Abstract
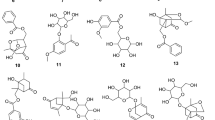
The deposited strain of the hazimicin producer, Micromonospora echinospora ssp. challisensis NRRL 12255 has considerable biosynthetic capabilities as revealed by genome scanning. Among these is a locus containing both type I and type II PKS genes. The presumed products of this locus, TLN-05220 (1) and TLN-05223 (2), bear a core backbone composed of six fused rings starting with a 2-pyridone moiety. The structures were confirmed by conventional spectral analyses including MS, and 1D and 2D NMR experiments. Comparison of both the 1H and 13C NMR data of the newly isolated compound with those of echinosporamicin and bravomicin A led us to propose a revision of the structure of the latter to include a 2-pyridone instead of the pyran originally postulated. Both compounds (1 and 2) possessed strong antibacterial activity against a series of gram-positive pathogens including several strains of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and vancomycin-resistant Enterococci (VRE), and cytotoxic activities against several human tumor cell lines. The TLN compounds are the first of this group with reported anticancer activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Accession codes
References
Alarco, A. M., Banskota, A., McAlpine, J., Farnet, C., Falardeau, P. & Zazopoulos, E. Profiling of new antitumor natural products discovered using a genomics/cheminformatics-based drug discovery platform. Proc. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 47, A1992 (2006).
Gross, H. Genome mining—a concept for the discovery of new natural products. Curr. Opin. Drug Discov. Devel. 12, 207–219 (2009).
Zazopoulos, E. et al. A genomics-guided approach for discovering and expressing cryptic metabolic pathways. Nat. Biotechnol. 21, 187–190 (2003).
Zazopoulos, E. & Farnet, C. M. Improving drug discovery from microorganisms. Natural Products: Drug Discovery and Therapeutic Medicine (eds Zhang, L. and Demain, A. L.) 95–106 (Humana Press Inc., Totowa, NJ, USA, 2005).
McAlpine, J. B. et al. Microbial genomics as a guide to drug discovery and structural elucidation: ECO-02301, a novel antifungal agent, as an example. J. Nat. Prod. 68, 493–496 (2005).
Banskota, A. H. et al. Isolation and identification of three new 5-Alkenyl-3,3(2H)-furanones from two Streptomyces species using a genomic screening approach. J. Antibiot. 59, 168–176 (2006).
Waitz, J. A., Marquez, J. A., Patel, M. G. & Horan, A. C. Broad spectrum antibiotic complex produced by a novel micromonospora. US 4,440,751, April 3 (2001).
Sørensen, D., McAlpine, J. B., Piraee, M., Farnet, C. M. & Zazopoulos, E. Genome scanning technology reveals an antibacterial compound (ECO-0501) of a new structural class from the vancomycin-producer Amycolatopsis orientalis 44th ICAAC: no. F-720a, Washington, DC (2004).
McAlpine, J. B. et al. The power of genomic analysis in the discovery of novel secondary metabolites 46th Annual Meeting of American Society of Pharmacognosy: no. O-21, Corvallis, OR, USA (2005).
Gurevich, A. I. et al. The structure of albofungin. Tet. Lett. 13, 1751–1754 (1972).
Carter, G. T., Goodman, J. J., Torrey, M. J., Borders, D. B. & Gould, S. J. Biosynthetic origin of the carbon skeleton of sisaomicin A, a hexacyclic xanthone antibiotic. J. Org. Chem. 54, 4321–4323 (1989).
He, H., Yang, H. Y., Luckman, S. W. & Bernam, V. S. Antibiotic P175-A and semisynthetic derivatives thereof US Patent Application. US 2004/0220195 Nov. 4, (2004).
He, H. et al. Echinosporamicin, a new antibiotic produced by Micromonospora echinospora ssp. echinospora, LL-P175. Helv Chim. Acta 87, 1385–1391 (2004).
Shu, Y-Z., Chen, J., Lam, K. S., Veitch, J. A. & Brown, D. Antibiotic Bravomicins US Patent 5, 994, 543, Nov. 30, (1999).
Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically; Approved Standard-Fifth Edition (NCCLS document M7-A5, ISBN 1-56238-394-9 Pennsylvania, USA).
Plumb, J. A., Milroy, R. & Kaye, S. B. Effects of the pH dependence of 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-tetrazolium bromide-formazan absorption on chemosensitivity determined by a novel tetrazolium-based assay. Cancer Res. 49, 4435–4440 (1989).
Acknowledgements
We thank Professor André B. Charette of the Université de Montréal for the use of his polarimeter.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Part IV in a series on Genomic Analysis for the Discovery of Novel Secondary Metabolites. TLN-05220 was previously referred to as ECO-3396.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Banskota, A., Aouidate, M., Sørensen, D. et al. TLN-05220, TLN-05223, new Echinosporamicin-type antibiotics, and proposed revision of the structure of bravomicins. J Antibiot 62, 565–570 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2009.77
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2009.77
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Unveiling the bioactive potential of Actinomycetota from the Tagus River estuary
International Microbiology (2024)
-
Recent progress on the development of antibiotics from the genus Micromonospora
Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering (2016)