Abstract
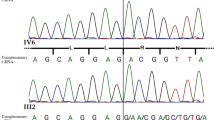
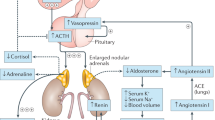
We have designed a rapid and convenient strategy to determine nine of the most common mutations in the 21-hydroxylase gene (CYP21). The frequency of the mutations was investigated in 34 Japanese patients affected with congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) caused by 21-hydroxylase deficiency. We characterized 82% of the CAH chromosomes. The most frequent mutations were a C/A to G substitution in intron 2 in the salt-wasting form of the disease and an I172N in the simple virilizing form. Three de novo mutations were found. Two homozygous mutations (S268T and N493S) were detected by direct sequencing of all exons of CYP21 in two siblings, who had a normal genotype at all positions screened. We successfully applied these methods for prenatal diagnosis in one family. These procedures proved to be sensitive and rapid for the detection of the most common known mutations in the CYP21 gene and may be useful for genetic screening.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: March 29, 1999 / Accepted: May 11, 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asanuma, A., Ohura, T., Ogawa, E. et al. Molecular analysis of Japanese patients with steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency. J Hum Genet 44, 312–317 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s100380050167
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s100380050167
This article is cited by
-
EMQN best practice guidelines for molecular genetic testing and reporting of 21-hydroxylase deficiency
European Journal of Human Genetics (2020)
-
Structure-based activity prediction of CYP21A2 stability variants: A survey of available gene variations
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Ethnic disparity in 21-hydroxylase gene mutations identified in Pakistani congenital adrenal hyperplasia patients
BMC Endocrine Disorders (2011)
-
Genotyping of CYP21A2 for Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Screening using Allele-Specific Primer Extension followed by Bead Array Hybridization
Molecular Diagnosis & Therapy (2009)