Abstract
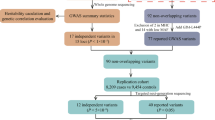
Panic disorder (PD) is an anxiety disorder characterized by recurrent and unexpected panic attacks, subsequent worry and phobic avoidance. Although a number of association and linkage studies have been conducted, no gene has been identified as a susceptibility locus. We previously conducted a genome-wide association analysis of PD in 200 Japanese patients and the same number of controls, using a 500 K single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) chip. In this study, we report a replication analysis of PD using the DigTag2 assay. The second stage sample consisted of 558 Japanese patients and 566 controls. Thirty-two markers were tested in a replication sample. As a result, no significant association was found after correction for multiple testing. However, the difference was observed at the nominal allele P-value <0.05 for two SNPs (rs6733840 and rs132617). We also conducted haplotype analyses of SNPs in the APOL3 and CLU genes. Our results failed to show any significant association with PD in these genes. Further studies on these variants with a larger sample size may be worth testing to confirm the results.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Eaton, W. W., Kessler, R. C., Wittchen, H. U. & Magee, W. J. Panic and panic disorder in the United States. Am. J. Psychiatry 151, 413–420 (1994).
Weissman, M. M., Bland, R. C., Canino, G. J., Faravelli, C., Greenwald, S., Hwu, H. G. et al. The cross-national epidemiology of panic disorder. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 54, 305–309 (1997).
Crowe, R. R., Noyes, R., Pauls, D. L. & Slymen, D. A family study of panic disorder. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 40, 1065–1069 (1983).
Goldstein, R. B., Wickramaratne, P. J., Horwath, E. & Weissman, M. M. Familial aggregation and phenomenology of ‘early’-onset (at or before age 20 years) panic disorder. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 54, 271–278 (1997).
Hettema, J. M., Neale, M. C. & Kendler, K. S. A review and meta-analysis of the genetic epidemiology of anxiety disorders. Am. J. Psychiatry 158, 1568–1578 (2001).
Kendler, K. S., Neale, M. C., Kessler, R. C., Heath, A. C. & Eaves, L. J. Major depression and generalized anxiety disorder. Same genes, (partly) different environments? Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 49, 716–722 (1992).
Torgersen, S. Genetics of neurosis. The effects of sampling variation upon the twin concordance ratio. Br. J. Psychiatry 142, 126–132 (1983).
Gelernter, J., Bonvicini, K., Page, G., Woods, S. W., Goddard, A. W., Kruger, S. et al. Linkage genome scan for loci predisposing to panic disorder or agoraphobia. Am. J. Med. Genet. 105, 548–557 (2001).
Fyer, A. J., Hamilton, S. P., Durner, M., Haghighi, F., Heiman, G. A., Costa, R. et al. A third-pass genome scan in panic disorder: evidence for multiple susceptibility loci. Biol. Psychiatry 60, 388–401 (2006).
Knowles, J. A., Fyer, A. J., Vieland, V. J., Weissman, M. M., Hodge, S. E., Heiman, G. A. et al. Results of a genome-wide genetic screen for panic disorder. Am. J. Med. Genet. 81, 139–147 (1998).
Crowe, R. R., Goedken, R., Samuelson, S., Wilson, R., Nelson, J., Noyes, Jr. R. et al. Genomewide survey of panic disorder. Am. J. Med. Genet. 105, 105–109 (2001).
Thorgeirsson, T. E., Oskarsson, H., Desnica, N., Kostic, J. P., Stefansson, J. G., Kolbeinsson, H. et al. Anxiety with panic disorder linked to chromosome 9q in Iceland. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 72, 1221–1230 (2003).
Smoller, J. W., Acierno, J. S. Jr., Rosenbaum, J. F., Biederman, J., Pollack, M. H., Meminger, S. et al. Targeted genome screen of panic disorder and anxiety disorder proneness using homology to murine QTL regions. Am. J. Med. Genet. 105, 195–206 (2001).
Weissman, M. M., Fyer, A. J., Haghighi, F., Heiman, G., Deng, Z., Hen, R. et al. Potential panic disorder syndrome: clinical and genetic linkage evidence. Am. J. Med. Genet. 96, 24–35 (2000).
Hamilton, S. P., Fyer, A. J., Durner, M., Heiman, G. A., Baisre de Leon, A., Hodge, S. E. et al. Further genetic evidence for a panic disorder syndrome mapping to chromosome 13q. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 2550–2555 (2003).
Rothe, C., Gutknecht, L., Freitag, C., Tauber, R., Mossner, R., Franke, P. et al. Association of a functional 1019C>G 5-HT1A receptor gene polymorphism with panic disorder with agoraphobia. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 7, 189–192 (2004).
Inada, Y., Yoneda, H., Koh, J., Sakai, J., Himei, A., Kinoshita, Y. et al. Positive association between panic disorder and polymorphism of the serotonin 2A receptor gene. Psychiatry Res. 118, 25–31 (2003).
Rothe, C., Koszycki, D., Bradwejn, J., King, N., De Luca, V., Shaikh, S. et al. Association study of serotonin-2A receptor gene polymorphism and panic disorder in patients from Canada and Germany. Neurosci. Lett. 363, 276–279 (2004).
Ebihara, M., Ohba, H., Hattori, E., Yamada, K. & Yoshikawa, T. Transcriptional activities of cholecystokinin promoter haplotypes and their relevance to panic disorder susceptibility. Am. J. Med. Genet. 118, 32–35 (2003).
Deckert, J., Nothen, M. M., Franke, P., Delmo, C., Fritze, J., Knapp, M. et al. Systematic mutation screening and association study of the A1 and A2a adenosine receptor genes in panic disorder suggest a contribution of the A2a gene to the development of disease. Mol. Psychiatry 3, 81–85 (1998).
Deckert, J., Catalano, M., Syagailo, Y. V., Bosi, M., Okladnova, O., Di Bella, D. et al. Excess of high activity monoamine oxidase A gene promoter alleles in female patients with panic disorder. Hum. Mol. Genet. 8, 621–624 (1999).
Hamilton, S. P., Slager, S. L., Heiman, G. A., Deng, Z., Haghighi, F., Klein, D. F. et al. Evidence for a susceptibility locus for panic disorder near the catechol-O-methyltransferase gene on chromosome 22. Biol. Psychiatry 51, 591–601 (2002).
Woo, J. M., Yoon, K. S., Choi, Y. H., Oh, K. S., Lee, Y. S. & Yu, B. H. The association between panic disorder and the L/L genotype of catechol-O-methyltransferase. J. Psychiatr. Res. 38, 365–370 (2004).
Otowa, T., Yoshida, E., Sugaya, N., Yasuda, S., Nishimura, Y., Inoue, K. et al. Genome-wide association study of panic disorder in the Japanese population. J. Hum. Genet. 54, 122–126 (2009).
American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders 4th ed. (American Psychiatric Association, Washington DC, 1994).
Sheehan, D. V., Lecrubier, Y., Sheehan, K. H., Amorim, P., Janavs, J., Weiller, E. et al. The Mini-International Neuropsychiatric Interview (MINI): the development and validation of a structured diagnostic psychiatric interview for DSM-IV and ICD-10. J. Clin. Psychiatry 59 (Suppl 20), 22–33; Quiz 34–57 (1998).
Miyagawa, T., Nishida, N., Ohashi, J., Kimura, R., Fujimoto, A., Kawashima, M. et al. Appropriate data cleaning methods for genome-wide association study. J. Hum. Genet. 53, 886–893 (2008).
Nishida, N., Tanabe, T., Hashido, K., Hirayasu, K., Takasu, M., Suyama, A. et al. DigiTag assay for multiplex single nucleotide polymorphism typing with high success rate. Anal. Biochem. 346, 281–288 (2005).
Nishida, N., Tanabe, T., Takasu, M., Suyama, A. & Tokunaga, K. Further development of multiplex single nucleotide polymorphism typing method, the DigiTag2 assay. Anal. Biochem. 364, 78–85 (2007).
Purcell, S., Neal, B., Todd-Brown, K., Thomas, L., Ferreira, M. A., Bender, D. et al. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 81, 559–575 (2007).
Lewontin, R. C. The Interaction of Selection and Linkage. I. General Considerations; Heterotic Models. Genetics 49, 49–67 (1964).
Gabriel, S. B., Schaffner, S. F., Nguyen, H., Moore, J. M., Roy, J., Blumenstiel, B. et al. The structure of haplotype blocks in the human genome. Science 296, 2225–2229 (2002).
Barret, J. C., Fry, B., Maller, J. & Daly, M. J. Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 21, 263–265 (2005).
Ohashi, J., Yamamoto, S., Tsuchiya, N., Hatta, Y., Komata, T., Matsushita, M. et al. Comparison of statistical power between 2 * 2 allele frequency and allele positivity tables in case-control studies of complex disease genes. Ann. Hum. Genet. 65, 197–206 (2001).
Ohashi, J. & Tokunaga, K. The expected power of genome-wide linkage disequilibrium testing using single nucleotide polymorphism markers for detecting a low-frequency disease variant. Ann. Hum. Genet. 66, 297–306 (2002).
Vanhollebeke, B. & Pays, E. The function of apolipoproteins L. Cell Mol. Life. Sci. 63, 1937–1944 (2006).
Mimmack, M. L., Ryan, M., Baba, H., Navarro-Ruiz, J., Iritani, S., Faull, R. L. et al. Gene expression analysis in schizophrenia: reproducible up-regulation of several members of the apolipoprotein L family located in a high-susceptibility locus for schizophrenia on chromosome 22. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 99, 4680–4685 (2002).
McGhee, K. A., Morris, D. W., Schwaiger, S., Nangle, J. M., Donohoe, G., Clarke, S. et al. Investigation of the apolipoprotein-L (APOL) gene family and schizophrenia using a novel DNA pooling strategy for public database SNPs. Schizophr. Res. 76, 231–238 (2005).
Jones, S. E. & Jomary, C. Clusterin. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 34, 427–431 (2002).
Danik, M., Chabot, J. G., Hassan-Gonzalez, D., Suh, M. & Quirion, R. Localization of sulfated glycoprotein-2/clusterin mRNA in the rat brain by in situ hybridization. J. Comp. Neurol. 334, 209–227 (1993).
DeMattos, R. B., Cirrito, J. R., Parsadanian, M., May, P. C., O'Dell, M. A., Taylor, J. W. et al. ApoE and clusterin cooperatively suppress Abeta levels and deposition: evidence that ApoE regulates extracellular Abeta metabolism in vivo. Neuron 41, 193–202 (2004).
Hayward, C., Taylor, C. B., Roth, W. T., King, R. l & Agras, W. S. Plasma lipid levels in patients with panic disorder or agoraphobia. Am. J. Psychiatry 146, 917–919 (1989).
Agargun, M. Y., Kara, H., Algun, E., Sekeroglu, R. & Trakcioglu, M. High cholesterol levels in patients with sleep panic. Biol. Psychiatry. 40, 1064–1065 (1996).
Hakkoum, D., Imhof, A., Vallet, P. G., Boze, H., Moulin, G., Charnay, Y. et al. Clusterin increases post-ischemic damages in organotypic hippocampal slice cultures. J. Neurochem. 106, 1791–1803 (2008).
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Priority Areas ‘Comprehensive Genomics’ and ‘Applied Genomics’ (no. 17019029) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan. We are grateful to Ms Yoshimi Ishibashi, Ms Yuko Ogasawara and Ms Kayoko Kato for excellent technical assistance. Most important, we thank the individuals who have participated in and contributed to this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Otowa, T., Tanii, H., Sugaya, N. et al. Replication of a genome-wide association study of panic disorder in a Japanese population. J Hum Genet 55, 91–96 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2009.127
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2009.127
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Genetic and epigenetic analyses of panic disorder in the post-GWAS era
Journal of Neural Transmission (2020)
-
Genetics of Anxiety Disorders
Current Psychiatry Reports (2019)
-
Candidate genes in panic disorder: meta-analyses of 23 common variants in major anxiogenic pathways
Molecular Psychiatry (2016)
-
Translational Approaches to Anxiety: Focus on Genetics, Fear Extinction and Brain Imaging
Current Psychiatry Reports (2013)
-
Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies for panic disorder in the Japanese population
Translational Psychiatry (2012)