Abstract
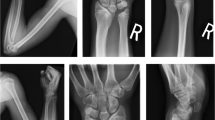
Heterozygous aberrations of SHOX gene have been reported to be responsible for Léri–Weill dyschondrosteosis (LWD) and small portion of idiopathic short stature. The study was established to assess effectiveness of using phenotype ‘scoring form’ in patients indicated for SHOX gene defect analysis. The submitted study is based on a retrospective group of 352 unrelated patients enrolled as a part of the routine diagnostic practice and analyzed for aberrations affecting the SHOX gene. All participants were scanned for deletion/duplication within the main pseudoautosomal region (PAR1) using the multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA) method. The phenotype ‘scoring form’ is used in our laboratory practice to preselect patients for subsequent mutation analysis of SHOX gene-coding sequences. The overall detection rate was 11.1% but there was a significant increase in frequency of SHOX gene defect positive with increasing achieved score (P<0.0001). The most frequent aberration was a causal deletion within PAR1. In three probands, MLPA analysis indicated a more complex rearrangement. Madelung deformity or co-occurrence of disproportionate short stature, short forearm and muscular hypertrophy had represented the most potent markers to determine the likelihood of SHOX gene defect detection. We conclude that appliance of phenotype ‘scoring form’ had saved excessive sample analysis and enabled effective routine diagnostic testing.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Gatta, V., Palka, C., Chiavaroli, V., Franchi, S., Cannataro, G., Savastano, M. et al. Spectrum of phenotypic anomalies in four families with deletion of the SHOX enhancer region. BMC Med. Genet. 15, 87 (2014).
Jorge, A. A., Souza, S. C., Nishi, M. Y., Billerbeck, A. E., Liborio, D. C., Kim, C. A. et al. SHOX mutations in idiopathic short stature and Leri-Weill dyschondrosteosis: frequency and phenotypic variability. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 66, 130–135 (2007).
Munns, C. J., Haase, H. R., Crowther, L. M., Hayes, M. T., Blaschke, R., Rappold, G. et al. Expression of SHOX in human fetal and childhood growth plate. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 89, 4130–4135 (2004).
Clement-Jones, M., Schiller, S., Rao, E., Blaschke, R. J., Zuniga, A., Zeller, R. et al. The short stature homeobox gene SHOX is involved in skeletal abnormalities in Turner syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 9, 695–702 (2000).
Fukami, M., Kato, F., Tajima, T., Yokoya, S. & Ogata, T. Transactivation function of an approximately 800-bp evolutionarily conserved sequence at the SHOX 3′ region: implication for the downstream enhancer. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 78, 167–170 (2006).
Durand, C., Bangs, F., Signolet, J., Decker, E., Tickle, C. & Rappold, G. Enhancer elements upstream of the SHOX gene are active in the developing limb. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 18, 527–532 (2010).
Durand, C., Roeth, R., Dweep, H., Vlatkovic, I., Decker, E., Schneider, K. U. et al. Alternative splicing and nonsense-mediated RNA decay contribute to the regulation of SHOX expression. PLoS ONE 6, e18115 (2011).
Ge, Y. & Porse, B. T. The functional consequences of intron retention: alternative splicing coupled to NMD as a regulator of gene expression. Bioessays 36, 236–243 (2014).
Rappold, G., Blum, W. F., Shavrikova, E. P., Crowe, B. J., Roeth, R., Quigley, C. A. et al. Genotypes and phenotypes in children with short stature: clinical indicators of SHOX haploinsufficiency. J. Med. Genet. 44, 306–313 (2007).
Schouten, J. P., McElgunn, C. J., Waaijer, R., Zwijnenburg, D., Diepvens, F. & Pals, G. Relative quantification of 40 nucleic acid sequences by multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification. Nucleic Acids Res. 30, e57 (2002).
Hirschfeldova, K., Solc, R., Baxova, A., Zapletalova, J., Kebrdlova, V., Gaillyova, R. et al. SHOX gene defects and selected dysmorphic signs in patients of idiopathic short stature and Leri-Weill dyschondrosteosis. Gene 491, 123–127 (2012).
Schmitt, K., Lazzeroni, L. C., Foote, S., Vollrath, D., Fisher, E. M., Goradia, T. M. et al. Multipoint linkage map of the human pseudoautosomal region, based on single-sperm typing: do double crossovers occur during male meiosis? Am. J. Hum. Genet. 55, 423–430 (1994).
May, C. A., Shone, A. C., Kalaydjieva, L., Sajantila, A. & Jeffreys, A. J. Crossover clustering and rapid decay of linkage disequilibrium in the Xp/Yp pseudoautosomal gene SHOX. Nat. Genet. 31, 272–275 (2002).
Veatch, O. J., Goldman, S. E., Adkins, K. W. & Malow, B. A. Melatonin in children with autism spectrum disorders: how does the evidence fit together? J. Nat. Sci. 1, e125 (2015).
Solc, R., Hirschfeldova, K., Kebrdlova, V. & Baxova, A. Analysis of common SHOX gene sequence variants and ~4.9-kb PAR1 deletion in ISS patients. J. Genet. 93, 505–508 (2014).
Rosilio, M., Huber-Lequesne, C., Sapin, H., Carel, J. C., Blum, W. F. & Cormier-Daire, V. Genotypes and phenotypes of children with SHOX deficiency in France. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 97, E1257–E1265 (2012).
Rappold, G. A., Fukami, M., Niesler, B., Schiller, S., Zumkeller, W., Bettendorf, M. et al. Deletions of the homeobox gene SHOX (short stature homeobox) are an important cause of growth failure in children with short stature. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 87, 1402–1406 (2002).
Acknowledgements
We thank the following doctors for prolonged collaboration: Eva Al Taji, Alice Baxova, Rastislav Beharka, Andrea Gregorova, Stanislava Kolouskova, Jan Lebl, Barbora Obermannova, Ales Panczak, Ivana Plasilova, Sarka Prasilova, Stepanka Pruhova, Antonin Sipek, Jana Soukalova, Zdenek Sumnik, Jirina Zapletalova, and Jana Zidovska.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hirschfeldova, K., Florianova, M., Kebrdlova, V. et al. Detection of SHOX gene aberrations in routine diagnostic practice and evaluation of phenotype scoring form effectiveness. J Hum Genet 62, 253–257 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2016.117
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2016.117
This article is cited by
-
Screening of the SHOX/PAR1 region using MLPA and miRNA expression profiling in a group of Egyptian children with non-syndromic short stature
Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics (2020)
-
Skeletal Dysplasias: What Every Bone Health Clinician Needs to Know
Current Osteoporosis Reports (2017)