Abstract
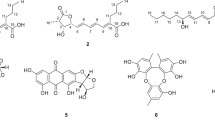
Three new sterigmatocystin derivatives, oxisterigmatocystin A (1), oxisterigmatocystin B (2) and oxisterigmatocystin C (3), together with one known compound, 5-methoxysterigmatocystin (4), were isolated from the deep-sea-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor. The structures of the new compounds were elucidated by spectroscopic methods. The cytotoxicities of compounds 1–4 were evaluated against the A-549 and HL-60 cell lines. Compound 4 exhibited moderate cytotoxicities against the A-549 and HL-60 cell lines with IC50 value of 3.86 and 5.32 μM, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Lee, Y. et al. Bioactive metabolites from the sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Arch. Pharm. Res. 33, 231–235 (2010).
Li, G. et al. Brevianamide J, a new indole alkaloid dimer from fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Org. Lett. 11, 3714–3717 (2009).
Belofsky, G. N., Jensen, P. R., Renner, M. K. & Fenical, W. New cytotoxic sesquiterpenoid nitrobenzoyl esters from a marine isolate of the fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Tetrahedron 54, 1715–1724 (1998).
Fremlin, L. J., Piggott, A. M., Lacey, E. & Capon, R. J. Cottoquinazoline A and cotteslosins A and B, metabolites from an Australian marine-derived strain of Aspergillus versicolor. J. Nat. Prod. 72, 666–670 (2009).
Cai, S. et al. Two new indole alkaloids from the marine-derived bacterium Aeromonas sp. CB101. Helv. Chim. Acta. 93, 791–795 (2010).
Li, D. et al. Trisorbicillinone A, a novel sorbicillin trimer, from a deep sea fungus, Phialocephala sp. FL30r. Tetrahedron Lett. 48, 5235–5238 (2007).
Li, D. et al. Two new bisorbicillinoids isolated from a deep sea fungus, Phialocephala sp. FL30r. J. Antibiot. 60, 317–320 (2007).
Du, L. et al. New alkaloids and diterpenes from a deep ocean sediment derived fungus Penicillium sp. Tetrahedron 65, 1033–1039 (2009).
Du, L. et al. Alkaloids from a deep ocean sediment-derived fungus Penicillium sp. and their antitumor activities. J. Antibiot. 63, 165–170 (2010).
Shao, C. et al. 1H and 13C NMR assignments for two anthraquinones and two xanthones from the mangrove fungus (ZSUH-36). Magn. Reson. Chem. 45, 434–438 (2007).
Zhu, F. & Lin, Y. Three xanthones from a marine-derived mangrove endophytic fungus. Chem. Nat. Comp. 43, 132–135 (2007).
Ashley, D. L., Orti, D. L. & Hill, R. H. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance evidence for two configurations of the hemiacetals of aflatoxin B1 and sterigmatocystin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 35, 782–785 (1987).
Skehan, P. et al. New colorimetric cytotoxicity assay for anticancer-drug screening. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 82, 1107–1112 (1990).
Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 65, 55–63 (1983).
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Chinese National Science Fund (No. 30772640 and 30973627) and the Shandong Provincial Natural Science Fund (No. ZR2009CZ016). The antitumor assay was performed at the Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences. We also thank Dr Wendy Strangman of UBC for the advice on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, S., Zhu, T., Du, L. et al. Sterigmatocystins from the deep-sea-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor. J Antibiot 64, 193–196 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2010.154
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2010.154
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Secondary metabolites of a deep sea derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor CXCTD-06-6a and their bioactivity
Journal of Ocean University of China (2014)
-
Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of versicolorins and 5-methoxysterigmatocystin in A549 cells
Archives of Toxicology (2012)