Abstract
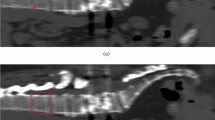
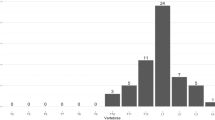
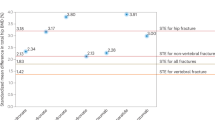
We previously reported 2 osteoporosis-susceptibility genes—formiminotransferase N-terminal sub-domain containing gene (FONG) and thrombospondin, type 1, domain-containing 7A (THSD7A)—in which we identified two common single-nucleotide polymorphisms, rs7605378 (FONG) and rs12673692 (THSD7A). The former was associated with a predisposition to osteoporosis and the latter with bone mineral density. To further elucidate the importance of these polymorphisms in the pathogenesis of osteoporosis, we examined their association with the incidence of vertebral fracture. DNA extracted from the renal cortex of 2427 consecutive Japanese autopsies (1331 men, mean age: 79 years; 1096 women, mean age: 82 years) were examined in this study. The presence or absence of vertebral fracture during each subject’s lifetime was determined by a thorough examination of the clinical records, as well as autopsy reports. After adjustments for sex and age at autopsy, logistic regression analysis revealed that homozygotes for the risk alleles of rs7605378 (A-allele) or rs12673629 (A-allele) possess an increased risk of vertebral fracture. The subjects simultaneously homozygous for both the risk alleles of rs7605378 (AA genotype) and rs12673629 (AA genotype) showed significantly higher risk of vertebral fracture (odds ratio 2.401, 95% confidence interval 1.305–4.416, P=0.0048) than those who had at least one non-risk allele of either rs7605378 (AC/CC genotypes) or rs12673629 (AG/GG genotypes). The results suggest that Japanese subjects homozygous for the risk alleles of rs7605378 and rs12673629 have a higher risk of vertebral fracture.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Reginster, J. Y. & Burlet, N. Osteoporosis: a still increasing prevalence. Bone 38, S4–S9 (2006).
Orimo, H., Hayashi, Y., Fukunaga, M., Sone, T., Fujiwara, S., Shiraki, M. et al. Diagnostic criteria for primary osteoporosis: year 2000 revision. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 19, 331–337 (2001).
Albagha, O. M. & Ralston, S. H. Genetic determinants of susceptibility to osteoporosis. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. North Am. 32, 65–81 (2003).
Peacock, M., Turner, C. H., Econs, M. J. & Foroud, T. Genetics of osteoporosis. Endocr. Rev. 23, 303–326 (2002).
Hirschhorn, J. N. & Gennari, L. Bona fide genetic associations with bone mineral density. N. Engl. J. Med. 358, 2403–2405 (2008).
Ralston, S. H. & de Crombrugghe, B. Genetic regulation of bone mass and susceptibility to osteoporosis. Genes Dev. 20, 2492–2506 (2006).
Kou, I., Takahashi, A., Urano, T., Fukui, N., Ito, H., Hosoi, T. et al. Common variants in FONG on chromosome 2q33.1 confer risk of osteoporosis in Japanese. PLoS One 6, e19641 (2011).
Mori, S., Kou, I., Sato, H., Emi, M., Ito, H., Hosoi, T. et al. Association of genetic variations of genes encoding thrombospondin, type 1, domain-containing 4 and 7A with low bone mineral density in Japanese women with osteoporosis. J. Hum. Genet. 53, 694–697 (2008).
Fuku, N., Mori, S., Murakami, H., Gando, Y., Zhou, H., Ito, H. et al. Association of 29C>T polymorphism in the transforming growth factor-β1 gene with lean body mass in community-dwelling Japanese population. Geriatric. Gerontol. Int. 12, 292–297 (2012).
Yoshimura, N., Kinoshita, H., Oka, H., Muraki, S., Mabuchi, A., Kawaguchi, H. et al. Cumulative incidence and changes in the prevalence of vertebral fractures in a rural Japanese community: a 10-year follow-up of the Miyama cohort. Archiv. Osteoporos. 1, 43–49 (2006).
Murley, L. L. & MacKenzie, R. E. The two monofunctional domains of octameric formiminotransferase-cyclodeaminase exist as dimers. Biochemistry 34, 10358–10364 (1995).
Morimoto, R., Uehara, S., Yatsushiro, S., Juge, N., Hua, Z., Senoh, S. et al. Secretion of L-glutamate from osteoclasts through transcytosis. EMBO J. 25, 4175–4186 (2006).
Young, G. D. & Murphy-Ullrich, J. E. The tryptophan-rich motifs of the thrombospondin type 1 repeats bind VLAL motifs in the latent transforming growth factor-beta complex. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 47633–47642 (2004).
Cohen, M. M. TGF-beta/Smad signaling system and its pathologic correlates. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 116, 1–10 (2003).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant (No 09042037) from the Leading Project for Personalized Medicine of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, H., Mori, S., Kou, I. et al. Association of the formiminotransferase N-terminal sub-domain containing gene and thrombospondin, type 1, domain-containing 7A gene with the prevalence of vertebral fracture in 2427 consecutive autopsy cases. J Hum Genet 58, 109–112 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2012.145
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2012.145
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Bone composition: relationship to bone fragility and antiosteoporotic drug effects
BoneKEy Reports (2013)