Abstract
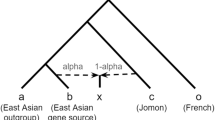
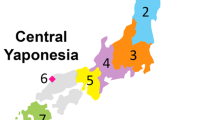
Historic Japanese culture evolved from at least two distinct migrations that originated on the Asian continent. Hunter-gatherers arrived before land bridges were submerged after the last glacial maximum (>12,000 years ago) and gave rise to the Jomon culture, and the Yayoi migration brought wet rice agriculture from Korea beginning ~2,300 years ago. A set of 81 Y chromosome single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) was used to trace the origins of Paleolithic and Neolithic components of the Japanese paternal gene pool, and to determine the relative contribution of Jomon and Yayoi Y chromosome lineages to modern Japanese. Our global sample consisted of >2,500 males from 39 Asian populations, including six populations sampled from across the Japanese archipelago. Japanese populations were characterized by the presence of two major (D and O) and two minor (C and N) clades of Y chromosomes, each with several sub-lineages. Haplogroup D chromosomes were present at 34.7% and were distributed in a U-shaped pattern with the highest frequency in the northern Ainu and southern Ryukyuans. In contrast, haplogroup O lineages (51.8%) were distributed in an inverted U-shaped pattern with a maximum frequency on Kyushu. Coalescent analyses of Y chromosome short tandem repeat diversity indicated that haplogroups D and C began their expansions in Japan ~20,000 and ~12,000 years ago, respectively, while haplogroup O-47z began its expansion only ~4,000 years ago. We infer that these patterns result from separate and distinct genetic contributions from both the Jomon and the Yayoi cultures to modern Japanese, with varying levels of admixture between these two populations across the archipelago. The results also support the hypothesis of a Central Asian origin of Jomonese ancestors, and a Southeast Asian origin of the ancestors of the Yayoi, contra previous models based on morphological and genetic evidence.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Aikens CM, Higuchi T (1982) Prehistory of Japan. Academic Press, New York, NY
Bandelt HJ, Forster P, Rohl A (1999) Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Mol Biol Evol 16:37–48
Bannai M, Tokunaga K, Imanishi T, Harihara S, Fujisawa K, Juji T, Omoto K (1996) HLA class II alleles in Ainu living in Hidaka District, Hokkaido, northern Japan. Am J Phys Anthropol 101:1–9
Capelli C, Wilson JF, Richards M, Stumpf MP, Gratrix F, Oppenheimer S, Underhill P, Pascali VL, Ko TM, Goldstein DB (2001) A predominantly indigenous paternal heritage for the Austronesian-speaking peoples of insular Southeast Asia and Oceania. Am J Hum Genet 68:432–443
Cavalli-Sforza LL, Menozzi P, Piazza A (1994) The history and geography of human genes. Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ
Chard C (1974) Northeast Asia in prehistory. University of Wisconsin Press, Madison, WI
Cruciani F, Santolamazza P, Shen PD, Macaulay V, Moral P, Olckers A, Modiano D, Holmes S, Destro-Bisol G, Coia V, Wallace DC, Oefner PJ, Torroni A, Cavalli-Sforza LL, Scozzari R, Underhill PA (2002) A back migration from Asia to sub-Saharan Africa is supported by high-resolution analysis of human Y-chromosome haplotypes. Am J Hum Genet 70:1197–1214
De Knijff P (2000) Messages through bottlenecks: on the combined use of slow and fast evolving polymorphic markers on the human Y chromosome. Am J Hum Genet 67:1055–1061
Deng W, Shi B, He X, Zhang Z, Xu J, Li B, Yang J, Ling L, Dai C, Qiang B, Shen Y, Chen R (2004) Evolution and migration history of the Chinese population inferred from Chinese Y-chromosome evidence. J Hum Genet 49:339–348
Diamond J (1998) Japanese roots. Discover 19:86–94
Diamond J, Bellwood P (2003) Farmers and their languages: the first expansions. Science 300:597–603
Excoffier L, Smouse PE, Quattro JM (1992) Analysis of molecular variance inferred from metric distances among DNA haplotypes: application to human mitochondrial DNA restriction data. Genetics 131:479–491
Hammer MF, Horai S (1995) Y chromosomal DNA variation and the peopling of Japan. Am J Hum Genet 56:951–962
Hammer MF, Zegura SL (2002) The human Y chromosome haplogroup tree: nomenclature and phylogeography of its major divisions. Annu Rev Anthropol 31:303–321
Hammer MF, Karafet TM, Redd AJ, Jarjanazi H, Santachiara-Benerecetti S, Soodyall H, Zegura SL (2001) Hierarchical patterns of global human Y-chromosome diversity. Mol Biol Evol 18:1189–1203
Hammer MF, Blackmer F, Garrigan D, Nachman MW, Wilder JA (2003) Human population structure and its effects on sampling Y chromosome sequence variation. Genetics 164:1495–1509
Hanihara K (1991) Dual structure model for the population history of Japanese. Jpn Rev 2:1–33
Horai S, Murayama K, Hayasaka K, Matsubayashi S, Hatori Y, Fucharoen G, Harihara S, Park KS, Omoto K, Pan I-H (1996) mtDNA polymorphism in East Asian populations, with special reference to the peopling of Japan. Am J Hum Genet 59:579–590
Howells WW (1966) The Jomon people of Japan: a study by discriminant analysis of Japanese and Ainu crania. Papers of the Peabody Museum of Archaeology and Ethnology, Harvard University, 57:1–43
Hurles ME, Nicholson J, Bosch E, Renfrew C, Sykes BC, Jobling MA (2002) Y chromosomal evidence for the origins of oceanic-speaking peoples. Genetics 160:289–303
Jobling MA, Tyler-Smith C (2003) The human Y chromosome: an evolutionary marker comes of age. Nat Rev Genet 4:598–612
Karafet TM, Zegura SL, Posukh O, Osipova L, Bergen A, Long J, Goldman D, Klitz W, Harihara S, de Knijff P, Wiebe V, Griffiths RC, Templeton AR, Hammer MF (1999) Ancestral Asian source(s) of New World Y-Chromosome founder haplotypes. Am J Hum Genet 64:817–831
Karafet T, Xu L, Du R, Wang W, Feng S, Wells RS, Redd AJ, Zegura SL, Hammer MF (2001) Paternal population history of East Asia: sources, patterns, and microevolutionary processes. Am J Hum Genet 69:615–628
Karafet TM, Lansing JS, Redd AJ, Reznikova S, Watkins JC, Surata SPK, Arthawiguna WA, Mayer L, Bamshad M, Jorde LB, Hammer MF (2005) A Balinese Y chromosome perspective on the peopling of Indonesia: genetic contributions from pre-Neolithic hunter-gatherers, Austronesian farmers, and Indian traders. Hum Biol 77:93–114
Kayser M, de Knijff P, Dieltjes P, Krawczak M, Nagy M, Zerjal T, Pandya A, Tyler-Smith C, Roewer L (1997) Applications of microsatellite-based Y chromosome haplotyping. Electrophoresis 18:1602–1607
Kayser M, Brauer S, Weiss G, Underhill PA, Roewer L, Schiefenhovel W, Stoneking M (2000) Melanesian origin of Polynesian Y chromosomes. Curr Biol 10:1237–1246
Koyama S (1992) Prehistoric Japanese populations: a subsistence-demographic approach. In: Japanese as a member of the Asian and Pacific populations. Kyoto, Japan
Kruskal JB (1964) Multidimensional scaling by optimizing goodness of fit to a nonmetric hypothesis. Pyschometrika 29:1–27
Matsumoto T, Imamura O, Yamabe Y, Kuromitsu J, Tokutake Y, Shimamoto A, Suzuki N, Satoh M, Kitao S, Ichikawa K, Kataoka H, Sugawara K, Thomas W, Mason B, Tsuchihashi Z, Drayna D, Sugawara M, Sugimoto M, Furuichi Y, Goto M (1997) Mutation and haplotype analyses of the Werner’s syndrome gene based on its genomic structure: genetic epidemiology in the Japanese population. Hum Genet 100:123–130
Minch E (1997) Microsat. Stanford, UK
Mizoguchi Y (1986) Contributions of prehistoric Far East populations to the population of modern Japan: a Q-mode path analysis based on cranial measurements. In: Akazawa T, Aikens CM (eds) Prehistoric hunter gatherers in Japan, vol Bull No. 27. University of Tokyo Press, Tokyo, pp 107–136
Nei M (1995) The origins of human populations: genetic, linguistic, and archeological data. In: Brenner S, Hanihara K (eds) The original past of modern humans as viewed from DNA. World Scientific, Singapore, pp 71–91
Omoto K, Misawa S (1976) The genetic relations of the Ainu. In: Kirk RL, Thorne AG (eds) The origins of the Australians. The Australian Institute of Aboriginal Studies, Canberra, pp 365–376
Omoto K, Saitou N (1997) Genetic origins of the Japanese: a partial support for the dual structure hypothesis. Am J Phys Anthropol 102:437–446
Ono A, Sato H, Tsutsumi T, Kudo Y (2002) Radiocarbon dates and archaeology of the Late Pleistocene in the Japanese islands. Radiocarbon 44:477–494
Ossenberg N (1986) Isolate conservatism and hybridization in the population history of Japan: the evidence of nonmetric cranial traits. In: Akazawa T, Aikens CM (eds) Prehistoric hunter gatherers in Japan, vol Bull No. 27. University of Tokyo, Tokyo, pp 199–215
Redd AJ, Agellon AB, Kearney VA, Contreras VA, Karafet T, Park H, de Knijff P, Butler JM, Hammer MF (2002a) Forensic value of 14 novel STRs on the human Y chromosome. Forensic Sci Int 130:97–111
Redd AJ, Roberts-Thomson J, Karafet T, Bamshad M, Jorde LB, Naidu JM, Walsh B, Hammer MF (2002b) Gene flow from the Indian subcontinent to Australia: evidence from the Y chromosome. Curr Biol 12:673–677
Rohlf FJ (1998) NTSYS-pc: numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system. Sekauket, NY
Ruofu D, Yip VF (1993) Ethnic groups in China. Science Press, Beijing
Santos FR, Pandya A, Kayser M, Mitchell RJ, Liu A, Singh L, Destro-Bisol G, Novelletto A, Qamar R, Mehdi SQ, Adhikari R, de Knijff P, Tyler-Smith C (2000) A polymorphic L1 retroposon insertion in the centromere of the human Y chromosome. Hum Mol Genet 9:421–430
Schneider S, Roessli D, Excoffier L (2000) Arlequin: a software for population genetic analysis. release 1.1, Geneva
Sokal RR, Thomson BA (1998) Spatial genetic structure of human populations in Japan. Hum Biol 70:1–22
Stumpf MP, Goldstein DB (2001) Genealogical and evolutionary inference with the human Y chromosome. Science 291:1738–1742
Su B, Xiao J, Underhill P, Deka R, Zhang W, Akey J, Huang W, Shen D, Lu D, Luo J, Chu J, Tan J, Shen P, Davis R, Cavalli-Sforza L, Chakraborty R, Xiong M, Du R, Oefner P, Chen Z, Jin L (1999) Y-Chromosome evidence for a northward migration of modern humans into Eastern Asia during the last Ice Age. Am J Hum Genet 65:1718–1724
Su B, Xiao C, Deka R, Seielstad MT, Kangwanpong D, Xiao J, Lu D, Underhill P, Cavalli-Sforza L, Chakraborty R, Jin L (2000) Y chromosome haplotypes reveal prehistorical migrations to the Himalayas. Hum Genet 107:582–590
Suzuki H (1981) Racial history of the Japanese. In: Schwidetzky I (ed) Rassengeschichte der Menschheit, 8. Lieferung. Oldenbourg, Munich, pp 7–69
Tajima A, Pan IH, Fucharoen G, Fucharoen S, Matsuo M, Tokunaga K, Juji T, Hayami M, Omoto K, Horai S (2002) Three major lineages of Asian Y chromosomes: implications for the peopling of east and southeast Asia. Hum Genet 110:80–88
Tajima A, Hayami M, Tokunaga K, Juji T, Matsuo M, Marzuki S, Omoto K, Horai S (2004) Genetic origins of the Ainu inferred from combined DNA analyses of maternal and paternal lineages. J Hum Genet 49:187–193
Takamiya H (2002) Peopling of Western Japan, focusing on Kyushu, Shikoku, and Ryukyu Archipelago. Radiocarbon 44:495–502
Tanaka M, Cabrera VM, Gonzalez AM, Larruga JM, Takeyasu T, Fuku N, Guo LJ, et al. (2004) Mitochondrial genome variation in eastern Asia and the peopling of Japan. Genome Res 14:1832–1850
Thangaraj K, Singh L, Reddy AG, Rao VR, Sehgal SC, Underhill PA, Pierson M, Frame IG, Hagelberg E (2003) Genetic affinities of the Andaman Islanders, a vanishing human population. Curr Biol 13:86–93
Turner CG (1976) Dental evidence on the origins of the Ainu and Japanese. Science 193:911–913
Turner CG (1990) Major features of sundadonty and sinodonty, including suggestions about East Asian microevolution, population history and late Pleistocene relationships with Australian aboriginals. Am J Phys Anthropol 82:295–317
Underhill PA, Shen P, Lin AA, Jin L, Passarino G, Yang WH, Kauffman E, Bonne-Tamir B, Bertranpetit J, Francalacci P, Ibrahim M, Jenkins T, Kidd JR, Mehdi SQ, Seielstad MT, Wells RS, Piazza A, Davis RW, Feldman MW, Cavalli-Sforza LL, Oefner PJ (2000) Y chromosome sequence variation and the history of human populations. Nat Genet 26:358–361
Wen B, Xie X, Gao S, Li H, Shi H, Song X, Qian T, Xiao C, Jin J, Su B, Lu D, Chakraborty R, Jin L (2004) Analyses of genetic structure of Tibeto-Burman populations reveals sex-biased admixture in southern Tibeto-Burmans. Am J Hum Genet 74:856–865
Wilder JA, Mobasher Z, Hammer MF (2004) Genetic evidence for unequal effective population sizes of human females and males. Mol Biol Evol 21:2047–2057
Wilson IJ, Balding DJ (1998) Genealogical inference from microsatellite data. Genetics 150:499–510
YCC (2002) A nomenclature system for the tree of Y chromosomal binary haplogroups. Genome Res 12:339–348
Zhivotovsky LA, Underhill PA, Cinnioglu C, Kayser M, Morar B, Kivisild T, Scozzari R, Cruciani F, Destro-Bisol G, Spedini G, Chambers GK, Herrera RJ, Yong KK, Gresham D, Tournev I, Feldman MW, Kalaydjieva L (2004) The effective mutation rate at Y chromosome short tandem repeats, with application to human population-divergence time. Am J Hum Genet 74:50–61
Acknowledgements
We thank Ji Park and Alan Redd for technical assistance and data analysis, and Elizabeth Wood for comments on earlier versions of the manuscript. This research was supported by NSF grant OPP-9806759 to M.F.H.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dedicated to the memory of Satoshi Horai
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hammer, M.F., Karafet, T.M., Park, H. et al. Dual origins of the Japanese: common ground for hunter-gatherer and farmer Y chromosomes. J Hum Genet 51, 47–58 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10038-005-0322-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10038-005-0322-0
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
An update and frequency distribution of Y chromosome haplogroups in modern Japanese males
Journal of Human Genetics (2024)
-
Y chromosome analysis for common surnames in the Japanese male population
Journal of Human Genetics (2021)
-
Origin and Spread of the ALDH2 Glu504Lys Allele
Phenomics (2021)
-
Origin of ethnic groups, linguistic families, and civilizations in China viewed from the Y chromosome
Molecular Genetics and Genomics (2021)
-
Population genomics of East Asian ethnic groups
Hereditas (2020)