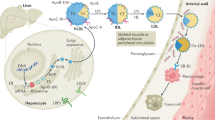
Abstract
Factors predisposing to the phenotypic features of high total cholesterol (T-Cho) in human plasma have not been clearly defined. Here we report an association between two variations in the apolipoprotein B48 receptor gene (APOB48R) and plasma T-Cho levels among 352 adult individuals in Japan. By analyzing phenotypic associations between age- and gender-adjusted levels of plasma T-Cho, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol (LDL-C), and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol (HDL-C), we detected a significant correlation between genotypes of the A419P variation and adjusted T-Cho levels. Among homozygous G-allele carriers (n=265), heterozygous carriers (n=78), and homozygous minor C-allele carriers (n=9), T-Cho levels were 2.43±0.21 mg/cm3, 2.48±0.24 mg/cm3, and 2.63±0.21 mg/cm3, respectively, indicating a codominant T-Cho-elevating effect of the minor C-allele (r=0.15, P=0.007). A similar effect was detected for c.934-960/del (r=0.13, P=0.015). Linkage disequilibrium (LD) analysis detected significant LD among eight variant sites that included neighboring loci. Our results indicate that variations in APOB48R and nearby genes are among the many factors involved in hypercholesterolemia. The etiological studies should now include consideration of this novel aspect of the mechanism(s) leading to hypercholesterolemic disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Brown ML, Ramprasad MP, Umeda PK, Tanaka A, Kobayashi Y, Watanabe T, Shimoyamada H, Kuo WL, Li R, Song R, Bradley WA, Gianturco SH (2000) A macrophage receptor for apolipoprotein B48: cloning, expression, and atherosclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 7488–7493
Cullen P, Funke H, Schulte H, Assmann G (1997) Lipoproteins and cardiovascular risk-from genetics to CHD prevention. J Atheroscler Thromb 4:51–58
Daniel TO, Schneider WJ, Goldstein JL, Brown MS (1983) Visualization of lipoprotein receptors by ligand blotting. J Biol Chem 258: 4606–4611
de Knijff P, van den Maagdenberg AM, Frants RR, Havekes LM (1994). Genetic heterogeneity of apolipoprotein E and its influence on plasma lipid and lipoprotein levels. Hum Mutat 4:178–194
Fredman D, White SJ, Susanna P, Eichler EE, Den Dunnen JT, Brookes AJ (2004) Complex SNP-related sequence variation in segmental genome duplications. Nat Genet 36:861–866
Fujita Y, Ezura Y, Emi M, Ono S, Takada D, Takahashi K, Uemura K, Iino Y, Katayama Y, Bujo H, Saito Y (2003) Hypertriglyceridemia associated with amino acid variation N985Y of RP1 Gene. J Hum Genet 48:305–308
Goldstein JL, Hobbs HH, Brown MS (1995) Familial Hypercholesterolaemia. In: Scriver CT, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D (eds) The metabolic and molecular bases of inherited disease. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 1981–2030
Hattori H, Hirayama T, Nobe Y, Nagano M, Kujiraoka T, Egashira T, Ishii J, Tsuji M, Emi M (2002) Eight novel mutations and functional impairments of the LDL receptor in familial hypercholesterolemia in the north of Japan. J Hum Genet 47:80–87
Hegele RA (2001) Monogenic dislipidemias: window on determinants of plasma lipoprotein metabolism. Am J Hum Genet 69:1161–1177
Ishii J, Nagano M, Kujiraoka T, Ishihara M, Egashira T, Takada D, Tsuji M, Hattori H, Emi M (2002) Clinical variant of Tangier disease in Japan: mutation of the ABCA1 gene in hypoalphalipoproteinemia with corneal lipidosis. J Hum Genet 47:366–369
Kita T (2001) Brief report of the study groups on primary hyperlipidemia in general Japanese 2001, organized by Japanese Ministry of the Health, Labor and Welfare. http://webabst.niph.go.jp/pdf/2002/200207010001.pdf (http://webabst.niph.go.jp/), in Japanese
Livak KJ (1999) Allelic discrimination using fluorogenic probes and the 5’ nucleotide assay. Genet Anal 14:143–149
Lyamichev V, Mast AL, Hall JG, Prudent JR, Kaiser MW, Takova T, Kwiatkowski RW, Sander TJ, de Arruda M, Arco DA, Neri BP, Brow MA (1999) Polymorphism identification and quantitative detection of genomic DNA by invasive cleavage of oligonucleotide probes. Nat Biotechnol 17:292–296
Mein CA, Barratt BJ, Dunn MG, Siegmund T, Smith AN, Esposito L, Nutland S, Stevens HE, Wilson AJ, Philips MS, Jarvis N, Law S, de Arruda M, Todd JA (2000) Evaluation of single nucleotide polymorphism typing with invader on PCR amplidons and its automation. Genome Res 10:330–343
Millar PT, Sardina IB, Saccona NL, Putzel J, Laitinen T, Cao A, Kere J, Pilia G, Rice JP, Kwok PY (2000) Juxtaposed regions of extensive minimal linkage disequilibrium in human Xq25 and Xq28. Nat Genet 25:324–328
Ng PC, Henikoff S (2002) Accounting for human polymorphisms predicted to affect protein function. Genome Res 12:436–446
Thompson EA, Deeb S, Walker D, Motulsky AG (1988). The detection of linkage disequilibrium between closely linked markers: RFLPs at the AI-CIII apolioprotein genes. Am J Hum Genet 42:113–124
Reich DE, Cargill M, Bolk S, Ireland J, Sabeti PC, Richter DJ, Lavery T, Kouyoumjian R, Farhadian SF, Ward R, Lander E (2001) Linkage disequilibrium in the human genome. Nature 411:199–204
Yang C, Chen S, Gianturco SH, Bradley WA, Sparrow JT, Tanimura M, Li W, Sparrow DA, DeLoof H, Rosseneu M (1986) Sequence, structure, receptor-binding domains and internal repeats of human apolipoprotein B-100. Nature 323:738–742
Zannis VI, Breslow JL (1985) Genetic mutations affecting human lipoprotein metabolism. Adv Hum Genet 14:125–215
Acknowledgements
We thank Mitsuko Kajita, Mina Kodaira, Miho Kawagoe, Tamami Uchida, and Naoko Tsuruta for their expert technical assistance. This work was supported by a grant for Strategic Research from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports, and Culture of Japan; by a Research Grant for Research from the Ministry of Health and Welfare of Japan; and by a Research for the Future Program Grant of The Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujita, Y., Ezura, Y., Bujo, H. et al. Association of nucleotide variations in the apolipoprotein B48 receptor gene (APOB48R) with hypercholesterolemia. J Hum Genet 50, 203–209 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10038-005-0240-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10038-005-0240-1