Abstract
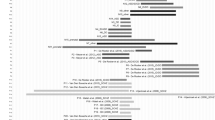
Here, we report on a patient with a 625 kb duplication in Xp22.12, detected by array comparative genomic hybridization (CGH). The duplicated region contains only one gene, RPS6KA3, that results in partial duplication. The same duplication was present in his mother and his maternal uncle. This partial duplication inhibits the RPS6KA3 expression, mimicking the effect of loss-of-function mutations associated with Coffin-Lowry syndrome (CLS). The phenotype of the patient here presented is not fully evocative of this syndrome because he does not present some of the facial, digital and skeletal abnormalities that are considered the main diagnostic features of CLS. This case is one of the few examples where RPS6KA3 mutations are associated with a non-specific X-linked mental retardation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Allen, R. C., Zoghbi, H. Y., Moseley, A. B., Rosenblatt, H. M. & Belmont, J. W. Methylation of HpaII and HhaI sites near the polymorphic CAG repeat in the human androgen-receptor gene correlates with X chromosome inactivation. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 51, 1229–1239 (1992).
Livak, K. J. & Schmittgen, T. D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real time quantitative PCR and the 2^[-delta delta C(T)] Method. Methods 25, 402–408 (2001).
Schmittgen, T. D. & Livak, K. J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CTmethod. Nat. Protoc. 3, 1101–1108 (2008).
Hauge, C. & Frödin, M. RSK and MSK in MAP kinase signalling. J. Cell. Sci. 119, 3021–3023 (2006).
Darcq, E., Koebel, P., Del Boca, C., Pannetier, S., Kirstetter, A. S., Garnier, J. M. et al. RSK2 signaling in brain habenula contributes to place aversion learning. Learn. Mem. 18, 574–578 (2011).
Poirier, R., Jacquot, S., Vaillend, C., Soutthiphong, A. A., Libbey, M., Davis, S. et al. Deletion of the Coffin-Lowry syndrome gene Rsk2 in mice is associated with impaired spatial learning and reduced control of exploratory behavior. Behav. Genet. 37, 31–50 (2007).
Mehmood, T., Schneider, A., Sibille, J., Marques Pereira, P., Pannetier, S., Ammar, M. R. et al. Transcriptome profile reveals AMPA receptor dysfunction in the hippocampus of the Rsk2-knockout mice, an animal model of Coffin-Lowry syndrome. Hum. Genet. 129, 9255–9269 (2011).
Pereira, P. M., Heron, D. & Hanauer, A. The first large duplication of the RSK2 gene identified in a Coffin-Lowry syndrome patient. Hum. Genet. 122, 541–543 (2007).
Thienpont, B., de Ravel, T., Van Esch, H., Van Schoubroeck, D., Moerman, P., Vermeesch, J. R. et al. Partial duplication of the ATRX gene cause the ATR-X syndrome. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 15, 1094–1097 (2007).
Hanauer, A. & Young, I. D. Coffin-Lowry syndrome clinical and molecular features. J. Med. Genet. 39, 705–713 (2002).
Pereira, P. M., Schneider, A., Pannetier, S. & Heron, D. Coffin–Lowry syndrome. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 18, 627–633 (2010).
Manouvrier-Hanu, S., Amiel, J., Jacquot, S., Merienne, K., Moerman, A., Coëslier, A. et al. Unreported RSK2 missense mutation in two male sibs with an unusually mild form of Coffin-Lowry Syndrome. J. Med. Genet. 36, 775–778 (1999).
Merienne, K., Jacquot, S., Pannetier, S., Zeniou, M., Bankier, A., Gecz, J. et al. A missense mutation in RPS6KA3 (RSK2) responsible for non-specific mental retardation. Nat. Genet. 22, 13–14 (1999).
Field, M., Tarpey, P., Boyle, J., Edkins, S., Goodship, J., Luo, Y. et al. Mutations in the RSK2(RPS6KA3) gene cause Coffin–Lowry syndrome and nonsyndromic X-linked mental retardation. Clin. Genet. 70, 509–515 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bertini, V., Cambi, F., Bruno, R. et al. 625 kb microduplication at Xp22.12 including RPS6KA3 in a child with mild intellectual disability. J Hum Genet 60, 777–780 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2015.106
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2015.106