Abstract
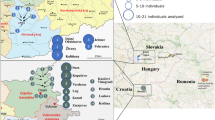
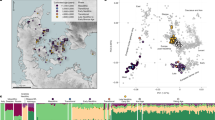
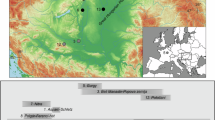
The area between the Dniester and the eastern Carpathian mountain range is at a geographical crossroads between eastern Europe and the Balkans. Little is known about the genetics of the population of this region. We performed an analysis of 12 binary autosomal markers in samples from six Dniester–Carpathian populations: two Moldavian, one Romanian, one Ukrainian and two Gagauz populations. The results were compared with gene frequency data from culturally and linguistically related populations from Southeast Europe and Central Asia. Small genetic differences were found among southeastern European populations (in particular those of the Dniester–Carpathian region). The observed homogeneity suggests either a very recent common ancestry of all southeastern European populations or strong gene flow between them. Despite this low level of differentiation, tree reconstruction and principle component analyses allowed a distinction between Balkan–Carpathian (Macedonians, Romanians, Moldavians, Ukrainians and Gagauzes) and eastern Mediterranean (Turks, Greeks and Albanians) population groups. The genetic affinities among Dniester–Carpathian and southeastern European populations do not reflect their linguistic relationships. The results indicate that the ethnic and genetic differentiations occurred in these regions to a considerable extent independently of each other. In particular, Gagauzes, a Turkic-speaking population, show closer affinities to their geographical neighbors than to other Turkic populations.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Alexeev VP (1974) Geography of human races (in Russian). Nauka, Moscow
Antunez-de-Mayolo G, Antunez-de-Mayolo A, Antunez-de-Mayolo P, Papiha PS, Hammer M, Yunis JJ, Yunis EJ, Damodaran Ch, Martinez de Pancorbo M, Caeiro HL, Puzyrev VP, Herrera RJ (2002) Phylogenetics of worldwide human populations as determined by polymorphic Alu insertions. Electrophoresis 23:3346–3356
Arcot SS, Fontius JJ, Deininger PL, Batzer MA (1995a) Identification and analysis of a “young” polymorphic Alu element. Biochim Biophys Acta 1263:99–02
Arcot SS, Wang Z, Weber JL, Deininger PL, Batzer MA (1995b) Alu repeats: a source for the genesis of primate microsatellites. Genomics 29:136–144
Batzer MA, Arcot SS, Phinney JM, Alegria-Hartman M, Kass DH, Milligan SM, Kimpton C, Gill P, Hochmeister M, Ioannou PA, Herrera RJ, Boudreau DA, Scheer WD, Keats BJ, Deininger PL, Stoneking M (1996) Genetic variation of recent Alu insertions in human populations. J Mol Evol 42:22–29
Calafell F, Underhill P, Tolun A, Angelicheva D, Kalaydjieva L (1996) From Asia to Europe: mitochondrial DNA sequence variability in Bulgarians and Turks. Ann Hum Genet 60:35–49
Cavalli-Sforza LL, Menozzi P, Piazza A (1994) The history and geography of human genes. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Cinnioğlu C, King R, Kivisild T, Kalfoglu E, Atasoy S, Cavalleri GL, Lillie AS, Roseman CC, Lin AA, Prince K, Oefner PJ, Shen P, Semino O, Cavalli-Sforza LL, Underhill PA (2004) Excavating Y chromosome haplotype strata in Anatolia. Hum Genet 114:127–148
Comas D, Calafell F, Benchemsi N, Helal A, Lefranc G, Stoneking M, Batzer MA, Bertranpetit J, Sajantila A (2000) Alu insertion polymorphisms in NW Africa and the Iberian Peninsula: evidence for a strong genetic boundary through the Gibraltar Straits. Hum Genet 107:312–319
Comas D, Schmid H, Braeuer S, Flaiz C, Busquets A, Calafell F, Bertranpetit J, Scheil H-G, Huckenbeck W, Efremovska L, Schmidt HD (2004) Alu insertion polymorphisms in the Balkans and the origins of the Aromuns. Ann Hum Genet 68:120–127
Dergachev VA (1999) The particularities of the cultural development of the region between the Carpathians and Dniester (in Russian). Stratum plus 2:169–221
Excoffier L, Smouse P, Quattro J (1992) Analysis of molecular variance inferred from metric distances among DNA haplotypes: application to human mitochondrial DNA restriction data. Genetics 131:479–491
Felsenstein J (1993) PHYLIP, version 3.5. University of Washington Press, Seattle
Guboglo MN (1967) The ethnic affiliation of the Gagauzes (in Russian). Sov Etnograf 3:160–167
Guo S, Thompson E (1992) Performing the exact test of Hardy–Weinberg proportion for multiple alleles. Biometrics 48:361–372
Jorde LB, Wooding SP (2004) Genetic variation, classification and ‘race’. Nat Genet 36:28–33
Khitrinskaya IYu, Stepanov VA, Puzyrev VP, Spiridonova MG, Voevoda MI (2003) Genetic differentiation of the population of Central Asia inferred from autosomal markers. Russ J Genet 39:1175–1183
Kutuev I, Khusainova R, Karunas A, Yunusbayev B, Fedorova S, Lebedev Y, Hunsmann G, Khusnutdinova E (2006) From East to West: patterns of genetic diversity of populations living in four Eurasian regions. Hum Hered 61:1–9
Majumder PP, Roy B, Banerjee S, Chakraborty M, Dey B, Mukherjee N, Roy M, Thakurta PG, Sil SK (1999) Human-specific insertion/deletion polymorphisms in Indian populations and their possible evolutionary implications. Eur J Hum Genet 7:435–446
Malaspina P, Tsopanomichalou M, Duman T, Stefan M, Silvestri A, Rinaldi B, Garcia O, Giparaki M, Plata E, Kozlov AI, Barbujani G, Vernesi C, Papola F, Ciavarella G, Kovatchev D, Kerimova MG, Anagnou N, Gavrila L, Veneziano L, Akar N, Loutradis A, Michalodimitrakis EN, Terrenato L, Novelletto A (2001) A multistep process for the dispersal of a Y chromosomal lineage in the Mediterranean area. Ann Hum Genet 65:339–349
Miller SA, Dykes DD, Polesky HF (1988) A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res 16:1215
Nasidze I, Risch GM, Robichaux M, Sherry ST, Batzer MA, Stoneking M (2001) Alu insertion polymorphisms and the genetic structure of human populations from the Caucasus. Eur J Hum Genet 9:267–272
Nei M (1973) Analysis of gene diversity in subdivided populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 70:3321–3323
Nei M (1987) Molecular evolutionary genetics. Columbia University Press, New York
Renfrew C (1987) Archaeology and language: the puzzle of Indo-European origins. Cape, London
Romualdi C, Balding D, Nasidze IS, Risch G, Robichaux M, Sherry ST, Stoneking M, Batzer MA, Barbujani G (2002) Patterns of human diversity, within and among continents, inferred from biallelic DNA polymorphisms. Genome Res 12:602–612
Schneider S, Roessli D, Excoffier L (2000) Arlequin Ver 2000 A software for population genetics data analysis. Genetics and biometry laboratory. University of Geneva, Switzerland
Sitnikova T, Rzhetsky A, Nei M (1995) Interior-branch and bootstrap tests of phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 12:319–333
StatSoft (1995) STATISTICA for Windows [Computer program manual]. Tulsa, OK
Stoneking M, Fontius JJ, Clifford SL, Soodyall H, Arcot SS, Saha N, Jenkins T, Tahir MA, Deininger PL, Batzer MA (1997) Alu insertion polymorphisms and human evolution: evidence for a larger population size in Africa. Genome Res 7:1061–1071
Tishkoff SA, Kidd KK (2004) Implications of biogeography of human populations for ‘race’ and medicine. Nat Genet 36:21–27
Varsahr AM, Spitsyn VA, Bychkovskaya LS, Kravchuk OI (2001) To the research of the gene pool of the Gagauz population of Moldavia. Anthropol Anz 59:11–17
Varsahr AM, Dubova NA, Kutuyev IA (2003) Serological researches in the south of Moldavia in connection with the problem of the ethnogeny of the Gagauzes, the Moldavians and the Bulgarians. Anthropol Anz 61:395–411
Varsahr AM, Scheil H-G, Schmidt HD (2006) Blood group and serum protein polymorphisms in a population group of Moldavians. Anthropol Anz 64:51–58
Velicanova MS (1975) Paleoanthropology of the Dniester–Pruth interfluvial (in Russian). Nauka, Moscow
Xiao FX, Yang JF, Cassiman JJ, Decorte R (2002) Diversity at eight polymorphic Alu insertion loci in Chinese populations shows evidence for European admixture in an ethnic minority population from northwest China. Hum Biol 74:555–568
Zhivotovsky LA (1991) Population Biometrics (in Russian). Nauka, Moscow
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to all donors for providing blood samples and to the people who contributed to their collection. We also thank B. Joffe, B. Nürnberger and the anonymous reviewers for helpful comments and suggestions. E.W. was supported by FCI and DFG, W. S. by the Volkswagen-Foundation and DFG, and A.V. by the DAAD. V.S. and M.S. were supported by the Russian Federation for basic research (grant 03-04-4902) and by a grant from the President of the Russian Federation (grant MD-88.2003.04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Varzari, A., Stephan, W., Stepanov, V. et al. Population history of the Dniester–Carpathians: evidence from Alu markers. J Hum Genet 52, 308–316 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10038-007-0113-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10038-007-0113-x
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The Carpathian range represents a weak genetic barrier in South-East Europe
BMC Genetics (2014)