Abstract
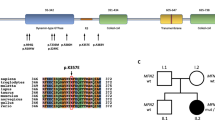
To study the genetic background of Japanese Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease (CMT) patients, we analyzed qualitative and quantitative changes in the disease-causing genes mainly by denaturing high performance liquid chromatography and multiplex ligation-dependent probe analysis in 227 patients with demyelinating CMT and 127 patients with axonal CMT. In demyelinating CMT, we identified 53 patients with PMP22 duplication, 10 patients with PMP22 mutations, 20 patients with MPZ mutations, eight patients with NEFL mutations, 19 patients with GJB1 mutations, one patient with EGR2 mutation, five patients with PRX mutations and no mutations in 111 patients. In axonal CMT, we found 14 patients with MFN2 mutations, one patient with GARS mutation, five patients with MPZ mutations, one patient with GDAP1 mutation, six patients with GJB1 mutations and no mutations in 100 patients. Most of the patients carrying PMP22, MPZ, NEFL, PRX and MFN2 mutations showed early onset, whereas half of the patients carrying PMP22 duplication and all patients with GJB1 or MPZ mutations showing axonal phenotype were adult onset. Our data showed that a low prevalence of PMP22 duplication and high frequency of an unknown cause are features of Japanese CMT. Low prevalence of PMP22 duplication is likely associated with the mild symptoms due to genetic and/or epigenetic modifying factors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Patel, P. I., Roa, B. B., Welcher, A. A., Schoener-Scott, R., Trask, B. J., Pentao, L. et al. The gene for the peripheral myelin protein PMP-22 is a candidate for Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A. Nat. Genet. 1, 159–165 (1992).
Bergoffen, J., Scherer, S. S., Wang, S., Scott, M. O., Bone, L. J., Paul, D. L. et al. Connexin mutations in X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Science 262, 2039–2042 (1993).
Hayasaka, K., Himoro, M., Sato, W., Takada, G., Uyemura, K., Shimizu, N. et al. Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy type 1B is associated with mutations of the myelin P0 gene. Nat. Genet. 5, 31–34 (1993).
Berger, P., Niemann, A. & Suter, U. Schwann cells and the pathogenesis of inherited motor and sensory neuropathies (Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease). Glia 54, 243–257 (2006).
Züchner, S. & Vance, J. M. Mechanisms of disease: a molecular genetic update on hereditary axonal neuropathies. Nat. Clin. Pract. Neurol. 2, 45–53 (2006).
Ikegami, T., Ikeda, H., Mitsui, T., Hayasaka, K. & Ishii, S. Novel mutation of the myelin Po gene in a pedigree with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1B. Am. J. Med. Genet. 71, 246–248 (1997b).
Ikegami, T., Ikeda, H., Aoyama, M., Matsuki, T., Imota, T., Fukuuchi, Y. et al. Novel mutations of the peripheral myelin protein 22 gene in two pedigrees with Dejerine-Sottas disease. Hum. Genet. 102, 294–298 (1998).
Ikegami, T., Lin, C., Kato, M., Itoh, A., Nonaka, I., Kurimura, M. et al. Four novel mutations of the connexin 32 gene in four Japanese families with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1. Am. J. Med. Genet. 80, 352–355 (1998).
Ikegami, T., Nicholson, G., Ikeda, H., Ishida, A., Johnston, H., Wise, G. et al. De novo mutation of the myelin Po gene in Dejerine-Sottas disease (hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy type III): two amino acid insertion after Asp 118. Hum. Mutat. Suppl. 1, S103–S105 (1998).
Numakura, C., Lin, C., Ikegami, T., Guldberg, P. & Hayasaka, K. Molecular analysis in Japanese patients with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease: DGGE analysis for PMP22, MPZ, and Cx32/GJB1 mutations. Hum Mutat 20, 392–398 (2002).
Numakura, C., Shirahata, E., Yamashita, S., Kanai, M., Kijima, K., Matsuki, T. et al. Screening of the early growth response 2 gene in Japanese patients with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1. J. Neurol. Sci. 210, 61–64 (2003).
Kijima, K., Numakura, C., Shirahata, E., Sawaishi, Y., Shimohata, M., Igarashi, S. et al. Periaxin mutation causes early-onset but slow-progressive Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. J. Hum. Genet. 49, 376–379 (2004).
Kijima, K., Numakura, C., Goto, T., Takahashi, T., Otagiri, T., Umetsu, K. et al. Small heat shock protein 27 mutation in a Japanese patient with distal hereditary motor neuropathy. J. Hum. Genet. 50, 473–476 (2005).
Kijima, K., Numakura, C., Izumino, H., Umetsu, K., Nezu, A., Shiiki, T. et al. Mitochondrial GTPase mitofusin 2 mutation in Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy type 2A. Hum. Genet. 116, 23–27 (2005).
Schouten, J. P., McElgunn, C. J., Waaijer, R., Zwijnenburg, D., Diepvens, F. & Pals, G. Relative quantification of 40 nucleic acid sequences by multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification. Nucleic Acids Res. 30, e57 (2002).
Ikegami, T., Ikeda, H., Chance, P. F., Kiyosawa, H., Yamamoto, M., Sobue, G. et al. Facilitated diagnosis of CMT1A duplication in chromosome 17p11.2-12: analysis with a CMT1A-REP repeat probe and photostimulated luminescence imaging. Hum. Mutat. 9, 563–566 (1997).
Mersiyanova, I. V., Perepelov, A. V., Polyakov, A. V., Sitnikov, V. F., Dadali, E. L., Oparin, R. B. et al. A new variant of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2 is probably the result of a mutation in the neurofilament-light gene. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 67, 37–46 (2000).
Baxter, R. V., Ben Othmane, K., Rochelle, J. M., Stajich, J. E., Hulette, C., Dew-Knight, S. et al. Ganglioside-induced differentiation-associated protein-1 is mutant in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 4A/8q21. Nat. Genet. 30, 21–22 (2002).
Slater, H., Bruno, D., Ren, H., La, P., Burgess, T., Hills, L. et al. Improved testing for CMT1A and HNPP using multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA) with rapid DNA preparations: comparison with the interphase FISH method. Hum. Mutat. 24, 164–171 (2004).
Mostacciuolo, M. L., Righetti, E., Zortea, M., Bosello, V., Schiavon, F., Vallo, L. et al. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type I and related demyelinating neuropathies: mutation analysis in a large cohort of Italian families. Hum. Mutat. 18, 32–41 (2001).
Boerkoel, C. F., Takashima, H., Garcia, C. A., Olney, R. K., Johnson, J., Berry, K. et al. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and related neuropathies: mutation distribution and genotype-phenotype correlation. Ann. Neurol. 51, 190–201 (2002).
Numakura, C., Lin, C., Oka, N., Akiguchi, I. & Hayasaka, K. Hemizygous mutation of the peripheral myelin protein 22 gene associated with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1. Ann. Neurol. 47, 101–103 (2000).
Abe, A., Nakamura, K., Kato, M., Numakura, C., Honma, T., Seiwa, C. et al. Compound heterozygous PMP22 deletion mutations causing severe Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1. J. Hum. Genet. 55, 771–773 (2010).
Lupski, J. R., de Oca-Luna, R. M., Slaugenhaupt, S., Pentao, L., Guzzetta, V., Trask, B. J. et al. DNA duplication associated with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A. Cell 66, 219–232 (1991).
Blair, I. P., Nash, J., Gordon, M. J. & Nicholson, G. A. Prevalence and origin of de novo duplications in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A: first report of a de novo duplication with a maternal origin. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 58, 472–476 (1996).
Ikegami, T., Akiba, K., Imaizumi, M., Yoshinari, M., Suzuki, H., Haginoya, K. et al. Severe vincristine neuropathy in an asymptomatic patient with Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy type 1A. J. Japan Pediat. Society 102, 1210–1213 (1998).
Abe, A., Numakura, C., Saito, K., Koide, H., Oka, N., Honma, A. et al. Neurofilament light chain polypeptide gene mutations in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease: nonsense mutation probably causes a recessive phenotype. J. Hum. Genet. 54, 94–97 (2009).
Waxman, S. G. Determinants of conduction velocity in myelinated nerve fibers. Muscle Nerve 3, 141–150 (1980).
Sakaguchi, T., Okada, M., Kitamura, T. & Kawasaki, K. Reduced diameter and conduction velocity of myelinated fibers in the sciatic nerve of a neurofilament-deficient mutant quail. Neurosci. Lett. 153, 65–68 (1993).
Yum, S. W., Zhang, J. X., Mo, K., Li, J. & Scherer, S. S. Neurofilaments are required for the maintenance of myelinated axons: analysis of the first homozygous mutation in NEFL associated with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Ann. Neurol. 66, S17 (2009).
Verhoeven, K., Claeys, K. G., Züchner, S., Schröder, J. M., Weis, J., Ceuterick, C. et al. MFN2 mutation distribution and genotype/phenotype correlation in Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 2. Brain 129, 2093–2102 (2006).
Calvo, J., Funalot, B., Ouvrier, R. A., Lazaro, L., Toutain, A., De Mas, P. et al. Genotype-phenotype correlations in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2 caused by mitofusin 2 mutations. Arch. Neurol. 66, 1511–1516 (2009).
Abe, A. & Hayasaka, K. The GARS gene is rarely mutated in Japanese patients with Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy. J. Hum. Genet. 54, 310–312 (2009).
Huang, J., Wu, X., Montenegro, G., Price, J., Wang, G., Vance, J. M. et al. Copy number variations are a rare cause of non-CMT1A Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. J. Neurol. 257, 735–741 (2010).
Nicholson, G. A., Magdelaine, C., Zhu, D., Grew, S., Ryan, M. M., Sturtz, F. et al. Severe early-onset axonal neuropathy with homozygous and compound heterozygous MFN2 mutations. Neurology 70, 1678–1681 (2008).
Lawson, V. H., Graham, B. V. & Flanigan, K. M. Clinical and electrophysiologic features of CMT2A with mutations in the mitofusin 2 gene. Neurology 65, 197–204 (2005).
Chung, K. W., Kim, S. B., Park, K. D., Choi, K. G., Lee, J. H., Eun, H. W. et al. Early onset severe and late-onset mild Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease with mitofusin 2 (MFN2) mutations. Brain 129, 2103–2118 (2006).
Shy, M. E., Jani, A., Krajewski, K., Grandis, M., Lewis, R. A., Li, J. et al. Phenotypic clustering in MPZ mutations. Brain 127, 371–384 (2004).
Garcia, C. A., Malamut, R. E., England, J. D., Parry, G. S., Liu, P. & Lupski, J. R. Clinical variability in two pairs of identical twins with the Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A duplication. Neurology 45, 2090–2093 (1995).
Szigeti, K., Wiszniewski, W., Saifi, G. M., Sherman, D. L., Sule, N., Adesina, A. M. et al. Functional, histopathologic and natural history study of neuropathy associated with EGR2 mutations. Neurogenetics 8, 257–262 (2007).
Ikegami, T., Nicholson, G., Ikeda, H., Ishida, A., Johnston, H., Wise, G. et al. A novel homozygous mutation of the myelin Po gene producing Dejerine-Sottas disease (hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy type III). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 222, 107–110 (1996).
Lin, C., Numakura, C., Ikegami, T., Shizuka, M., Shoji, M., Nicholson, G. et al. Deletion and nonsense mutations of the connexin 32 gene associated with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 188, 239–244 (1999).
Acknowledgements
We thank the patients and their families for their cooperation and Ms Kishikawa for the excellent assistance in molecular analyses. This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Science, Culture and Sports of Japan, and Grants-in-Aid from the Research Committee of Charcot–Marie–Tooth Disease and the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abe, A., Numakura, C., Kijima, K. et al. Molecular diagnosis and clinical onset of Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease in Japan. J Hum Genet 56, 364–368 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2011.20
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2011.20
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Clinical genetics of Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease
Journal of Human Genetics (2023)
-
PMP22 Gene–Associated Neuropathies: Phenotypic Spectrum in a Cohort from India
Journal of Molecular Neuroscience (2020)
-
Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease type 2A with an autosomal-recessive inheritance: the first report of an adult-onset disease
Journal of Human Genetics (2018)
-
Genotype–phenotype correlation and frequency of distribution in a cohort of Chinese Charcot–Marie–Tooth patients associated with GDAP1 mutations
Journal of Neurology (2018)
-
Severe phenotypes in a Charcot–Marie–Tooth 1A patient with PMP22 triplication
Journal of Human Genetics (2015)