Abstract
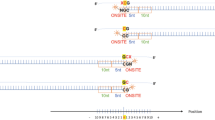
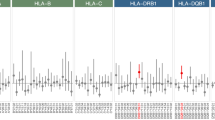
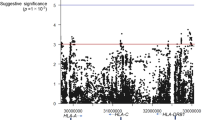
Essential hypersomnia (EHS) exhibits excessive daytime sleepiness without cataplexy and is associated with the HLA-DRB1*1501-DQB1*0602 haplotype, similar to narcolepsy with cataplexy. Single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs1154155 located in the T-cell receptor α (TCRA) locus has been recently identified as a novel genetic marker of susceptibility for narcolepsy with cataplexy. We investigated whether the SNP was associated with EHS in the Japanese population. We found a significant association with EHS patients possessing the HLA-DRB1*1501-DQB1*0602 haplotype, compared with HLA-matched healthy individuals (Pallele=0.008; Ppositivity=5 × 10−4), whereas no significant association was observed for EHS patients without this haplotype. Thus, TCRA is a plausible candidate for susceptibility to EHS patients positive for the HLA-DRB1*1501-DQB1*0602 haplotype.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Juji, T., Satake, M., Honda, Y. & Doi, Y. HLA antigens in Japanese patients with narcolepsy. All the patients were DR2 positive. Tissue Antigens 24, 316–319 (1984).
Mignot, E., Lin, L., Rogers, W., Honda, Y., Qiu, X., Lin, X. et al. Complex HLA-DR and -DQ interactions confer risk of narcolepsy-cataplexy in three ethnic groups. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 68, 686–699 (2001).
Langdon, N., Welsh, K. I., van Dam, M., Vaughan, R. W. & Parkes, D. Genetic markers in narcolepsy. Lancet 2, 1178–1180 (1984).
Hallmayer, J., Faraco, J., Lin, L., Hesselson, S., Winkelmann, J., Kawashima, M. et al. Narcolepsy is strongly associated with the T-cell receptor alpha locus. Nat. Genet. 41, 708–711 (2009).
Anderson, K. N., Pilsworth, S., Sharples, L. D., Smith, I. E. & Shneerson, J. M. Idiopathic hypersomnia: a study of 77 cases. Sleep 30, 1274–1281 (2007).
Mignot, E., Lammers, G. J., Ripley, B., Okun, M., Nevsimalova, S., Overeem, S. et al. The role of cerebrospinal fluid hypocretin measurement in the diagnosis of narcolepsy and other hypersomnias. Arch. Neurol. 59, 1553–1562 (2002).
Miyagawa, T., Honda, M., Kawashima, M., Shimada, M., Tanaka, S., Honda, Y. et al. Polymorphism located between CPT1B and CHKB, and HLA-DRB1*1501-DQB1*0602 haplotype confer susceptibility to CNS hypersomnias (essential hypersomnia). PLoS One 4, e5394 (2009).
Honda, Y., Juji, T., Matsuki, K., Naohara, T., Satake, M., Inoko, H. et al. HLA-DR2 and Dw2 in narcolepsy and in other disorders of excessive somnolence without cataplexy. Sleep 9, 133–142 (1986).
Honda, Y., Takahashi, Y., Honda, M., Watanabe, Y., Sato, T., Miki, T. et al. Genetic Aspects of Narcolepsy. Sleep and Sleep Disorders: From Molecule to Behavior. (Academic Press, New York, 1998).
Komada, Y., Inoue, Y., Mukai, J., Shirakawa, S., Takahashi, K. & Honda, Y. Difference in the characteristics of subjective and objective sleepiness between narcolepsy and essential hypersomnia. Psychiatry. Clin. Neurosci. 59, 194–199 (2005).
Miyagawa, T., Kawashima, M., Nishida, N., Ohashi, J., Kimura, R., Fujimoto, A. et al. Variant between CPT1B and CHKB associated with susceptibility to narcolepsy. Nat. Genet. 40, 1324–1328 (2008).
Nishino, S., Ripley, B., Overeem, S., Lammers, G. J. & Mignot, E. Hypocretin (orexin) deficiency in human narcolepsy. Lancet 355, 39–40 (2000).
Kanbayashi, T., Inoue, Y., Chiba, S., Aizawa, R., Saito, Y., Tsukamoto, H. et al. CSF hypocretin-1 (orexin-A) concentrations in narcolepsy with and without cataplexy and idiopathic hypersomnia. J. Sleep. Res. 11, 91–93 (2002).
Acknowledgements
We thank all participants in this study. This study was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Priority Areas ‘Comprehensive Genomics’ and ‘Applied Genomics’ from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan and by a Grant-in-Aid for JSPS fellows, Astellas Foundation for Research on Metabolic Disorders and Takeda Science Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miyagawa, T., Honda, M., Kawashima, M. et al. Polymorphism located in TCRA locus confers susceptibility to essential hypersomnia with HLA-DRB1*1501-DQB1*0602 haplotype. J Hum Genet 55, 63–65 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2009.118
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2009.118
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Polygenic risk score analysis revealed shared genetic background in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and narcolepsy
Translational Psychiatry (2020)
-
A variant at 9q34.11 is associated with HLA-DQB1*06:02 negative essential hypersomnia
Journal of Human Genetics (2018)
-
Narcolepsy Type 1 as an Autoimmune Disorder: Evidence, and Implications for Pharmacological Treatment
CNS Drugs (2017)
-
Genome-wide association analysis identifies genetic variations in subjects with myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome
Translational Psychiatry (2016)
-
Evaluation of polygenic risks for narcolepsy and essential hypersomnia
Journal of Human Genetics (2016)