Figure 1
From: X-exome sequencing of 405 unresolved families identifies seven novel intellectual disability genes
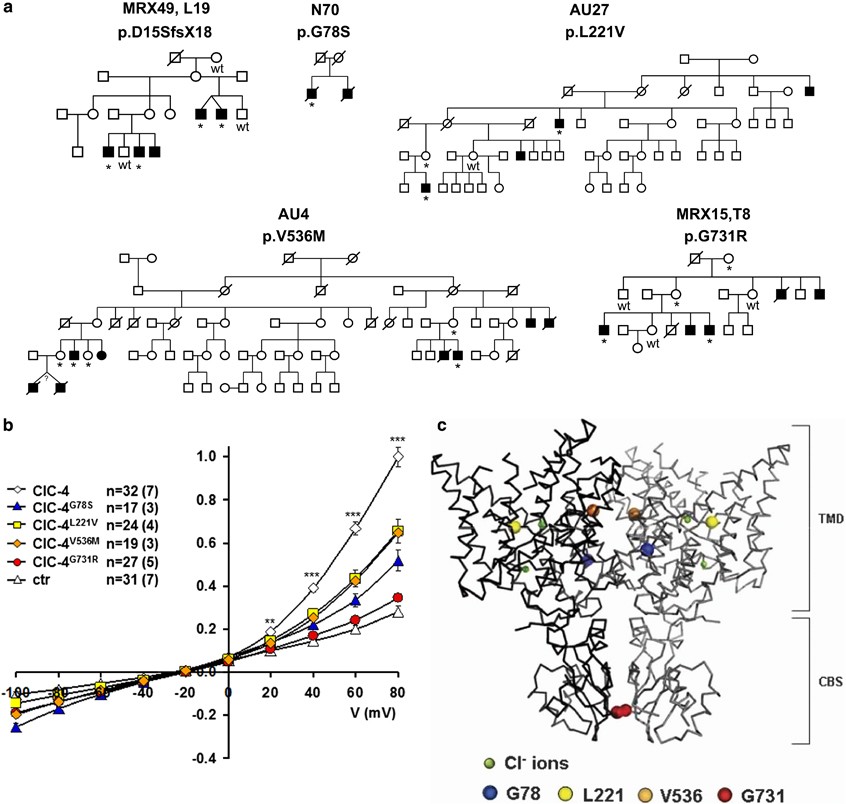
Apparently pathogenic CLCN4 mutations identified in the screen and functional analysis of the missense variants. (a) Pedigrees of families with CLCN4 likely pathogenic mutations. Individuals tested for co-segregation with X-linked intellectual disability (XLID) and the results are indicated, *=mutation carrier, wt=subject does not carry the mutation. (b) Current–voltage relationships of the electrogenic Cl−/H+ exchanger protein ClC-4 and its mutants expressed in Xenopus oocytes, shown as mean values of normalized steady-state currents from several oocytes (numbers indicated in figure, in parentheses: number of frogs). Compared with the strongly outwardly-rectifying currents of wild-type ClC-4,36, 121 currents were much smaller or even absent with CIC-4 mutant proteins carrying p.Gly78Ser, p.Leu221Val, p.Val536Met and p.Gly731Arg substitutions. ctr, non-injected controls; error bars, s.e.m. Two-tailed t-test was used for statistical comparisons (**P<0.01, ***P<0.001 compared with wild-type ClC-4 currents). (c) Analogous positions of amino acids mutated in ClC-4 highlighted in the crystal structure of CmClC.63 Amino acids are displayed as spheres in colors like in (b). The small green spheres represent Cl− ions. CLC transporters form dimers of identical subunits (shown in different shades) and include a transmembrane domain (TMD) and two cytosolic cystathionine-β-synthase (CBS) domains.
