the Geconcerteerde Onderzoeksacties (GOA) of the KU Leuven. We thank Mrs Lizette van Berckelaer (Rega Institute, Leuven) for excellent technical assistance, and Dr Marina I Reznikova and Nataly M Malutina (Gause Institute, Moscow) for HPLC analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tevyashova, A., Zbarsky, E., Balzarini, J. et al. Modification of the antibiotic olivomycin I at the 2′-keto group of the side chain. Novel derivatives, antitumor and topoisomerase I-poisoning activity. J Antibiot 62, 37–41 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2008.7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2008.7
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Olivomycin A – an Antitumor Antibiotic of the Aureolic Acid Group (Review)
Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal (2016)
-
Role of the acyl groups in carbohydrate chains in cytotoxic properties of olivomycin A
The Journal of Antibiotics (2013)