Abstract
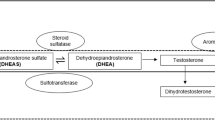
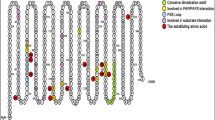
Steroid sulfatase (STS) is an enzyme that hydrolyzes steroid sulfates such as dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA-S) and estrone sulfate. STS has a key role in the synthesis of steroid hormones in placenta and breast cancer cells. Recently, we have identified six novel single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and one nonsynonymous SNP (V476M) in the STS gene in a Japanese population. To clarify the effects of SNPs in the 5′-flanking region or 5′ untranslated region on transcriptional activity, a reporter gene assay was conducted. In addition, DHEA-S desulfatase activity of a variant (Met at codon 476)-type enzyme was compared with that of the wild (Wd)-type enzyme in COS-1 cells. The transcriptional activities were significantly decreased (155A) and increased (−2837A and −1588C) in MCF-7 cells. On the other hand, no significant difference was found in expression levels of STS protein or specific activities of DHEA-S desulfation between Wd and the variant enzymes. This is the first report on the effects of various SNPs in the STS gene detected in Japanese healthy subjects.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Accession codes
References
Obaya, A. J. Molecular cloning and initial characterization of three novel human sulfatases. Gene 372, 110–117 (2006).
Warren, J. C. & French, A. P. Distribution of steroid sulfatase in human tissues. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 25, 278–282 (1965).
French, A. P. & Warren, J. C. Properties of steroid sulphatase and arylsulphatase activities of human placenta. Biochem. J. 105, 233–241 (1967).
Reed, M. J., Purohit, A., Woo, L. W., Newman, S. P. & Potter, B. V. Steroid sulfatase: molecular biology, regulation, and inhibition. Endocrin. Rev. 26, 171–205 (2005).
Duncan, L., Purohit, A., Howarth, N. M., Potter, B. V. & Reed, M. J. Inhibition of estrone sulfatase activity by estrone-3-methylthiophosphonate: a potential therapeutic agent in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 53, 298–303 (1993).
Billich, A., Nussbaumer, P. & Lehr, P. Stimulation of MCF-7 breast cancer cell proliferation by estrone sulfate and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate/ inhibition by novel non-steroidal steroid sulfatase inhibitors. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 73, 225–235 (2000).
Selcer, K. W., Kabler., H., Sarap, J., Xiao, Z. & Li, P. K. Inhibition of steryl sulfatase activity in LNCaP human prostate cancer cells. Steroids 67, 821–826 (2002).
Yen, P. H., Allen, E., Marsh, B., Mohandas, T., Wang, N. & Taggart, R. T. Cloning and expression of steroid sulfatase cDNA and the frequent occurrence of deletions in STS deficiency: implications for X-Y interchange. Cell 49, 433–454 (1987).
Hernandez-Guzman, F. G., Higashiyama, T., Osawa, Y. & Ghosh, D. Purification, characterization and crystallization of human placental estrone/dehydroepiandrosterone sulfates, a membrane-bound enzyme of endoplasmic reticulum. J. Steroid. Biochem. 78, 441–450 (2001).
Hernandez-Guzman, F. G., Higashiyama, T., Pangborm, W., Osawa, Y. & Ghosh, D. Structure of human estrone sulfatase suggests functional roles of membrane association. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 22989–22997 (2003).
Conary, J., Nauerth, A., Burns, G., Hasilki, A. & von Figura, K. Steroid sulfatase. Biosynthesis and processing in normal and mutant fibroblasts. Eur. J. Biochem. 158, 71–76 (1986).
Stein, C., Hille, A., Seidel, J., Rijnbout, S., Waheen, A., Schmidt, B. et al. Cloning and expression of human steroid-sulfatase. Membrane topology, glycosylation, and subcellular distribution in BHK-21 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 264, 13865–13872 (1989).
Alperin, E. S. & Shapiro, L. J. Characterization of point mutations in patients with X-linked ichthyosis. Effects on the structure and function of the steroid sulfatase protein. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 20756–20763 (1997).
Sugawara, T., Simazu, H., Hoshi, N., Fujimoto, Y., Nakajima, A. & Fujimoto, S. PCR diagnosis of X-linked ichthyosis: identification of a novel mutation (E560P) of the steroid sulfatase gene. Hum. Mutat. 15, 296 (2000).
Bonifas, J. M., Morely, B. J., Oakey, R. E., Kan, Y. W. & Epstein, E. H. Cloning of a cDNA for steroid sulfatase: frequent occurrence of gene deletions in patients with recessive X chromosome-linked ichthyosis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 84, 9248–9251 (1987).
Ballabio, A., Parenti, G., Garrozzo, R., Sebastio, O., Andria, G., Buckle, V. et al. Isolation and characterization of steroid sulfatase cDNA clone: genomic deletions in patients with X-chromosome-linked ichthyosis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 84, 4519–4523 (1987).
Oyama, N., Satoh, M., Iwatsuki, K. & Kaneko, F. Novel point mutations in the steroid sulfatase gene in patients with X-linked ichthyosis: transfection analysis using the mutant gene. J. Invest. Dermatol. 114, 1195–1199 (2000).
Elias, P. M., Williams, M. L., Maloney, M. E., Bonifas, J. A., Brown, B. E., Grayson, S. et al. Stratum corneum lipids in disorders of cornification. Steroid sulfatase and cholesterol sulfate in normal desquamation and the pathogenesis of recessive X-linked ichthyosis. J. Clin. Invest. 74, 1414–1421 (1984).
Liao, H., Waters, A. J., Goudie, D. R., Aitken, D. A., Graham, G., Smith, F. J. et al. Filaggrin mutations are genetic modifying factors exacerbating X-linked ichthyosis. J. Invest. Dermatol. 127, 2795–2798 (2007).
Winge, M. C., Hoppe, T., Liedén, A., Nordenskjöld, M., Vahlquist, A., Wahlgren, C. F. et al. Novel point mutation in the STS gene in a patient with X-linked recessive ichthyosis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 63, 62–64 (2011).
Brookes, K. J., Hawi, Z., Kirley., A., Barry, E., Gill, M. & Kent, L. Association of the steroid sulfatase (STS) gene with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 147B, 1531–1535 (2008).
Brookes, K. J., Hawi, Z., Park, J., Scott, S., Gill, M. & Kent, L. Polymorphisms of the steroid sulfatase (STS) gene are associated with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and influence brain tissue mRNA expression. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 153B, 1417–1424 (2010).
Utsumi, T., Yoshimura, N., Takeuchi, S., Ando, J., Maruta, M., Maeda, K. et al. Steroid sulfatase expression is an independent predictor of recurrence in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 59, 377–381 (1999).
Miyoshi., Y., Ando, A., Hasegawa, S., Ishitobi, M., Taguchi, T., Tamaki, Y. et al. High expression of steroid sulfatase mRNA predicts poor prognosis in patients with estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 9, 2288–2293 (2003).
Yoshimura, N., Harada, N., Bukholm, I., Karesen, R., Borresen-Dale, A. L. & Kristensen, V. N. Intratumoral mRNA expression of genes from the estradiol metabolic pathway and clinical and histopathological parameters of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 6, R46–R55 (2006).
Sarakibi, W. A. L., Mokbel, R., Salhab, M., Jiang, W. G., Reed, M. J. & Mokbel, K. The role of STS and OATP-B mRNA expression in predicting the clinical outcome in human breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 26, 4985–4990 (2006).
Stanway, S. J., Purohit, A., Woo, L. W., Sufi, S., Vigushin, D., Ward, R. et al. Phase I study of STX 64 (677 Coumate) in breast cancer patients: the first study of a steroid sulfatase inhibitor. Clin. Cancer Res. 12, 1585–1592 (2006).
Stanway, S. J., Delavault, P., Purohit, A., Woo, L. W., Thurieau, C., Potter, B. L. et al. Steroid sulfatase: a new target for the endocrine therapy of breast cancer. Oncologist 12, 370–374 (2007).
Matsumoto, J., Ariyoshi, N., Ishii, I. & Kitada, M. Six novel single nucleotide polymorphisms of the steroid sulfatase gene in a Japanese population. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 25, 403–407 (2010).
Sugawara, T., Nomura, E. & Hoshi, N. Both N-terminal and C-terminal regions of steroid sulfatase are important for enzyme activity. J. Endocrinol. 188, 365–374 (2006).
Li, X. M., Alperin, E. S., Salido, E., Gong, Y., Yen, P. H. & Shapiro, L. J. Characterization of the promoter region of human steroid sulfatase: a gene which escapes X inactivation. Somat. Cell Mol. Genet. 22, 105–117 (1996).
Valle, L. D., Toffolo, V., Nardi, A., Bernante, P., Di Loddo, R., Parnigotto, P. P. et al. Tissue-specific transcriptional initiation and activity of steroid sulfatase complementing dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate uptake and intracrine steroid activations in human adipose tissue. J. Endocrinol. 190, 129–139 (2006).
Valle, L. D., Toffolo, V., Nardi, A., Fiore, C., Armanini, D., Bernante, P. et al. The expression of the steroid sulfatase-encoding gene is driven by alternative first exons. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 107, 22–29 (2007).
Zaichuk, T., Ivancic, D., Scholtens, D., Schiller, C. & Khan, S. A. Tissue-specific transcripts of human steroid sulfatase are under control of estrogen signaling pathways in breast carcinoma. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 105, 76–84 (2007).
Nardi, A., Pomari, E., Zambon, D., Belvedere, P., Colombo, L. & Valle, L. D. Transcriptional control of human steroid sulfatase. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 115, 68–74 (2009).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid (No. 20390157) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science and Global COE Program (Global Center for Education and Research in Immune System Regulation and Treatment), MEXT, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsumoto, J., Ariyoshi, N., Ishii, I. et al. Functional characterization of seven single-nucleotide polymorphisms of the steroid sulfatase gene found in a Japanese population. J Hum Genet 58, 267–272 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2013.12
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2013.12