Abstract
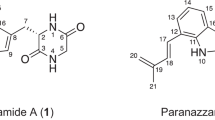
During the search for new antitrypanosomal drug leads, three new antitrypanosomal compounds, cardinalisamides A–C (1–3), were isolated from cultures of the insect pathogenic fungus Cordyceps cardinalis NBRC 103832. Their structures were elucidated using MS analyses and extensive 2D-heteronuclear NMR. The absolute configurations of 1–3 were addressed by chemical degradation and Marfey’s analysis. 1–3 showed in vitro antitrypanosomal activity against Trypanosoma brucei brucei with IC50 values of 8.56, 8.65 and 8.63 μg ml−1, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
WHO. Home page of World Health Organization. http://www.who.int/trypanosomiasis_african/en/ (2013).
Toriizuka, Y. et al. New lycorine-type alkaloid from Lycoris traubii and evaluation of antitrypanosomal and antimalarial activities of lycorine derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 16, 10182–10189 (2008).
Abdel-Sattar, E. et al. Acylated pregnane glycosides from Caralluma tuberculata and their antiparasitic activity. Phytochemistry 69, 2180–2186 (2008).
Ishiyama, A. et al. In vitro and in vivo antitrypanosomal activities of three peptide antibiotics: leucinostatin A and B, alamethicin I and tsushimycin. J. Antibiot. 62, 303–308 (2009).
Iwatsuki, M. et al. Antitrypanosomal peptaibiotics, trichosporins B-VIIa and B-VIIb, produced by Trichoderma polysporum FKI-4452. J. Antibiot. 63, 331–333 (2010).
Hashida, J. et al. Pyrenocine I, a new pyrenocine analog produced by Paecilomyces sp. FKI-3573. J. Antibiot. 63, 559–561 (2010).
Niitsuma, M. et al. Sinefungin VA and dehydrosinefungin V, new antitrypanosomal antibiotics produced by Streptomyces sp. K05-0178. J. Antibiot. 63, 673–679 (2010).
Inahashi, Y. et al. Spoxazomicins A-C, novel antitrypanosomal alkaloids produced by an endophytic actinomycete, Streptosporangium oxazolinicum K07-0460T. J. Antibiot 64, 303–307 (2011).
Lin, X., Chen, J. & Zheng, S. A medicated tea for health protection comprising Chinese caterpillar fungus, and preparation method thereof, from Faming Zhuanli Shenqing, CN 1155384 A 19970730 (1997).
Isaka, M., Tanticharoen, M., Kongsaeree, P. & Thebtaranonth, Y. Structures of Cordypyridones A-D, antimalarial N-Hydroxy- and N-Methoxy-2-pyridones from the insect pathogenic fungus Cordyceps nipponica. J. Org. Chem. 66, 4803–4808 (2001).
Rukachaisirikul, V., Pramjit, S., Pakawatchai, C., Isaka, M. & Supothina, S. 10-membered macrolides from the insect pathogenic fungus Cordyceps militaris BCC 2816. J. Nat. Prod. 67, 1953–1955 (2004).
Isaka, M., Kittakoop, P., Kirtikara, K., Hywel-Jones, N. L. & Thebtaranonth, Y. Bioactive substances from insect pathogenic fungi. Acc. Chem. Res. 38, 813–823 (2005).
Russell, R. & Paterson, M. Cordyceps—A traditional Chinese medicine and another fungal therapeutic biofactory? Phytochemistry 69, 1469–1495 (2008).
Haritakun, R., Sappan, M., Suvannakad, R., Tasanathai, K. & Isaka, M. An antimycobacterial cyclodepsipeptide from the entomopathogenic fungus Ophiocordyceps communis BCC 16475. J. Nat. Prod. 73, 75–78 (2010).
Sung, G. H. & Spatafora, J. W. Cordyceps cardinalis sp. Nov., a new species of Cordyceps with an east Asian-eastern North America distribution. Mycologia 96, 658–666 (2004).
Marfey, P. Determination of D-amino acids. II. Use of a bifunctional reagent, 1,5-difluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene. Carlsberg. Res. Commun. 49, 591–596 (1984).
Fujii, K. et al. A non-empirical method using LC/MS for determination of the absolute configuration of constituent amino acids in a peptide: elucidation of limitations of Marfey’s method and of its separation mechanism. Anal. Chem. 69, 3346–3352 (1997).
Fujii, K., Ikai, Y., Oka, H., Suzuki, M. & Harada, K. A nonempirical method using LC/MS for determination of the absolute configuration of constituent amino acids in a peptide: combination of Marfey's method with mass spectrometry and its practical application. Anal. Chem. 69, 5146–5151 (1997).
Otoguro, K. et al. Selective and potent in vitro antitrypanosomal activities of 10 microbial metabolites. J. Antibiot. 61, 372–378 (2008).
Otoguro, K. et al. Potent antimalarial activities of polyether antibiotic, X-206. J. Antibiot. 54, 658–663 (2001).
Acknowledgements
We are indebted to Dr M Tanaka for measurements of the 600 MHz NMR spectra, Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences of this University. This work was supported by a grant from MEXT (the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan)-Senryaku project (No. S0891078).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Umeyama, A., Takahashi, K., Grudniewska, A. et al. In vitro antitrypanosomal activity of the cyclodepsipeptides, cardinalisamides A–C, from the insect pathogenic fungus Cordyceps cardinalis NBRC 103832. J Antibiot 67, 163–166 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2013.93
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2013.93
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Medicinal fungi: a source of antiparasitic secondary metabolites
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (2018)