Abstract
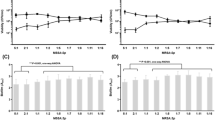
An in vitro study aimed to evaluate the effect of N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) or sub-ICs of erythromycin on antimicrobial susceptibility of staphylococcal biofilms was performed. Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis strains were isolated from patients with prosthetic joint infections using a previously published sonication procedure. Conventional susceptibility studies were performed using microdilution according to the CLSI procedures. Biofilm susceptibility was performed using the Calgary methodology. The addition of NAC showed no effect with the S. aureus strains, and a strain-dependent effect with the S. epidermidis strains. No effect was detected with erythromycin for almost all tested strains.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
del Pozo, J. L. & Patel, R. The challenge of treating biofilm-associated bacterial infections. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 82, 204–209 (2007).
Del Pozo, J. L. & Patel, R. Clinical practice. Infection associated with prosthetic joints. N. Engl. J. Med. 361, 787–794 (2009).
Tande, A. J. & Patel, R. Prosthetic joint infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 27, 302–345 (2014).
Trampuz, A. & Zimmerli, W. Antimicrobial agents in orthopaedic surgery: prophylaxis and treatment. Drugs 66, 1089–1105 (2006).
Trampuz, A. & Zimmerli, W. Diagnosis and treatment of implant-associated septic arthritis and osteomyelitis. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 10, 394–403 (2008).
Arciola, C. R. et al. Detection of biofilm formation in Staphylococcus epidermidis from implant infections. Comparison of a PCR-method that recognizes the presence of ica genes with two classic phenotypic methods. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 76, 425–430 (2006).
Arciola, C. R., Campoccia, D. & Montanaro, L. Detection of biofilm-forming strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis and S. aureus. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2, 478–484 (2002).
Esteban, J. et al. Biofilm development by clinical isolates of Staphylococcus spp. from retrieved orthopedic prostheses. Acta Orthop. 81, 674–679 (2010).
Taj, Y., Essa, F., Aziz, F. & Kazmi, S. U. Study on biofilm-forming properties of clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 6, 403–409 (2012).
Valour, F. et al. Staphylococcus epidermidis in orthopedic device infections: the role of bacterial internalization in human osteoblasts and biofilm formation. PLoS ONE 8, e67240 (2013).
Molina-Manso, D. et al. In vitro susceptibility to antibiotics of staphylococci in biofilms isolated from orthopaedic infections. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 41, 521–523 (2013).
de la Fuente-Nunez, C., Reffuveille, F., Fernandez, L. & Hancock, R. E. Bacterial biofilm development as a multicellular adaptation: antibiotic resistance and new therapeutic strategies. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 16, 580–589 (2013).
Mah, T. F. Biofilm-specific antibiotic resistance. Future Microbiol. 7, 1061–1072 (2012).
Mah, T. F. & O'Toole, G. A. Mechanisms of biofilm resistance to antimicrobial agents. Trends Microbiol. 9, 34–39 (2001).
Sun, F. et al. Biofilm-associated infections: antibiotic resistance and novel therapeutic strategies. Future Microbiol. 8, 877–886 (2013).
Xu, K. D., McFeters, G. A. & Stewart, P. S. Biofilm resistance to antimicrobial agents. Microbiology 146, 547–549 (2000).
Yonezawa, H., Osaki, T. & Kamiya, S. Biofilm Formation by and Its Involvement for Antibiotic Resistance. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 914791 (2015).
Cordero-Ampuero, J., Esteban, J. & Garcia-Cimbrelo, E. Oral antibiotics are effective for highly resistant hip arthroplasty infections. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 467, 2335–2342 (2009).
Cordero-Ampuero, J., Esteban, J., Garcia-Cimbrelo, E., Munuera, L. & Escobar, R. Low relapse with oral antibiotics and two-stage exchange for late arthroplasty infections in 40 patients after 2-9 years. Acta Orthop. 78, 511–519 (2007).
Del Pozo, J. L. & Patel, R. Are antibiotics and surgery sufficient to treat biofilm-associated infections? Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 31, 641–642 (2013).
Aslam, S., Trautner, B. W., Ramanathan, V. & Darouiche, R. O. Combination of tigecycline and N-acetylcysteine reduces biofilm-embedded bacteria on vascular catheters. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 51, 1556–1558 (2007).
El-Feky, M. A. et al. Effect of ciprofloxacin and N-acetylcysteine on bacterial adherence and biofilm formation on ureteral stent surfaces. Pol. J. Microbiol. 58, 261–267 (2009).
Leite, B. et al. Combined effect of linezolid and N-acetylcysteine against Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 31, 655–659 (2013).
Leite, B. et al. Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms control by N-acetylcysteine and rifampicin. Am. J. Ther. 20, 322–328 (2013).
Tateda, K., Hirakata, Y., Furuya, N., Ohno, A. & Yamaguchi, K. Effects of sub-MICs of erythromycin and other macrolide antibiotics on serum sensitivity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 37, 675–680 (1993).
Wozniak, D. J. & Keyser, R. Effects of subinhibitory concentrations of macrolide antibiotics on Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Chest 125, 62S–69S (2004).
Esteban, J. et al. PCR-hybridization after sonication improves diagnosis of implant-related infection. Acta Orthop. 83, 299–304 (2012).
Molina-Manso, D. et al. In vitro susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis isolated from prosthetic joint infections. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 65, 505–508 (2012).
CLSI Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: Twenty-Fifth Informational Supplement. CLSI document M100-S25 (Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne, PA, USA, (2015).
Donlan, R. M. Biofilm formation: a clinically relevant microbiological process. Clin. Infect. Dis. 33, 1387–1392 (2001).
Arciola, C. R., Campoccia, D., Ehrlich, G. D. & Montanaro, L. Biofilm-based implant infections in orthopaedics. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 830, 29–46 (2015).
Dodds, M. G., Grobe, K. J. & Stewart, P. S. Modeling biofilm antimicrobial resistance. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 68, 456–465 (2000).
Cordero-Ampuero, J., Esteban, J. & Garcia-Rey, E. Results after late polymicrobial, gram-negative, and methicillin-resistant infections in knee arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 468, 1229–1236 (2010).
Trampuz, A., Osmon, D. R., Hanssen, A. D., Steckelberg, J. M. & Patel, R. Molecular and antibiofilm approaches to prosthetic joint infection. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 414, 69–88 (2003).
Esteban, J. & Cordero-Ampuero, J. Treatment of prosthetic osteoarticular infections. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 12, 899–912 (2011).
Marchese, A., Bozzolasco, M., Gualco, L., Debbia, E. A., Schito, G. C. & Schito, A. M. Effect of fosfomycin alone and in combination with N-acetylcysteine on E. coli biofilms. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 22, 95–100 (2003).
Olofsson, A. C., Hermansson, M. & Elwing, H. N-acetyl-L-cysteine affects growth, extracellular polysaccharide production, and bacterial biofilm formation on solid surfaces. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 69, 4814–4822 (2003).
Ceri, H. et al. The Calgary Biofilm Device: new technology for rapid determination of antibiotic susceptibilities of bacterial biofilms. J. Clin. Microbiol. 37, 1771–1776 (1999).
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by a grant from the Spanish Ministry of Science (FUNCOATCSD2008-00023) and the Spanish MINECO (MAT2013-48224-C2-2-R).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
JE and RF-R have received travel grants from Pfizer, Novartis, bioMérieux and Alere and research grants from Wyeth and Laboratorios Leti. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Molina-Manso, D., Del-Prado, G., Gómez-Barrena, E. et al. Effect of different agents with potential antibiofilm activity on antimicrobial susceptibility of biofilms formed by Staphylococcus spp. isolated from implant-related infections. J Antibiot 69, 686–688 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2016.9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2016.9
This article is cited by
-
Impact of N-Acetylcysteine and Antibiotics Against Single and Dual Species Biofilms of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Achromobacter xylosoxidans
Current Microbiology (2023)
-
N-acetyl cysteine versus chlorhexidine mouthwashes in prevention and treatment of experimental gingivitis: a randomized, triple-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial
Clinical Oral Investigations (2019)
-
Antibacterial effect of antibiotic-loaded SBA-15 on biofilm formation by Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis
The Journal of Antibiotics (2017)