Abstract
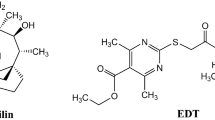
Protein synthesis inhibition is a highly successful target for developing clinically effective and safe antibiotics. There are several targets within the ribosomal machinery, and small ribosomal protein S4 (RPSD) is one of the newer targets. Screening of microbial extracts using antisense-sensitized rpsD Staphylococcus aureus strain led to isolation of okilactomycin and four new congeners from Streptomyces scabrisporus. The major compound, okilactomycin, was the most active, with a minimum detection concentration of 3–12 μg ml−1 against antisense assay, and showed an MIC of 4–16 μg ml−1 against Gram-positive bacteria, including S. aureus. The congeners were significantly less active in all assays, and all compounds showed a slight preferential inhibition of RNA synthesis over DNA and protein synthesis. Antisense technology, due to increased sensitivity, continues to yield new, even though weakly active, antibiotics.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Klevens, R. M. et al. Invasive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in the United States. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 298, 1763–1771 (2007).
Poehlsgaard, J. & Douthwaite, S. The bacterial ribosome as a target for antibiotics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 3, 870–881 (2005).
Singh, S. B. & Barrett, J. F. Empirical antibacterial drug discovery—foundation in natural products. Biochem. Pharmacol. 71, 1006–1015 (2006).
Ramakrishnan, V. Ribosome structure and the mechanism of translation. Cell 108, 557–572 (2002).
Culver, G. M. Assembly of the 30S ribosomal subunit. Biopolymers 68, 234–249 (2003).
Ogle, J. M., Carter, A. P. & Ramakrishnan, V. Insights into the decoding mechanism from recent ribosome structures. Trends Biochem. Sci. 28, 259–266 (2003).
Grundy, F. J. & Henkin, T. M The rpsD gene, encoding ribosomal protein S4, is autogenously regulated in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 173, 4595–4602 (1991).
Forsyth, R. A. et al. A genome-wide strategy for the identification of essential genes in Staphylococcus aureus. Mol. Microbiol. 43, 1387–1400 (2002).
Young, K. et al. Discovery of FabH/FabF inhibitors from natural products. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 50, 519–526 (2006).
Singh, S. B., Phillips, J. W. & Wang, J. Highly sensitive target based whole cell antibacterial discovery strategy by antisense RNA silencing. Curr. Opin. Drug Discov. Devel. 10, 160–166 (2007).
Wang, J. et al. Platensimycin is a selective FabF inhibitor with potent antibiotic properties. Nature 441, 358–361 (2006).
Wang, J. et al. Platencin is a dual fabf and fabh inhibitor with potent in vivo antibiotic properties. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 104, 7612–7616 (2007).
Singh, S. B. et al. Isolation, structure, and absolute stereochemistry of platensimycin, a broad spectrum antibiotic discovered using an antisense differential sensitivity strategy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 11916–11920 and 15547 (2006).
Jayasuriya, H. et al. Isolation and structure of platencin: a novel FabH and FabF dual inhibitor with potent broad spectrum antibiotic activity produced by Streptomyces platensis MA7339. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 46, 4684–4688 (2007).
Singh, S. B. et al. Discovery of lucensimycins A and B from Streptomyces lucensis MA7349 using an antisense strategy. Org. Lett. 8, 5449–5452 (2006).
Ondeyka, J. G. et al. Coniothyrione, a chlorocyclopentandienylbenzopyrone as a bacterial protein synthesis inhibitor discovered by antisense technology. J. Nat. Prod. 70, 668–670 (2007).
Zhang, C. et al. Isolation, structure and antibacterial activity of pleosporone from a pleosporalean ascomycete discovered by using antisense strategy. Bioorg. Med. Chem. (2008); e-pub ahead of print 12 April 2008; doi:10:1016/j.bmc.2008.04.18.
Zhang, C. et al. Isolation, structure and antibacterial activity of phaeosphenone from a Phaeosphaeria sp. discovered by antisense strategy. J. Nat. Prod. 71, 1304–1307 (2008).
Imai, H. et al. Okilactomycin, a novel antibiotic produced by a Streptomyces species. II. Structure determination. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 40, 1483–1489 (1987).
Smith, A. B. III, Basu, K. & Bosanac, T. Total synthesis of (−)-okilactomycin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 14872–14874 (2007).
Imai, H. et al. Okilactomycin, a novel antibiotic produced by a Streptomyces species. I. Taxonomy, fermentation, isolation and characterization. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 40, 1475–1482 (1987).
Weisburg, W. G., Barns, S. M., Pelletier, D. A. & Lane, D. J. 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J. Bacteriol. 173, 697–703 (1991).
Lane, D. J. 16S/23S rRNA Sequencing, in Nucleic Acid Techniques in Bacterial Systematics (eds Stackebrandt, E. & Goodfellow, M.) 115–175 (Wiley, New York, 1991).
Saitou, N. & Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 4, 406–425 (1987).
Jukes, T. H. & Cantor, C. Evolution of Protein Molecules, in Mammalian Protein Metabolism 21–132 (Academic Press, New York, 1969).
Kodali, S. et al. Determination of selectivity and efficacy of fatty acid synthesis inhibitors. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 1669–1677 (2005).
Onishi, H. R. et al. Antibacterial agents that inhibit lipid A biosynthesis. Science 274, 980–982 (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Ondeyka, J., Zink, D. et al. Discovery of okilactomycin and congeners from Streptomyces scabrisporus by antisense differential sensitivity assay targeting ribosomal protein S4. J Antibiot 62, 55–61 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2008.8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2008.8
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Bioinformatic comparison of three Embleya species and description of steffimycins production by Embleya sp. NF3
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (2022)
-
Systematics-guided bioprospecting for bioactive microbial natural products
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek (2012)
-
Current approaches to exploit actinomycetes as a source of novel natural products
Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology (2011)
-
Bioprospecting microbial natural product libraries from the marine environment for drug discovery
The Journal of Antibiotics (2010)
-
Coelomycin, a highly substituted 2,6-dioxo-pyrazine fungal metabolite antibacterial agent discovered by Staphylococcus aureus fitness test profiling
The Journal of Antibiotics (2010)