Abstract
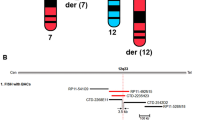
The 16p13.3 breakpoints of two de novo translocations of chromosome 16, t(1;16) and t(14;16), were shown by initial mapping studies to have physically adjacent breakpoints. The translocations were ascertained in patients with abnormal phenotypes characterized by predominant epilepsy in one patient and mental retardation in the other. Distamycin/DAPI banding showed that the chromosome 1 breakpoint of the t(1;16) was in the pericentric heterochromatin therefore restricting potential gene disruption to the 16p13.3 breakpoint. The breakpoints of the two translocations were localized to a region of 3.5 and 115 kb respectively and were approximately 900 kb apart. The mapping was confirmed by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) of clones that spanned the breakpoints to metaphase spreads derived from the patients. The mapping data showed both translocations disrupted the ataxin-2-binding protein 1 (A2BP1) gene that encompasses a large genomic region of 1.7 Mb. A2BP1 encodes a protein that is known to interact with the spinocerebellar ataxia type 2 (SCA2) protein. It is proposed that disruption of the A2BP1 gene is a cause of the abnormal phenotype of the two patients. Ninety-six patients with sporadic epilepsy and 96 female patients with mental retardation were screened by SSCP for potential mutations of A2BP1. No mutations were found, suggesting that disruption of the A2BP1 gene is not a common cause of sporadic epilepsy or mental retardation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Callen DF, Baker E, Eyre HJ, Chernos JE, Bell JA, Sutherland GR (1990) Reassessment of two apparent deletions of chromosome 16p to an ins(11;16) and a t(1;16) by chromosome painting. Ann Genet 33:219–221
Callen DF, Lane SA, Kozman H, Kremmidiotis G, Whitmore SA, Lowenstein M, Doggett NA, Kenmochi N, Page DC, Maglott DR et al (1995) Integration of transcript and genetic maps of chromosome 16 at near-1-Mb resolution: demonstration of a “hot spot” for recombination at 16p12. Genomics 29:503–511
Callen DF, Eyre H, McDonnell S, Schuffenhauer S, Bhalla K (2002) A complex rearrangement involving simultaneous translocation and inversion is associated with a change in chromatin compaction. Chromosoma 111:170–175
Kiehl TR, Shibata H, Vo T, Huynh DP, Pulst SM (2001) Identification and expression of a mouse ortholog of A2BP1. Mamm Genome 12:595–601
Shibata H, Huynh DP, Pulst SM (2000) A novel protein with RNA-binding motifs interacts with ataxin-2. Hum Mol Genet 9:1303–1313
Warburton D (1991) De novo balanced chromosome rearrangements and extra marker chromosomes identified at prenatal diagnosis: clinical significance and distribution of breakpoints. Am J Hum Genet 49:995–1013
Acknowledgments
The National Health and Medical Research Council funded this research. We would like to thank Raman Kumar and Ross McKirdy for performing the RT-PCR assays.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhalla, K., Phillips, H.A., Crawford, J. et al. The de novo chromosome 16 translocations of two patients with abnormal phenotypes (mental retardation and epilepsy) disrupt the A2BP1 gene. J Hum Genet 49, 308–311 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10038-004-0145-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10038-004-0145-4
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Enhanced long-term potentiation and impaired learning in mice lacking alternative exon 33 of CaV1.2 calcium channel
Translational Psychiatry (2022)
-
Rett syndrome linked to defects in forming the MeCP2/Rbfox/LASR complex in mouse models
Nature Communications (2021)
-
In vitro dexamethasone treatment does not induce alternative ATM transcripts in cells from Ataxia–Telangiectasia patients
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Concentration-dependent splicing is enabled by Rbfox motifs of intermediate affinity
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2020)
-
The effect of Rbfox2 modulation on retinal transcriptome and visual function
Scientific Reports (2020)