Abstract
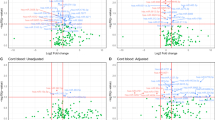
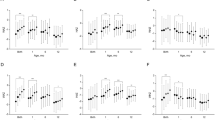
To assess whether adiponectin gene (ADIPOQ) polymorphism is associated with intrauterine fetal growth and cord blood adiponectin, we investigated eight single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs; rs182052, rs710445, rs16861205, rs12495941, rs1501299, rs3774261, rs2082940 and rs266729) in ADIPOQ and birth weight and cord blood adiponectin in 526 healthy neonates. We found that the neonates carrying the G allele of rs266729 had a significantly greater birth weight s.d. score than those homozygous for the C allele (CC: −0.06±0.75 versus CG: 0.20±0.64 versus GG: 0.07±0.78; P=1.65 × 10−3, adjusted P=9.90 × 10−3). However, this difference was not significant after adjustment for cord blood adiponectin (P=0.04, adjusted P=0.26). The rs266729 SNP was strongly associated with cord blood adiponectin; neonates with rs266729 GG had the highest adiponectin (CC: 34.1±20.2 versus CG: 44.3±26.1 versus GG: 54.1±36.7 μg ml–1, P=2.80 × 10−9, adjusted P=1.68 × 10−8). This association remained after adjustment for birth weight s.d. score (P=6.63 × 10−8, adjusted P=3.98 × 10−7). Our results suggest that the influence of the rs266729 SNP in ADIPOQ on birth weight may be dependent on circulating adiponectin.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Arita, Y., Kihara, S., Ouchi, N., Takahashi, M., Maeda, K., Miyagawa, J. et al. Paradoxical decrease of an adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in obesity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 257, 79–83 (1999).
Weyer, C., Funahashi, T., Tanaka, S., Hotta, K., Matsuzawa, Y., Pratley, R. E. et al. Hypoadiponectinemia in obesity and type 2 diabetes: close association with insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 86, 1930–1935 (2001).
Maeda, N., Takahashi, M., Funahashi, T., Kihara, S., Nishizawa, H., Kishida, K. et al. PPARgamma ligands increase expression and plasma concentrations of adiponectin, an adipose-derived protein. Diabetes 50, 2094–2099 (2001).
Yamauchi, T., Kamon, J., Waki, H., Terauchi, Y., Kubota, N., Hara, K. et al. The fat-derived hormone adiponectin reverses insulin resistance associated with both lipoatrophy and obesity. Nat. Med. 7, 941–946 (2001).
Schondorf, T., Maiworm, A., Emmison, N., Forst, T. & Pfutzner, A. Biological background and role of adiponectin as marker for insulin resistance and cardiovascular risk. Clin. Lab. 51, 489–494 (2005).
Gluckman, P. D., Sizonenko, S. V. & Bassett, N. S. The transition from fetus to neonate--an endocrine perspective. Acta Paediatr. 88 (Suppl), 7–11 (1999).
Fowden, A. L. The role of insulin in fetal growth. Early Hum. Dev. 29, 177–181 (1992).
Sivan, E., Mazaki-Tovi, S., Pariente, C., Efraty, Y., Schiff, E., Hemi, R. et al. Adiponectin in human cord blood: relation to fetal birth weight and gender. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 88, 5656–5660 (2003).
Chan, T. F., Yuan, S. S., Chen, H. S., Guu, C. F., Wu, L. C., Yeh, Y. T. et al. Correlations between umbilical and maternal serum adiponectin levels and neonatal birthweights. Acta. Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 83, 165–169 (2004).
Tsai, P. J., Yu, C. H., Hsu, S. P., Lee, Y. H., Chiou, C. H., Hsu, Y. W. et al. Cord plasma concentrations of adiponectin and leptin in healthy term neonates: positive correlation with birthweight and neonatal adiposity. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf). 61, 88–93 (2004).
Kamoda, T., Saitoh, H., Saito, M., Sugiura, M. & Matsui, A. Serum adiponectin concentrations in newborn infants in early postnatal life. Pediatr. Res. 56, 690–693 (2004).
Lindsay, R. S., Walker, J. D., Havel, P. J., Hamilton, B. A., Calder, A. A. & Johnstone, F. D. Adiponectin is present in cord blood but is unrelated to birth weight. Diabetes Care. 26, 2244–2249 (2003).
Barker, D. J., Winter, P. D., Osmond, C., Margetts, B. & Simmonds, S. J. Weight in infancy and death from ischaemic heart disease. Lancet 2, 577–580 (1989).
Barker, D. J., Hales, C. N., Fall, C. H., Osmond, C., Phipps, K. & Clark, P. M. Type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus, hypertension and hyperlipidaemia (syndrome X): relation to reduced fetal growth. Diabetologia 36, 62–67 (1993).
Vasseur, F., Helbecque, N., Dina, C., Lobbens, S., Delannoy, V., Gaget, S. et al. Single-nucleotide polymorphism haplotypes in the both proximal promoter and exon 3 of the APM1 gene modulate adipocyte-secreted adiponectin hormone levels and contribute to the genetic risk for type 2 diabetes in French Caucasians. Hum. Mol. Genet. 11, 2607–2614 (2002).
Hara, K., Boutin, P., Mori, Y., Tobe, K., Dina, C., Yasuda, K. et al. Genetic variation in the gene encoding adiponectin is associated with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes in the Japanese population. Diabetes 51, 536–540 (2002).
Richardson, D. K., Schneider, J., Fourcaudot, M. J., Rodriguez, L. M., Arya, R., Dyer, T. D. et al. Association between variants in the genes for adiponectin and its receptors with insulin resistance syndrome (IRS)-related phenotypes in Mexican Americans. Diabetologia 49, 2317–2328 (2006).
Bouatia-Naji, N., Meyre, D., Lobbens, S., Seron, K., Fumeron, F., Balkau, B. et al. ACDC/adiponectin polymorphisms are associated with severe childhood and adult obesity. Diabetes 55, 545–550 (2006).
Nishida, H., Sakanoue, M., Kurachi, K., Asada, M., Kubo, S. & Funakawa, H. Fetal growth curves of Japanese. Acta Pediatr. Japonica 20, 90–97 (in Japanese) (1984).
De Bakker, P. I., Yelensky, R., Pe′er, I., Gabriel, S. B., Daly, M. J. & Altshuler, D. Efficiency and power in genetic association studies. Nat. Genet. 37, 1217–1223 (2005).
Barrett, J. C., Fry, B., Maller, J. & Daly, M. J. Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 21, 263–265 (2005).
Rothenbacher, D., Nieters, A., Weyermann, M. & Brenner, H. Adiponectin polymorphisms, cord blood levels of adiponectin, and body composition. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 120, 469–470 (2007).
Gonzalez, J. R., Armengol, L., Sole, X., Guino, E., Mercader, J. M., Estivill, X. et al. SNPassoc: an R package to perform whole genome association studies. Bioinformatics 23, 644–645 (2007).
Li, J. & Ji, L. Adjusting multiple testing in multilocus analyses using the eigenvalues of a correlation matrix. Heredity 95, 221–227 (2005).
Kajantie, E., Hytinantti, T., Hovi, P. & Andersson, S. Cord plasma adiponectin: a 20-fold rise between 24 weeks gestation and term. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 89, 4031–4036 (2004).
Mazaki-Tovi, S., Kanety, H., Pariente, C., Hemi, R., Efraty, Y., Schiff, E. et al. Determining the source of fetal adiponectin. J. Reprod. Med. 52, 774–778 (2007).
Inami, I., Okada, T., Fujita, H., Makimoto, M., Hosono, S., Minato, M. et al. Impact of serum adiponectin concentration on birth size and early postnatal growth. Pediatr. Res. 61, 604–606 (2007).
Kotani, Y., Yokota, I., Kitamura, S., Matsuda, J., Naito, E. & Kuroda, Y. Plasma adiponectin levels in newborns are higher than those in adults and positively correlated with birth weight. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf). 61, 418–423 (2004).
Mazaki-Tovi, S., Kanety, H., Pariente, C., Hemi, R., Yinon, Y., Wiser, A. et al. Adiponectin and leptin concentrations in dichorionic twins with discordant and concordant growth. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 94, 892–898 (2009).
Nemet, D., Wang, P., Funahashi, T., Matsuzawa, Y., Tanaka, S., Engelman, L. et al. Adipocytokines, body composition, and fitness in children. Pediatr. Res. 53, 148–152 (2003).
Yang, W. S., Lee, W. J., Funahashi, T., Tanaka, S., Matsuzawa, Y., Chao, C. L. et al. Weight reduction increases plasma levels of an adipose-derived anti-inflammatory protein, adiponectin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 86, 3815–3819 (2001).
Korner, A., Wabitsch, M., Seidel, B., Fischer-Posovszky, P., Berthold, A., Stumvoll, M. et al. Adiponectin expression in humans is dependent on differentiation of adipocytes and down-regulated by humoral serum components of high molecular weight. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 337, 540–550 (2005).
Enzi, G., Zanardo, V., Caretta, F., Inelmen, E. M. & Rubaltelli, F. Intrauterine growth and adipose tissue development. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 34, 1785–1790 (1981).
Sun, H., Gong, Z. C., Yin, J. Y., Liu, H. L., Liu, Y. Z., Guo, Z. W. et al. The association of adiponectin allele 45T/G and -11377C/G polymorphisms with Type 2 diabetes and rosiglitazone response in Chinese patients. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 65, 917–926 (2008).
Gong, M., Long, J., Liu, Q. & Deng, H. C. Association of the ADIPOQ rs17360539 and rs266729 polymorphisms with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 325, 78–83 (2010).
Zhang, D., Ma, J., Brismar, K., Efendic, S. & Gu, H. F. A single nucleotide polymorphism alters the sequence of SP1 binding site in the adiponectin promoter region and is associated with diabetic nephropathy among type 1 diabetic patients in the Genetics of Kidneys in Diabetes Study. J. Diabetes Complications 23, 265–272 (2009).
Yang, M., Qiu, C. C., Chen, W., Xu, L. L., Yu, M. & Xiang, H. D. Identification of a regulatory single nucleotide polymorphism in the adiponectin (APM1) gene associated with type 2 diabetes in Han nationality. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 21, 454–459 (2008).
Fu, Y., Luo, N., Klein, R. L. & Garvey, W. T. Adiponectin promotes adipocyte differentiation, insulin sensitivity, and lipid accumulation. J. Lipid Res. 46, 1369–1379 (2005).
Viengchareun, S., Zennaro, M. C., Pascual-Le Tallec, L. & Lombes, M. Brown adipocytes are novel sites of expression and regulation of adiponectin and resistin. FEBS Lett. 532, 345–350 (2002).
Bueno, A. C., Espineira, A. R., Fernandes-Rosa, F. L., De Souza, R. M., De Castro, M., Moreira, A. C. et al. Adiponectin: serum levels, promoter polymorphism, and associations with birth size and cardiometabolic outcome in young adults born large for gestational age. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 162, 53–60 (2010).
Populaire, C., Mori, Y., Dina, C., Vasseur, F., Vaxillaire, M., Kadowaki, T. et al. Does the −11377 promoter variant of APM1 gene contribute to the genetic risk for type 2 diabetes mellitus in Japanese families? Diabetologia 46, 443–445 (2003).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saito, M., Kamoda, T., Nishimura, K. et al. Association of adiponectin polymorphism with cord blood adiponectin concentrations and intrauterine growth. J Hum Genet 57, 109–114 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2011.134
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2011.134
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
MIR146A and ADIPOQ genetic variants are associated with birth weight in relation to gestational age: a cohort study
Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics (2022)
-
A commentary on Association of adiponectin polymorphism with cord blood adiponectin concentrations and intrauterine growth
Journal of Human Genetics (2012)