Abstract
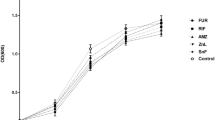
The lack of active antimicrobial agents against multidrug-resistant (MDR) Acinetobacter baumannii has posed great threat to the public health. Combination therapies with antibiotics owning different antimicrobial mechanisms have been proposed as good options for treating MDR A. baumannii infections. This study was aimed to investigate the in vitro effects of tigecycline in combination with colistin and sulbactam against MDR A. baumannii. A total of 70 strains from two hospitals in China were examined in the study. The checkerboard method was used for determining synergistic activity of different antibiotic combinations. Tigecycline/colistin combination displayed synergistic and partial synergistic activity in 24.3% of the isolates, whereas the tigecycline/sulbactam combination showed synergistic and partial synergistic activity in 64.3% of the isolates. Neither of the combinations showed antagonism in this study. In addition, for evaluating the ability of combinations on resistance prevention, mutant prevention concentrations (MPCs) of tigecycline, colistin, sulbactam alone and tigecycline in combination with colistin and sulbactam were studied against MDR A. baumannii. Compared with tigecycline used alone, combination therapies could achieve lower MPCs of tigecycline. However, when the MPCs of dual-drug therapy were in conjunction with clinical pharmacokinetic profiles, combinations may not strictly curb the occurrence of resistance at current dosage regimen. In summary, this study suggested that combination therapy was a good option for treating MDR A. baumannii infections. But the finding that combination with these drugs at current dosage regimen may not prevent emergence of resistance warranted further studies on dosage of combined antibiotics required for achieving resistance prevention.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Falagas, M. E. & Rafailidis, P. I. Attributable mortality of Acinetobacter baumannii: no longer a controversial issue. Crit. Care 11, 134 (2007).
Perez, F. et al. Global challenge of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 51, 3471–3484 (2007).
Bosó-Ribelles, V., Romá-Sánchez, E., Carmena, J., Cáceres, C. & Bautista, D. Tigecycline: a new treatment choice against Acinetobacter baumannii. Recent Pat. Antiinfect. Drug Discov. 3, 117–122 (2008).
Jean, S. S. & Hsueh, P. R. Current review of antimicrobial treatment of nosocomial pneumonia caused by multidrug-resistant pathogens. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 12, 2145–2148 (2011).
Cooper, T. W., Pass, S. E., Brouse, S. D. & Hall Ii, R. G. Can pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic principles be applied to the treatment of multidrug-resistant acinetobacter? Ann. Pharmacother. 45, 229–240 (2011).
Sun, Y. et al. The emergence of clinical resistance to tigecycline. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 41, 110–116 (2013).
Anthony, K. B. et al. Clinical and microbiological outcomes of serious infections with multidrug-resistant gram-negative organisms treated with tigecycline. Clin. Infect. Dis. 46, 567–570 (2008).
Hawley, J. S., Murray, C. K. & Jorgensen, J. H. Colistin heteroresistance in acinetobacter and its association with previous colistin therapy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 52, 351–352 (2008).
Ko, K. S. et al. High rates of resistance to colistin and polymyxin B in subgroups of Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from Korea. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 60, 1163–1167 (2007).
Entenza, J. M. & Moreillon, P. Tigecycline in combination with other antimicrobials: a review of in vitro, animal and case report studies. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 34, 8.e1-8.e9 (2009).
National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards (NCCLS). Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Information Supplement. M100, S21 (2011).
Pillai, S. K., Moellering, R. C. & Eliopoulos, G. M. Antimicrobial Combinations in Antibiotics in Laboratory Medicine 5th edn ed Lorian V. L., 365–424 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, (2005).
Moody, J. Synergism testing: broth microdilution checkerboard and broth macrodilution method in Clinical Microbiology Procedures Handbook ed Isenberg H. D.), 2nd edn 1–28 ASM: Washington, DC, (2004).
Drlica, K. The mutant selection window and antimicrobial resistance. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 52, 11–17 (2003).
Zhao, X. & Drlica, K. Restricting the selection of antibiotic-resistant mutants: a general strategy derived from fluoroquinolone studies. Clin. Infect. Dis. 33 (Suppl 3), 147–156 (2001).
Zhanel, G. G., Mayer, M., Laing, N. & Adam, H. J. Mutant prevention concentrations of levofloxacin alone and in combination with azithromycin, ceftazidime, colistin (Polymyxin E), meropenem, piperacillin-tazobactam, and tobramycin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 50, 2228–2230 (2006).
Gootz, T. D. & Marra, A. Acinetobacter baumannii: an emerging multidrug-resistant threat. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 6, 309–325 (2008).
Chung, D. R. et al. High prevalence of multidrug-resistant nonfermenters in hospital-acquired pneumonia in Asia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 184, 1409–1417 (2011).
Peck, K. R. et al. In vitro time-kill studies of antimicrobial agents against blood isolates of imipenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, including colistin- or tigecycline-resistant isolates. J. Med. Microbiol. 61, 353–360 (2012).
Dizbay, M. et al. In vitro synergistic activity of tigecycline and colistin against XDR-Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 63, 51–53 (2010).
Principe, L., D'Arezzo, S., Capone, A., Petrosillo, N. & Visca, P. In vitro activity of tigecycline in combination with various antimicrobials against multidrug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 21, 8–18 (2009).
Deveci, A. et al. In vitro effects of sulbactam combinations with different antibiotic groups against clinical Acinetobacter baumannii isolates. J. Chemother. 24, 247–252 (2012).
Cai, Y. et al. In vitro antimicrobial activity and mutant prevention concentration of colistin against Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 54, 3998–3999 (2010).
Cui, J. C., Liu, Y. N. & Chen, L. A. Mutant prevention concentration of tigecycline for carbapenem-susceptible and -resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 63, 29–31 (2010).
Cai, Y. et al. Mutant prevention concentration of colistin alone and in combination with levofloxacin or tobramycin against multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 40, 477–478 (2012).
Daikos, G. L. et al. Serum bactericidal activity of three different dosing regimens of colistin with implications for optimum clinical use. J. Chemother. 22, 175–178 (2010).
Reitberg, D. P. et al. Multiple-dose pharmacokinetics and toleration of intravenously administered cefoperazone and sulbactam when given as single agents or in combination. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 32, 42–46 (1988).
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Grant 7112127 from the Beijing Municipal Natural Science Foundation of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ni, W., Cui, J., Liang, B. et al. In vitro effects of tigecycline in combination with colistin (polymyxin E) and sulbactam against multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. J Antibiot 66, 705–708 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2013.84
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2013.84
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Pharmacodynamic evaluation of suppression of in vitro resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii strains using polymyxin B-based combination therapy
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Clinical characteristics and risk factors of tigecycline-associated hypofibrinogenaemia in critically ill patients
European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology (2020)
-
In Vitro Synergistic Effect and Mutant Prevention Concentrations of Cefepime Alone or in Combination with Sulbactam Against OXA-48-positive Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates
Current Microbiology (2020)
-
In vitro activity of minocycline combined with aminoglycosides against Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase-producing K. pneumoniae
The Journal of Antibiotics (2018)
-
Synergistic combination of two antimicrobial agents closing each other’s mutant selection windows to prevent antimicrobial resistance
Scientific Reports (2018)