Abstract
Objective:
To compare transfusion requirements and erythropoietic response in preterms between schedules of rEPO administration once or three times per week, using the same weekly dose.
Study Design:
Prospective, randomized trial including infants weighing <1500 g at birth and/or were ⩽32 weeks’ gestation: Group 1 (60 infants) received subcutaneous rEPO at 250 units kg−1 per dose, three times weekly for 6 weeks; Group 2 (59 infants), at 750 units kg−1 per dose, once weekly for 6 weeks. Efficacy was evaluated based on the transfusion requirement, hemoglobin changes, reticulocyte counts, serum transferrin receptor (sTfR) and serum ferritin. The frequency of adverse effects was registered in both groups.
Result:
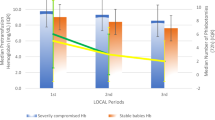
A total of 13 infants were transfused in each group (relative risk: 0.98; 95% confidence interval: 0.4 to 2.3). Phlebotomy loss and red blood cell transfusion volumes received were similar in both groups. Hemoglobin levels were lower at end of study in Group 2 (10.6±1.5 g dl−1 versus 11.5±1.4 g dl−1; P<0.003). At end of study, reticulocyte counts and sTfR values increased and serum ferritin values decreased, without significant differences between the two groups. Incidence of complications was similar in both groups.
Conclusion:
The once-weekly rEPO schedule for very low birth weight infants proved as effective as the three-times-weekly schedule, in relation to erythropoietic stimulus and transfusion requirement.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bierer R, Peceny MC, Hartenberger CH, Ohls RK . Erythropoietin concentrations and neurodevelopmental outcome in preterm infants. Pediatrics 2008; 118 (3): e635–e640.
Fauchere JC, Dame C, Vonthein R, Koller B, Arri S, Wolf M et al. An approach to using recombinant erythropoietin for neuroprotection in very preterm infants. Pediatrics 2008; 122 (2): 375–382.
Maier RF, Obladen M, Scigalla P, Linderkamp O, Duc G, Hieronimi G et al. The effect of epoietin beta (recombinant human erythropoietin) on the need for transfusion in very-low-birth-weight infants. European Multicentre Erythropoietin Study. N Eng J Med 1994; 330: 1173–1178.
Meyer MP, Meyer JH, Commerford A, Hann FM, Sive AA, Moller G et al. Recombinant human erythropoietin in the treatment of the anemia of prematurity: results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Pediatrics 1994; 93 (6): 918–923.
Shannon KM, Keith JF, Mentzer WC, Ehrenkranz RA, Brown MS, Widness JA et al. Recombinant human erythropoietin stimulates erythropoiesis and reduce erythrocyte transfusion in very low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 1995; 95: 1–8.
Carbonell-Estrany X, Figueras-Aloy J, Alvarez E . Erythropoietin and prematurity—where do we stand? J Perinat Med 2005; 33 (4): 277–286.
Strauss RG . Controversies in the management of the anemia of prematurity using single-donor red blood cell transfusions and/or recombinant human erythropoietin. Transf Med Rev 2006; 20 (1): 34–44.
Halperin DS, Wacker P, Lacourt G, Felix M, Babel JF, Aapro M et al. Effects of recombinant human erythropoietin in infants with the anemia of prematurity: a pilot study. J Pediatr 1990; 116: 779–786.
Kotto-Kome AC, García MG, Calhoun DA, Christensen RD . Effect of beginning recombinant erythropoietin treatment within the first week of life among very-low-birth-weight neonates, on ‘early’ and ‘late’ erythrocyte transfusion: a metanalysis. J Perinatol 2004; 24: 24–29.
Ohlsson A, Aher SM . Early erythropoietin for preventing red blood cell transfusion in preterm and/or low birth weight infants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2006; 3: CD004863.
Aher SM, Ohlsson A . Late erythropoietin for preventin red blood cell transfusión in preterm and/or low bith weight infants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2006; 3: CD004864.
Aher SM, Ohlsson A . Early versus late arythropoietin for preventing red blood cell transfusion in preterm and/or low birth weight infants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2006; 3: CD004865.
Morita M, Ohneda O, Yamashita T, Takahashi S, Suzuki N, Nakajima O et al. HLF/HIF-2α is a key factor in retinopathy of prematurity in association with erythropoietin. EMBO J 2003; 22 (5): 1134–1146.
Manzoni P, Maestri A, Gomirato G, Takagi H, Watanabe B, Matsui S . Erythropoietin as a retinal angiogenic factor. N Engl J Med 2005; 353 (20): 2190–2191.
Romagnoli C, Zecca E, Gallini F, Girlando P, Zuppa AA . Do recombinant human erythropoietin and iron supplementation increase the risk of retinopathy of prematurity? Eur J Pediatr 2000; 159: 627–628.
Maier RF, Obladen M, Kattner E, Natzschka J, Messer J, Ragazzoni BM et al. High versus low dose erythropoietin in extremely low birth weight infanst. J Pediatr 1998; 132: 870–886.
Donato H, Vain N, Rendo P, Vivas N, Prudent L, Larguía M et al. Effect of early versus late administration of human recombinant erythropoietin on transfusion requeriments in premature infants: results of a randomizes, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. Pediatrics 2000; 105: 1066–1072.
Langer J, Obladen M, Dame C . Urinary loss of erythropoietin after intravenous versus subcutaneous epoietin-beta in preterm infants. J Pediatr 2008; 152: 728–730.
Pasha YZ, Ahmadpour-Kacho M, Hajiamadi M, Hosseini MB . Enteral erhthropoietin increases plasma erythropoietin level in preterm infants: a randomized controlled trial. Indian Pediatr 2008; 45 (1): 25–28.
Maier RF, Obladen M, Müller-Hansen I, Kattner E, Merz U, Arlettaz R et al. Early treatment with arythropoietin â ameliorates anemia and reduces transfusion requeriments in infants with birth weights below 1000 g. J Pediatr 2002; 141 (1): 8–15.
Ohls RK, Ehrenkranz RA, Wright LL, Lemons JA, Korones SB, Stoll BJ et al. Effects of early erythropoietin therapy on the transfusion requeriments of preterm infants below 1250 g birth weight: a multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. Pediatrics 2001; 108 (4): 934–942.
Türker G, Sarper N, Gökalp AS, Usluer H . The effect of early recombinant erythropoietin and enteral iron supplementation on blood transfusion in preterm infants. Am J Perinatol 2005; 22 (8): 449–455.
Brown MS, Keith JF . Comparison between two and five doses a week of recombinant human erythropoietin for anemia of prematurity: a randomized trial. Pediatrics 1999; 104: 210–215.
Arif B, Ferhan K . Recombinant human erythropoietin therapy in low-bithweight preterm infants: A prospective controlled study. Pediatr Int 2005; 47: 67–71.
ICROP Panel. An International Classification of Retinopathy of Prematurity Pediatrics 1984; 74 (1): 127–133.
Ohls RK, Veerman MW, Christensen RD . Pharmacokinetics and effectiveness of recombinan erythropoietin administeres to preterm infants by continuous infusion in total parenteral nutrition solution. J Pediatr 1996; 128: 518–523.
Soubasi V, Kremenopoulos G, Diamanti E, Tsantali C, Sarafidis K, Tsakiris D . Follow-up of very low birth weight infants after erythropoietin treatment to prevent anemia of prematurity. J Pediatr 1995; 127: 291–297.
Lauterbach R, Kachlick P, Pawlik D, Bajorek I . Evaluation of treatment results for anemia of prematurity treated with various doses of human recombinant erythropoietin. Pediatr Pol 1995; 70: 739–744.
Bahar A, Karademir F . Recombinant human erythropoietin therapy in low-birthweight preterm infants: a prospective controlled study. Pediatr Int 2005; 47: 67–71.
Rocha VL, Benjamin AC, Procianoy RS . O efeito da eritropoietina humana recombinante no tratamento da anemia da prematuridade. J Pediatr (Rio J) 2001; 77 (2): 75–83.
Krallis N, Cholevas V, Mavridis A, Georgiou I, Bourantas K, Andronikou S . Effect of recombinant human erythropoietin in preterm infants. Eur J Haematol 1999; 63: 7176.
Kivivuori SM, Virtanen M, Raivio KO, Viinikka L, Siimes MA . Oral iron is sufficient for erythropoietin treatment of very low birth-weight infants. Eur J Pediatr 1999; 158: 147–151.
Beguin Y . Soluble transferrin receptor for the evaluation of erythropoiesis and iron status. Clin Chim Acta. 2003; 329: 9–22.
Kling PJ, Roberts RA, Widness JA . Plasma transferrin receptor levels and indices of erythropoiesis and iron status in healthy term infants. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 1998; 20: 309–314.
Ohls RK, Christensen RD . Recombinant erythropoietin compared with erythrocyte transfusion in the treatment of anemia of prematurity. J Pediatr 1991; 119: 781–788.
Moro M, Figueras J, Fernández C, Doménech E, Guzmán J, Jiménez R et al. Análisis de resultados de los datos de morbimortalidad del grupo SEN 1500. Informe anual 2005. Available at http://www.sen.org.Consulted 29-October-2009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
RCT was registered by the RCT Committee of our Hospital and was approved on 29 January 2004 with number 36/2003.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vázquez López, M., Llamas, M., Galera, R. et al. Comparison between one and three doses a week of recombinant erythropoietin in very low birth weight infants. J Perinatol 31, 118–124 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2010.80
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2010.80