Abstract
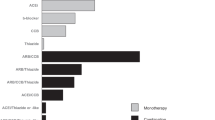
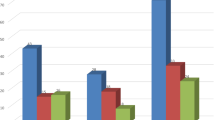
The prevalence of orthostatic hypotension (OH) in hypertensive patients ranges from 3 to 26%. Drugs are a common cause of non-neurogenic OH. In the present study, we retrospectively evaluated the medical records of 9242 patients with essential hypertension referred to our Hypertension Unit. We analysed data on supine and standing blood pressure values, age, sex, severity of hypertension and therapeutic associations of drugs, commonly used in the treatment of hypertension. OH was present in 957 patients (10.4%). Drug combinations including α-blockers, centrally acting drugs, non-dihydropyridine calcium-channel blockers and diuretics were associated with OH. These pharmacological associations must be administered with caution, especially in hypertensive patients at high risk of OH (elderly or with severe and uncontrolled hypertension). Angiotensin-receptor blocker (ARB) seems to be not related with OH and may have a potential protective effect on the development of OH.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mancia G, Fagard R, Narkiewicz K, Redon J, Zanchetti A, Bohm M et al. ESH/ESC Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). J Hypertens 2013; 31 (7): 1281–1357.
Vara Gonzalez L, Dominguez Rollan R, Fernandez Ruiz M, Josa Fernandez B, Ruiz Izquierdo F, Zabalo Amezqueta A et al. [Prevalence of orthostatic hypotension in elderly hypertensive patients in primary care]. Aten Primaria 2001; 28 (3): 151–157.
Fedorowski A, Burri P, Melander O . Orthostatic hypotension in genetically related hypertensive and normotensive individuals. J Hypertens 2009; 27 (5): 976–982.
Applegate WB DB, Black HR, Smith WM, Miller ST, Burlando AJ . Prevalence of postural hypotension at baseline in the Sistolic Hypertension in the Elderly Program (SHEP) cohort. J Am Geriatr Soc 1991; 39 (11): 1057–1064.
Strogatz DS, Keenan NL, Barnett EM, Wagner EH . Correlates of postural hypotension in a community sample of elderly blacks and whites. J Am Geriatr Soc 1991; 39 (6): 562–566.
Ooi WL, Barrett S, Hossain M, Kelley-Gagnon M, Lipsitz LA . Patterns of orthostatic blood pressure change and their clinical correlates in a frail, elderly population. JAMA 1997; 277 (16): 1299–1304.
Fedorowski A, Stavenow L, Hedblad B, Berglund G, Nilsson PM, Melander O . Orthostatic hypotension predicts all-cause mortality and coronary events in middle-aged individuals (The Malmo Preventive Project). Eur Heart J. 2010; 31 (1): 85–91.
Wu JS, Yang YC, Lu FH, Wu CH, Wang RH, Chang CJ . Population-based study on the prevalence and risk factors of orthostatic hypotension in subjects with pre-diabetes and diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009; 32 (1): 69–74.
Wu JS, Lu FH, Yang YC, Chang CJ . Postural hypotension and postural dizziness in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Arch Intern Med 1999; 159 (12): 1350–1356.
Spallone V, Morganti R, Fedele T, D’Amato C, Maiello MR . Reappraisal of the diagnostic role of orthostatic hypotension in diabetes. Clin Auton Res 2009; 19 (1): 58–64.
Franceschini N, Rose KM, Astor BC, Couper D, Vupputuri S . Orthostatic hypotension and incident chronic kidney disease: the atherosclerosis risk in communities Study. Hypertension 2010; 56 (6): 1054–1059.
Raiha I, Luutonen S, Piha J, Seppanen A, Toikka T, Sourander L . Prevalence, predisposing factors, and prognostic importance of postural hypotension. Arch Intern Med 1995; 155 (9): 930–935.
Rutan GH, Hermanson B, Bild DE, Kittner SJ, LaBaw F, Tell GS . Orthostatic hypotension in older adults. The Cardiovascular Health Study. CHS Collaborative Research Group. Hypertension 1992; 19 (6 Pt 1): 508–519.
Verwoert GC, Mattace-Raso FUS, Hofman A, Heeringa J, Stricker BHC, Breteler MMB et al. Orthostatic Hypotension and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in Elderly People: The Rotterdam Study. J Am Geriatr Soc 2008; 56 (10): 1816–1820.
Luukinen H, Koski K, Laippala P, Airaksinen KE . Orthostatic hypotension and the risk of myocardial infarction in the home-dwelling elderly. J Intern Med 2004; 255 (4): 486–493.
Kamaruzzaman S, Watt H, Carson C, Ebrahim S . The association between orthostatic hypotension and medication use in the British Women's Heart and Health Study. Age Ageing 2009; 39 (1): 51–56.
Masuo K, Mikami H, Ogihara T, Tuck ML . Changes in frequency of orthostatic hypotension in elderly hypertensive patients under medications. Am J Hypertens 1996; 9 (3): 263–268.
Poon IO, Braun U . High prevalence of orthostatic hypotension and its correlation with potentially causative medications among elderly veterans. J Clin Pharm Ther 2005; 30 (2): 173–178.
Fotherby MD, Potter JF . Orthostatic hypotension and anti-hypertensive therapy in the elderly. Postgrad Med J 1994; 70 (830): 878–881.
Luukinen H, Koski K, Laippala P, Kivela SL . Prognosis of diastolic and systolic orthostatic hypotension in older persons. Arch Intern Med 1999; 159 (3): 273–280.
Rose KM . Disorders of orthostatic blood pressure responses in hypertensive individuals: prognostic implications for cardiovascular disease? Am J Hypertens 2010; 23 (8): 817.
Fagard RH, De Cort P . Orthostatic hypotension is a more robust predictor of cardiovascular events than nighttime reverse dipping in elderly. Hypertension 2010; 56 (1): 56–61.
Forette F, McClaran J, Hervy MP, Bouchacourt P, Henry JF . Nicardipine in elderly patients with hypertension: a review of experience in France. Am Heart J 1989; 117 (1): 256–261.
Sica DA . Alpha1-adrenergic blockers: current usage considerations. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) 2005; 7 (12): 757–762.
Amerena J, Pappas S, Ouellet JP, Williams L, O'Shaughnessy D . ABPM comparison of the anti-hypertensive profiles of telmisartan and enalapril in patients with mild-to-moderate essential hypertension. J Int Med Res 2002; 30 (6): 543–552.
Oparil S, Dyke S, Harris F, Kief J, James D, Hester A et al. The efficacy and safety of valsartan compared with placebo in the treatment of patients with essential hypertension. Clin Ther 1996; 18 (5): 797–810.
Spinar J, Vitovec J, Pluhacek L, Spinarova L, Fischerova B, Toman J . First dose hypotension after angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor captopril and angiotensin II blocker losartan in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol 2000; 75 (2-3): 197–204.
Anthopoulos L, Apostolou T, Bonoris P, Foussas S, Lefkos N, Zombolos S . Comparative haemodynamic responses to the first dose of short- and long-acting ACE inhibitors in patients with congestive heart failure. Curr Med Res Opin 2001; 17 (4): 290–297.
Rose KM . Orthostatic hypotension predicts mortality in middle-aged adults: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. Circulation 2006; 114 (7): 630–636.
Rose KM, Tyroler HA, Nardo CJ, Arnett DK, Light KC, Rosamond W et al. Orthostatic hypotension and the incidence of coronary heart disease: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study. Am J Hypertens. 2000; 13 (6 Pt 1): 571–578.
Cleophas TJ . Paradoxical pressor effects of beta-blockers in standing elderly patients with mild hypertension: a beneficial side effect. Circulation 2002; 105 (14): 1669–1671.
Lowe FC . Coadministration of tamsulosin and three antihypertensive agents in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia: pharmacodynamic effect. Clin Ther 1997; 19 (4): 730–742.
Benvenuto LJ, Krakoff LR . Morbidity and mortality of orthostatic hypotension: implications for management of cardiovascular disease. Am J Hypertens 2011; 24 (2): 135–144.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Di Stefano, C., Milazzo, V., Totaro, S. et al. Orthostatic hypotension in a cohort of hypertensive patients referring to a hypertension clinic. J Hum Hypertens 29, 599–603 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2014.130
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2014.130
This article is cited by
-
Orthostatic hypotension and night-time dipper patterns in geriatric outpatients
Hypertension Research (2022)
-
Drug-Related Orthostatic Hypotension: Beyond Anti-Hypertensive Medications
Drugs & Aging (2020)