Abstract
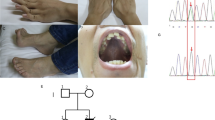
Of 100 patients with the clinical diagnosis of Leigh syndrome, 21 were found to have specific enzyme defects: 15 involving cytochrome c oxidase (COX); 4, pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDHC); one, complex I (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide [NADH]-coenzyme Q reductase) and one, complex II (succinate-ubiquinone reductase) deficiencies. In addition to the most common form of COX deficiency, mtDNA mutations in the adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase) 6 coding region were also commonly seen. Eighteen patients (18%) had mtDNA mutations at nucleotide position (np) 8993 or 9176. The mutated DNAs were present in a heteroplasmic state, comprising more than 90% of the DNA in muscle and/or blood samples from all patients. Patients with the T-to-G mutation at np 8993 usually had early onset of the disease with rapid progression, showing the typical clinical features of Leigh syndrome. On the other hand, those with the T-to-C 8993 mutation showed a milder and more chronic course. Patients with the mutation at np 9176 showed variable courses. Phylogenetic analysis of mtDNA D-loop sequences for the patients with the ATPase 6 mutations and normal Japanese subjects revealed that a T-to-G/C mutation at np 8993 and a T-to-C mutation at np 9176 occurred many times independently in the Japanese population.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: September 21, 1999 / Accepted: November 24, 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Makino, M., Horai, S., Goto, Y. et al. Mitochondrial DNA mutations in Leigh syndrome and their phylogenetic implications. J Hum Genet 45, 69–75 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s100380050014
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s100380050014
This article is cited by
-
Mitochondrial DNA 11777C>A Mutation Associated Leigh Syndrome: Case Report with a Review of the Previously Described Pedigrees
NeuroMolecular Medicine (2010)
-
The development of novel quantification assay for mitochondrial DNA heteroplasmy aimed at preimplantation genetic diagnosis of Leigh encephalopathy
Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics (2007)
-
Leigh syndrome caused by mitochondrial DNA G13513A mutation: frequency and clinical features in Japan
Journal of Human Genetics (2004)