Abstract
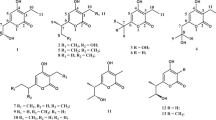
Four germicidin homologs were isolated from a liquid culture of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). These were identified as germicidins A, B and C, and surugapyrone A (germicidin D). Absolute stereochemistry of the chiral center in germicidins A and C is determined to be S. All germicidins inhibited germination of S. coelicolor A3(2) spores above 1 μg ml−1. S. coelicolor A3(2) spores collected from a single petri dish (9 cm i.d.) contained 5.4 μg of germicidin A (∼2.7 × 10−14 g per spore), which accounts for 2.3% of the spore extract, and contents of germicidins B, C and D were 0.2–0.8 μg. The activity of the spore extract corresponded well with the sum of the activity of each germicidin, which was estimated from the content and dose–response curve, which indicates that germicidins functions as self-germination inhibitors in S. coelicolor A3(2). Inhibitory action of germicidin A on spore germination was reversible and germicidin A inhibited not only spore germination but also hyphal elongation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Hirsch, C. F. & Ensign, J. C. Nutritionally defined conditions for germination of Streptomyces viridochromogenes spores. J. Bacteriol. 126, 13–23 (1976).
Hirsch, C. F. & Ensign, J. C. Some properties of Streptomyces viridochromogenes spores. J. Bacteriol. 134, 1056–1063 (1978).
Grund, A. D. & Ensign, J. C. Properties of the germination inhibitor of Streptomyces viridochromogenes spores. J. Gen. Microbiol. 131, 833–847 (1985).
Petersen, F., Zähner, H., Metzger, J. W., Freund, S. & Hummel, R. P. Germicidin, an autoregulative germination inhibitor of Streptomyces viridochromogenes NRRL B-1551. J. Antibiot. 46, 1126–1138 (1993).
Yoshida, M. & Kobayashi, K. Morphogenesis of the pathogenic Streptomyces sp. causing root tumor of melon on the culture medium. Ann. Phytopathol. Soc. Jpn. 60, 514–522 (1994) (in Japanese with English summary).
Yoshida, M., Nishiyama, T., Yamaguchi, T. & Kobayashi, K. Spore germination and its activation of the pathogenic Streptomyces sp. causing root tumor of melon. Ann. Phytopathol. Soc. Jpn. 60, 711–716 (1994) (in Japanese with English summary).
Aoki, Y. et al. Anthranilic acid, a spore germination inhibitor of phytopathogenic Streptomyces sp. B-9-1 causing root tumor of melon. Actinomycetologica 19, 48–54 (2005).
Aoki, Y. et al. Isolation and characterization of a spore germination inhibitor from Streptomyces sp. CB-1-1, a phytopathogen causing root tumor of melon. Biosci. Biotech. Biochem. 71, 986–992 (2007).
Aoki, Y. et al. Structural determination of hypnosin, a spore germination inhibitor of phytopathogenic Streptomyces sp. causing root tumor in melon (Cucumis sp.). J Agric. Food Chem. 55, 10622–10627 (2007).
Song, L. et al. Type III polyketide synthase β-ketoacyl-ACP starter unit and ethylmalonyl-CoA extender unit selectively discovered by Streptomyces coelicolor genome mining. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 54, 203–209 (2006).
Hashimoto, M. et al. Relationship between response to and production of the aerial mycelium-inducing substances pamamycin-607 and A-factor. Biosci. Biotech. Biochem. 67, 803–808 (2003).
DeJong, P. J. & McCoy, E. Qualitative analyses of vegetative cell walls and spore walls of some representative species of Streptomyces. Can. J. Microbiol. 12, 985–994 (1966).
Sugiyama, Y., Oya, A., Kudo, T. & Hirota, A. Surugapyrone A from Streptomyces coelicoflavus strain USF-6280 as a new DPPH radical-scavenger. J. Antibiot. 63, 365–369 (2010).
Grüschow, S., Buchholz, T. J., Seufert, W., Dordick, J. S. & Sherman, D. H. Substrate profile analysis and ACP-mediated acyl transfer in Streptomyces coelicolor type III polyketide synthases. Chem. Bio. Chem. 8, 863–868 (2007).
Kohl, W., Irschik, H., Reichenbach, H. & Höfle, G. Myxopyronin A und B—zwei neue Antibiotika aus Myxococcus fulvus Stamm Mx f50. Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1983, 1656–1667 (1983).
Pedras, M. S. C., Morales, V. M. & Taylor, J. L. Phomapyrones: three metabolites from the black leg fungus. Phytochemistry 36, 1315–1318 (1994).
Kawahara, N., Nozawa, K., Nakajima, S., Yamazaki, M. & Kawai, K. Sulfur-containing dioxopiperazine derivatives from Emericella heterothallica. Heterocycles 29, 397–402 (1989).
Matsuo, Y., Imagawa, H., Nishizawa, M. & Shizuri, Y. Isolation of an algal morphogenesis inducer from a marine bacterium. Science 307, 1598 (2005).
Gao, X., Matsuo, Y. & Snider, B. B. Synthesis of ent-thallusin. Org. Lett. 8, 2123–2126 (2006).
Gao, X., Matsuo, Y. & Snider, B. B. Synthesis of ent-thallusin. Org. Lett. 9, 379 (2007) (erratum).
Dickinson, J. M. Microbial pyran-2-ones and dihydropyran-2-ones. Nat. Prod. Rep. 10, 71–98 (1993).
McGlacken, G. P. & Fairlamb, I. J. 2-Pyrone natural products and mimetics: isolation, characterization and biological activity. Nat. Prod. Rep. 22, 369–385 (2005).
Scarselletti, R. & Faull, J. L. In vitro activity of 6-pentyl-α-pyrone, a metabolite of Trichoderma harzianum, in the inhibition of Rhizoctonia solani and Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici. Mycol. Res. 98, 1207–1209 (1994).
Pezet, R., Pont, V. & Tabacchi, R. Simple analysis of 6-pentyl-α-purone, a major antifungal metabolite of Trichoderma spp., useful for testing the antagonistic activity of these fungi. Phytochem. Anal. 10, 285–288 (1999).
Igarashi, Y. et al. Fistupyrone, a novel inhibitor of the infection of chinese cabbage by Alternalia brassicicola, from Streptomyces sp. TP-A0569. J. Antibiot. 53, 1117–1122 (2000).
Aremu, E. A. et al. Specific inhibition of spore germination of Alternalia brassicicola by fistupyrone from Streptomyces sp. TP-A0569. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 69, 211–217 (2003).
Acknowledgements
This study was supported, in part, by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) from Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (No. 20580109).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aoki, Y., Matsumoto, D., Kawaide, H. et al. Physiological role of germicidins in spore germination and hyphal elongation in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Antibiot 64, 607–611 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2011.59
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2011.59
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Germicidins H–J from Streptomyces sp. CB00361
The Journal of Antibiotics (2017)
-
Phenotypic variability and community interactions of germinating Streptomyces spores
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Investigation on antimicrobial agents of the terrestrial Streptomyces sp. BCC71188
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (2017)
-
Pharmacological Potential of Phylogenetically Diverse Actinobacteria Isolated from Deep-Sea Coral Ecosystems of the Submarine Avilés Canyon in the Cantabrian Sea
Microbial Ecology (2017)
-
Biosynthesis of phlorisovalerophenone and 4-hydroxy-6-isobutyl-2-pyrone in Escherichia coli from glucose
Microbial Cell Factories (2016)