Abstract
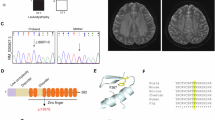
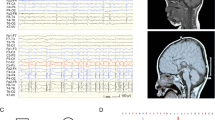
Vanishing white matter disease (VWM) is the first human hereditary disease known to be caused by defects in initiation of protein synthesis. Gene defects in each of the five subunits of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2B (eIF2B α–ɛ) are responsible for the disease, although the mechanism of the pathogenesis is not well understood. In our previous study, four novel eIF2Bɛ mutations were found in Chinese patients: p.Asp62Val, p.Cys335Ser, p.Asn376Asp and p.Ser610-Asp613del. Functional analysis was performed on these mutations and the recently reported p.Arg269X. Our data showed that all resulted in a decrease in the guanine nucleotide exchange (GEF) activity of the eIF2B complex. p.Arg269X and p.Ser610-Asp613del mutants displayed the lowest activity, followed by p.Cys335Ser, p.Asn376Asp and p.Asp62Val. p.Arg269X and p.Ser610-Asp613del could not produce stable eIF2Bɛ, leading to almost complete loss-of-function. No evidence was obtained for the three missense mutations in changes in eIF2Bɛ protein level or eIF2BɛSer540 phosphorylation, and disruption of holocomplex assembly, or binding to eIF2. All patients in our study had the classical phenotype. p.Asp62Val and p.Asn376Asp mutations caused only mildly decreased GEF activity, were probably responsible for relatively mild phenotype in cases of classical VWM.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Schiffmann, R. & van der Knaap, M. S. The latest on leukodystrophies. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 17, 187–192 (2004).
Vermeulen, G., Seidl, R., Mercimek-Mahmutoglu, S., Rotteveel, J. J., Scheper, G. C. & van der Knaap, M. S. Fright is a provoking factor in vanishing white matter disease. Ann. Neurol. 57, 560–563 (2005).
van der Knaap, M. S., Pronk, J. C. & Scheper, G. C. Vanishing white matter disease. Lancet. Neurol. 5, 413–423 (2006).
Leegwater, P. A., Pronk, J. C. & van der Knaap, M. S. Leukoencephalopathy with vanishing white matter: from magnetic resonance imaging pattern to five genes. J. Child. Neurol. 18, 639–645 (2003).
Leegwater, P. A., Vermeulen, G., Könst, A. A., Naidu, S., Mulders, J., Visser, A. et al. Subunits of the translation initiation factor eIF2B are mutant in leukoencephalopathy with vanishing white matter. Nat. Genet. 29, 383–388 (2001).
van der Knaap, M. S., Leegwater, P. A., Könst, A. A., Visser, A., Naidu, S., Oudejans, C. B. et al. Mutations in each of the five subunits of translation initiation factor eIF2B can cause leukoencephalopathy with vanishing white matter. Ann. Neurol. 51, 264–270 (2002).
Scheper, G. C., Proud, C. G. & van der Knaap, M. S. Defective translation initiation causes vanishing of cerebral white matter. Trends Mol. Med. 12, 159–166 (2006).
Scheper, G. C., van der Knaap, M. S. & Proud, C. G. Translation matters: protein synthesis defects in inherited disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 8, 711–723 (2007).
Scali, O., Di Perri, C. & Federico, A. The spectrum of mutations for the diagnosis of vanishing white matter disease. Neurol. Sci. 27, 271–277 (2006).
Pronk, J. C., van Kollenburg, B., Scheper, G. C. & van der Knaap, M. S. Vanishing white matter disease: a review with focus on its genetics. Ment. Retard. Dev. Disabil. Res. Rev. 12, 123–128 (2006).
Maletkovic, J., Schiffmann, R., Gorospe, J. R., Gordon, E. S., Mintz, M., Hoffman, E. P. et al. Genetic and clinical heterogeneity in eIF2B-related disorder. J. Child. Neurol. 23, 205–215 (2008).
Wu, Y., Pan, Y., Du, L., Wang, J., Gu, Q., Gao, Z. et al. Identification of novel EIF2B mutations in Chinese patients with vanishing white matter disease. J. Hum. Genet. 54, 74–77 (2009).
Li, W., Wang, X., van der Knaap, M. S. & Proud, C. G. Mutations linked to leukoencephalopathy with vanishing white matter impair the function of the eukaryotic initiation factor 2B complex in diverse ways. Mol. Cell. Biol. 24, 3295–3306 (2004).
Hiyama, T. B., Ito, T., Imataka, H. & Yokoyama, S. Crystal structure of the alpha subunit of human translation initiation factor 2B. J. Mol. Biol. 392, 937–951 (2009).
Pavitt, G. D. & Proud, C. G. Protein synthesis and its control in neuronal cells with a focus on vanishing white matter disease. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 37 (Part 6), 1298–1310 (2009).
Richardson, J. P., Mohammad, S. S. & Pavitt, G. D. Mutations causing childhood ataxia with central nervous system hypomyelination reduce eukaryotic initiation factor 2B complex formation and activity. Mol. Cell. Bio. 24, 2352–2363 (2004).
van Kollenburg, B., Thomas, A. A., Vermeulen, G., Bertrand, G. A., van Berkel, C. G., Pronk, J. C. et al. Regulation of protein synthesis in lymphoblasts from vanishing white matter patients. Neurobiol. Dis. 21, 496–504 (2006).
Kantor, L., Harding, H. P., Ron, D., Schiffmann, R., Kaneski, C. R., Kimball, S. R. et al. Heightened stress response in primary fibroblasts expressing mutant eIF2B genes from CACH/VWM leukodystrophy patients. Hum. Genet. 118, 99–106 (2005).
van Kollenburg, B., van Dijk, J., Garbern, J., Thomas, A. A., Scheper, G. C., Powers, J. M. et al. Glia-specific activation of all pathways of the unfolded protein response in vanishing white matter disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 65, 707–715 (2006).
Kantor, L., Pinchasi, D., Mintz, M., Hathout, Y., Vanderver, A. & ElroyStein, O. A point mutation in translation initiation factor 2B leads to a continuous hyper stress state in oligodendroglial-derived cells. PLoS. One. 3, e3783 (2008).
van der Knaap, M. S., Barth, P. G., Gabreëls, F. J., Franzoni, E., Begeer, J. H., Stroink, H. et al. A new leukoencephalopathy with vanishing white matter. Neurology 48, 845–855 (1997).
Fabian, J. R., Kimball, S. R., Heinzinger, N. K. & Jefferson, L. S. Subunit assembly and guanine nucleotide exchange activity of eukaryotic initiation factor-2B expressed in Sf9 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 12359–12365 (1997).
Pavitt, G. D. eIF2B, a mediator of general and gene-specific translational control. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 33, 1487–1492 (2005).
Kubica, N., Jefferson, L. S. & Kimball, S. R. Eukaryotic initiation factor 2B and its role in alterations in mRNA translation that occur under a number of pathophysiological and physiological conditions. Prog. Nucleic. Acid. Res. Mol. Biol. 81, 271–296 (2006).
Welsh, G. I., Miller, C. M., Loughlin, A. J., Price, N. T. & Proud, C. G. Regulation of eukaryotic initiation factor eIF2B: glycogen synthase kinase-3 phosphorylates a conserved serine which undergoes dephosphorylation in response to insulin. FEBS Lett. 421, 125–130 (1998).
Gomez, E. & Pavitt, G. D. Identification of domains and residues within the epsilon subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2B (eIF2Bepsilon) required for guanine nucleotide exchange reveals a novel activation function promoted by eIF2B complex formation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20, 3965–3976 (2000).
Horzinski, L., Huyghe, A., Cardoso, M. C., Gonthier, C., Ouchchane, L., Schiffmann, R. et al. Eukaryotic initiation factor 2B (eIF2B) GEF activity as a diagnostic tool for EIF2B-related disorders. PLoS. One. 4, e8318 (2009).
Wang, X. & Proud, C. G. A novel mechanism for the control of translation initiation by amino acids, mediated by phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 2B. Mol. Cell. Biol. 28, 1429–1442 (2008).
Fogli, A., Schiffmann, R., Bertini, E., Ughetto, S., Combes, P., Eymard-Pierre, E. et al. The effect of genotype on the natural history of eIF2B-related leukodystrophies. Neurology 62, 1509–1517 (2004).
Fogli, A. & Boespflug-Tanguy, O. The large spectrum of eIF2B-related diseases. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 34 (Part 1), 22–29 (2006).
van der Knaap, M. S., van Berkel, C. G., Herms, J., van Coster, R., Baethmann, M., Naidu, S. et al. eIF2B-related disorders: antenatal onset and involvement of multiple organs. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 73, 1199–1207 (2003).
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the patients’ families. This work was funded by National Key Research Project ‘11–5’ (2006BAI05A07), National Key Research Project ‘973’, (2007CB5119004), Natural Science Foundation of China (30772355, 30872793), Natural Science Foundation of Beijing (7082093), and program for New Century Excellent Talents in University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leng, X., Wu, Y., Wang, X. et al. Functional analysis of recently identified mutations in eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2Bɛ (eIF2Bɛ) identified in Chinese patients with vanishing white matter disease. J Hum Genet 56, 300–305 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2011.9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2011.9