Abstract
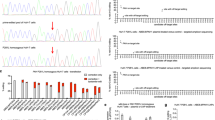
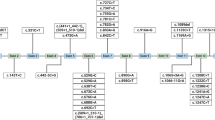
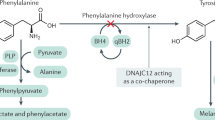
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is an inborn error of metabolism that results from a deficiency of phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH). We characterized the PAH mutations of 79 independent Korean patients with PKU or hyperphenylalaninemia. PAH nucleotide sequence analysis revealed 39 different mutations, including ten novel mutations. The novel mutations consisted of nine missense mutations (P69S, G103S, N207D, T278S, P281A, L293M, G332V, S391I, and A447P) and a novel splice site variant (IVS10−3C>G). R243Q, IVS4−1G>A, and E6−96A>G were the most prevalent mutations, as they accounted for 32% of the total mutant alleles in this study. Although some common characteristics of allele frequency and distribution were identified among oriental populations, several distinctive characteristics were revealed in Korean patients. Although the R413P allele is the most prevalent form (30.5%) in Japanese, we detected it in only five chromosomes from 158 independent chromosomes (3.2%). The A259T allele, which has not yet been found in oriental populations, was frequently found in this study. We also observed that tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) responsiveness was associated with specific genotypes (R53H, R241C, and R408Q), suggesting there are some correlations between phenotype and genotype.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Aoki K, Wada Y (1988) Outcome of the patients detected by newborn screening in Japan. Acta Paediatr Jpn 30:429–434
Bickel H, Bachmann C, Beckers R, Brandt NJ, Clayton BE, Corrado G, Feingold HJ, Giardini O, Hammersen G, Schonberg D (1981) Neonatal mass screening for metabolic disorders. Eur J Pediatr 137:133–139
Chien YH, Chiang SC, Huang A, Chou SP, Tseng SS, Huang YT, Hwu WL (2004) Mutation spectrum in Taiwanese patients with phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency and a founder effect for the R241C mutation. Hum Mutat 23:206
Erlandsen H, Stevens RC (2001) A structural hypothesis for BH4 responsiveness in patients with mild forms of hyperphenylalaninaemia and phenylketonuria. J Inherit Metab Dis 24:213–230
Guldberg P, Rey F, Zschocke J, Romano V, Francois B, Michiels L, Ullrich K, Hoffmann GF, Burgard P, Schmidt H, Meli C, Riva E, Dianzani I, Ponzone A, Rey J, Guttler F (1998) A European multicenter study of phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency: classification of 105 mutations and a general system for genotype-based prediction of metabolic phenotype. Am J Hum Genet 63:71–79
Kure S, Hou DC, Ohura T, Iwamoto H, Suzuki S, Sugiyama N, Sakamoto O, Fujii K, Matsubara Y, Narisawa K (1999) Tetrahydrobiopterin-responsive phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency. J Pediatr 135:375–378
Liu SR, Zuo QH (1986) Newborn screening for phenylketonuria in eleven districts. Chin Med J (Engl) 99:113–118
Okano Y, Hase Y, Lee D-H, Furuyama JI, Shintaku H, Oura T, Isshiki G (1992) Frequency and distribution of phenylketonuric mutations in Orientals. Hum Mutat 1:216–220
Okano Y, Hase Y, Lee DH, Takada G, Shigematsu Y, Oura T, Isshiki G (1994) Molecular and population genetics of phenylketonuria in Orientals: correlation between phenotype and genotype. J Inherit Metab Dis 17:156–159
Okano Y, Asada M, Kang Y, Nishi Y, Hase Y, Oura T, Isshiki G (1998) Molecular characterization of phenylketonuria in Japanese patients. Hum Genet 103:613–618
Park YS, Seoung CS, Lee SW, Oh KH, Lee DH, Yim J (1998) Identification of three novel mutations in Korean phenylketonuria patients: R53H, N207D, and Y325X. Hum Mutat Suppl 1:S121–S122
Pey AL, Desviat LR, Gamez A, Ugarte M, Perez B (2003) Phenylketonuria: genotype-phenotype correlations based on expression analysis of structural and functional mutations in PAH. Hum Mutat 21:370–378
Scriver CR, Hurtubise M, Konecki D, Phommarinh M, Prevost L, Erlandsen H, Stevens R, Waters PJ, Ryan S, McDonald D, Sarkissian C (2003) PAHdb 2003: what a locus-specific knowledgebase can do? Hum Mutat 21:333–344
Song F, Jin YW, Wang H, Yang YL, Zhang YM, Zhang T (2003) Ten novel mutations in the phenylalanine hydroxylase gene identified in Chinese patients with phenylketonuria. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao 25:142–144
Zschocke J (2003) Phenylketonuria mutations in Europe. Hum Mutat 21:345–356
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the members of the Korean PKU family support group for their contribution and cooperation in this research. This study was supported by an intramural research fund from the National Institute of Health, Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The first two authors contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, D.H., Koo, S.K., Lee, KS. et al. The molecular basis of phenylketonuria in Koreans. J Hum Genet 49, 617–621 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10038-004-0197-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10038-004-0197-5
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Neonatal screening and genotype-phenotype correlation of hyperphenylalaninemia in the Chinese population
Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases (2021)
-
Spectrum of PAH gene mutations in 1547 phenylketonuria patients from Iran: a comprehensive systematic review
Metabolic Brain Disease (2021)
-
Mutational and phenotypic spectrum of phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency in Zhejiang Province, China
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Analysis of the genotype-phenotype correlation in patients with phenylketonuria in mainland China
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Spectrum of PAH gene variants among a population of Han Chinese patients with phenylketonuria from northern China
BMC Medical Genetics (2017)