Abstract
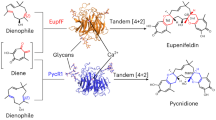
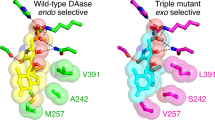
Frequent occurrence of [4+2] adducts in the secondary metabolites suggested involvement of Diels–Alderases (DAases) in their biosynthesis. However, a limited number of DAases were reported before early 2000s. Advancements in whole-genome sequencing and searching tool of the biosynthetic gene clusters of the secondary metabolites facilitate the identification of plausible DAases. Thus, during past 5 years, nine DAases have been characterized by genetic and biochemical analyses. These include a detailed functional analysis of SpnF that solely catalyzes [4+2] cycloaddition, a structural analysis of spirotetramate-forming enzyme PyrI4 complexed with the corresponding cycloadduct, and DAases catalyzing decalin formation and macrocyclic pyridine formation. Together with decalin-forming enzymes and macrocyclic pyridine-forming enzymes, these results provided sufficient data to discuss catalytic mechanism of DAases and nature’s strategy for molecular diversification of linear chain intermediates derived from polyketide and ribosomal peptide biosynthetic machinery.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Nicolaou, K. C., Snyder, S. A., Montagnon, T. & Vassilikogiannakis, G. The Diels–Alder reaction in total synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 41, 1668–1698 (2002).
Juhl, M. & Tanner, D. Recent applications of intramolecular Diels–Alder reactions to natural product synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 38, 2983–2992 (2009).
Klas, K., Tsukamoto, S., Sherman, D. H. & Williams, R. M. J. Org. Chem. 80, 11672–11685 (2015).
Kim, H. J., Ruszczycky, M. W. & Liu, H.-W. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 16, 124–131 (2012).
Oikawa, H. & Tokiwano, T. Enzymatic catalysis of the Diels–Alder reaction in the biosynthesis of natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 21, 321–352 (2004).
Oikawa, H. in Comprehensive Natural Products II Chemistry and Biology (eds Mander, L. & Liu, H. -W. 277–314 (Elsevier, Oxford, (2010).
Spole, J., Becker, H., Gupta, M. P., Beith, M. & Huch, V. Novel C-35 terpenoids from the panamanian liverwort Plagiochila moritziana . Tetrahedron 45, 5003–5014 (1989).
Kuo, Y. H., Chan, C. H. & Huang, S. L. A novel bicyclo[2.2.2]octane skeleton diterpene, obtunone, from the heartwood of Chamaecyparis obtusa var. formosana. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 46, 181–183 (1998).
Martins, D., Osshiro, E., Roque, N. F., Marks, V. & Gottlieb, H. E. A sesquiterpene dimer from Xylopia aromatic . Phytochemistry 48, 677–680 (1998).
Hofheinz, W. & Schonholzer, P. Ircinianin, a novel sesterterpene from a marine sponge. Helv. Chim. Acta 60, 1367–1370 (1977).
Sekita, S., Yoshihira, K., Natori, S. & Kuwano, H. Structures of chaetoglobosin A and B, cytotoxic metabolites of Chaetomium globosum . Tetrahedron Lett. 14, 2109–2112 (1973).
Aoyagi, Y. et al. Biomimetic synthesis of grandione from demethylsalvicanol via hetero-Diels–Alder type dimerization and structure revision of grandione. Tetrahedron Lett. 46, 7885–7887 (2005).
Oikawa, H., Katayama, K., Suzuki, Y. & Ichihara, A. Enzymatic activity catalysing exo-selective Diels–Alder reaction in solanapyrone biosynthesis. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1321–1322 (1995).
Kennedy, J. et al. Modulation of polyketide synthase activity by accessory proteins during lovastatin biosynthesis. Science 284, 1368–1372 (1999).
Watanabe, K. et al. Macrophomate synthase: Characterization, sequence, and expression in Escherichia coli of the novel enzyme catalyzing unusual multistep transformation of 2-pyrones to benzoates. J. Biochem. 127, 467–473 (2000).
Oikawa, H. et al. Macrophomate synthase: Unusual enzyme catalyzing multiple reactions from pyrones to benzoates. Tetrahedron Lett. 40, 6983–6986 (1999).
Fischbach, M. A. & Walsh, C. T. Assembly-line enzymology for polyketide and nonribosomal peptide antibiotics: Logic, machinery, and mechanisms. Chem. Rev. 106, 3468–3496 (2006).
Hoye, T. R. & Dvornikovs, V. Comparative Diels–Alder reactivities within a family of valence bond isomers: a biomimetic total synthesis of (+/-)-UCS1025A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 2550–2551 (2006).
Ichihara, A., Oikawa, H., Hayashi, K. & Sakamura, S. Structures of betaenones A and B, novel phytotoxins from Phoma betae Fr . J. Am. Chem. Soc. 105, 2907 (1983).
Ichihara, A. et al. A phytotoxin, betaenone C, and its related metabolites of Phoma betae Fr . Agric. Biol. Chem. 47, 2965 (1983).
Ugai, T. et al. Heterologous expression of highly reducing polyketide synthase involved in betaenone biosynthesis. Chem. Commun. 51, 1878–1881 (2015).
Miki, S. et al. Synthesis of (-)-probetaenone I: Structural conformation of biosynthetic precursor of betaenone B. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1, 1228–1229 (1990).
Jang, J. H. et al. Fusarisetin A, an acinar morphogenesis inhibitor from a soil fungus, Fusarium sp. FN080326. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 6865–6867 (2011).
Kato, K. et al. A new enzyme involved in the control of the stereochemistry in the decalin formation during equisetin biosynthesis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 460, 210–215 (2015).
Kakule, T. B., Zhang, S., Zhan, J. & Schmidt, E. W. Biosynthesis of the tetramic acids Sch210971 and Sch210972. Org. Lett. 17, 2295–2297 (2015).
Sato, M. et al. Involvement of lipocalin-like CghA in decalin-forming stereoselective intramolecular [4+2] cycloaddition. ChemBioChem 16, 2294–2298 (2015).
Kakule, T. B., Sardar, D., Lin, Z. & Schmidt, E. W. Two related pyrrolidinedione synthetase loci in Fusarium heterosporum ATCC74349 produce divergent metabolites. ACS Chem. Biol. 8, 1549–1557 (2013).
Kakule, T. B. et al. Native promoter strategy for high-yielding synthesis and engineering of fungal secondary metabolites. ACS. Synth. Biol. 4, 625–633 (2015).
Qiao, K., Chooi, Y.-H. & Tang, Y. Identification and engineering of the cytochalasin gene cluster from Aspergillus clavatus NRRL 1. Metab. Eng. 13, 723–732 (2011).
Singh, M. P. et al. Pyrroindomycins, novel antibiotics produced by Streptomyces rugosporus sp. LL-42D005. I. Isolation and structure determination. J. Antibiot. 47, 1250–1257 (1994).
Singh, M. P. et al. Pyrroindomycins, novel antibiotics produced by Streptomyces rugosporus sp. LL-42D005. II. Biological activities. J. Antibiot. 47, 1258–1265 (1994).
Tian, Z. et al. An enzymatic [4+2] cyclization cascade creates the pentacyclic core of pyrroindomycins. Nat. Chem. Biol. 11, 259–265 (2015).
Hashimoto, T. et al. Biosynthesis of versipelostatin: Identification of an enzyme-catalyzed [4+2]-cycloaddition required for macrocyclization of spirotetronate-containing polyketides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 572–575 (2015).
Jia, X.-Y. et al. Genetic characterization of the chlorothricin gene cluster as a model for spirotetronate antibiotic biosynthesis. Chem. Biol. 13, 575–585 (2006).
Zhang, H. et al. Elucidation of the kijanimicin gene cluster: Insights into the biosynthesis of spirotetronate antibiotics and nitrosugars. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 14670–14683 (2007).
Fang, J. et al. Cloning and characterization of the tetrocarcin A gene cluster from Micromonospora chalcea NRRL11289 reveals a highly conserved strategy for tetronate biosynthesis in spirotetronate antibiotics. J. Bacteriol. 190, 6014–6025 (2008).
Kasahara, K. et al. Solanapyrone synthase, a possible Diels–Alderase and iterative type I polyketide synthase encoded in a biosynthetic gene cluster from Alternaria solani . ChemBioChem 14, 1245–1252 (2010).
Ma, S. M. et al. Complete reconstitution of a highly reducing iterative polyketide synthase. Science 326, 589–592 (2009).
Kirst, H. A. et al. A83543A-D, unique fermentation-derived tetracyclic macrolides. Tetrahedron Lett. 32, 4839–4842 (1991).
Waldron, C et al. Cloning and analysis of the spinosad biosynthetic gene cluster of Saccharopolyspora spinosa . Chem. Biol. 8, 487–499 (2001).
Kim, H. J., Ruszczycky, M. W., Choi, S. H. & Liu, H.-W. Enzyme-catalysed [4+2] cycloaddition is a key step in the biosynthesis of spinosyn A. Nature 473, 109–112 (2001).
Fage, C. D. et al. The structure of SpnF, a standalone enzyme that catalyzes [4+2] cycloaddition. Nat. Chem. Biol. 11, 256–268 (2015).
Patel, A. et al. Dynamically complex [6+4] and [4+2] cycloadditions in the biosynthesis of spinosyn A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 3631–3634 (2016).
Walsh, C. T., Acker, M. G. & Bowers, A. A. Thiazolyl peptide antibiotic biosynthesis: a cascade of post-translational modifications on ribosomal nascent proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 27525–27531 (2010).
Wever, W. J. et al. Chemoenzymatic synthesis of thiazolyl peptide natural products featuring an enzyme-catalyzed forma [4+2] cycloaddition. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 3494–3497 (2015).
Hudson, G. A., Zhang, Z., Tietz, J. I., Mitchell, D. A. & van der Donk, W. A. In vitro biosynthesis of the core scaffold of the thiopeptide thiomuracin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 16012–16015 (2015).
Bowers, A. A., Acker, M. G., Young, T. S. & Walsh, C. T. Generation of thiocillin ring size variants by prepeptide gene replacement and in vivo processing by Bacillus cereus . J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 10313–10316 (2012).
Ortega, M. A. et al. Structure and mechanism of the tRNA-dependent lantibiotic dehydratase NisB. Nature 517, 509–512 (2015).
Zheng, Q. et al. Enzyme-dependent [4+2] cycloaddition depends on lid-like interaction of the N-terminal sequence with the catalytic core in PyrI4. Cell Chem. Biol. 23, 352–360 (2016).
Preiswerk, N. et al. Impact of scaffold rigidity on the design and evolution of an artificial Diels–Alderase. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 111, 8013–8018 (2014).
Serganov, A. et al. Structural basis for Diels–Alder ribozyme-catalyzed carbon-carbon bond formation. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 12, 218–224 (2005).
Siegel, J. B. et al. Computational design of an enzyme catalyst for a stereoselective bimolecular Diels–Alder reaction. Science 329, 309–313 (2010).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (A)15H01835 to HO.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Minami, A., Oikawa, H. Recent advances of Diels–Alderases involved in natural product biosynthesis. J Antibiot 69, 500–506 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2016.67
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2016.67
This article is cited by
-
Recent advances in the chemo-biological characterization of decalin natural products and unraveling of the workings of Diels–Alderases
Fungal Biology and Biotechnology (2022)
-
Catalytic mechanism and endo-to-exo selectivity reversion of an octalin-forming natural Diels–Alderase
Nature Catalysis (2021)
-
Efficient Lewis acid catalysis of an abiological reaction in a de novo protein scaffold
Nature Chemistry (2021)
-
Discovery and investigation of natural Diels–Alderases
Journal of Natural Medicines (2021)
-
Total synthesis of brevianamide A
Nature Chemistry (2020)