Abstract
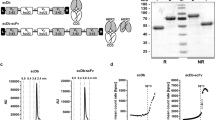
Clinical development of bispecific antibodies (BsAb) has been effectively stymied by the lack of efficient production methods. We therefore attempted to produce a humanized BsAb fragment using an expression system that has proved very successful for secretion of monospecific Ab fragments from E. coli. An anti-p185HER2/anti-CD3 BsF(ab′)2 was first recast into the diabody format and then periplasmically secreted from E. coli grown to high cell density in a fermentor. The diabody was recovered in very high yield (up to 935 mg/1) after protein A purification and predominantly (≥ 80 %) as a dimer as judged by size exclusion chromatography. Diabody dimers were found to be mainly functional heterodimers (∼75%) by titration with p185HER2 extracellular domain. The diabody binds p185HER2 extracellular domain and human T lymphocytes with affinities close to those of the parent BsF(ab′)2. Furthermore, the diabody is capable of simultaneous binding to tumor cells overexpressing p185HER2 and CD3 on T cells as shown by cellular rosetting. The diabody is equally potent as the parent BsF(ab′)2 in retargeting IL-2 activated T-enriched peripheral blood lymphocytes to lyse tumor cells overexpressing p185HER2.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Malavasi, F., De Monte, L.B., Funaro, A., Magnm, E., Bomno, L.D., Momo, M., Manani, M., Horenstein, A. and Natah, P.G. 1993. Cell surface receptors and bispecific monoclonal antibodies the link between science and medical oncology. Year Immunol. 7: 74–80.
Fanger, M.W., Morganelh, P.M. and Guyre, P.M. 1993. Use of bispeciflc antibodies in the therapy of tumors, p. 181–194. In: Immunoconjugate Therapy of Hematologic Maligancies, Rosen, Steven, T and Kuzel, T M (Eds) Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Milstein, C. and Cuello, A.C. 1983. Hybrid hybndomas and their use in immunohistochenustry. Nature 305: 537–540.
Brennan, M., Davison, P.F. and Paulus, H. 1985. Preparation of bispecific anti bodies by chemical recombination of monoclonal immunoglobulm Gl fragments. Science. 229: 81–83.
Glenme, M.J., McBride, H.M., Worth, A.T. and Stevenson, G.T. 1987. Preparation and performance of bispecific F(ab′γ)2 antibody containing thiother-hnked Fab′γ fragments. J. Immunol. 139: 2367–2375.
Holhger, H. and Winter, G. 1993. Engineering bispecific antibodies. Curr. Opin. Biotech. 4: 446–449.
Carter, P., Ridgway, J. and Zhu, Z. 1995. Toward the production of bispecific antibody fragments for clinical applications. J. Hematotherapy. 4: 463–470.
Holhger, P., Prospero, T. and Winter, G. 1993. “Diabodies” small bivalent and bispecific antibody fragments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90: 6444–6448.
Desplancq, D., King, D.J., Lawson, A.D.G. and Mountain, A. 1994. Multi menzation behaviour of single chain Fv variants for the tumor binding antibody B72.3. Protein Eng. 7: 1027–1033.
Whitlow, M., Filpula, D., Rollence, M.L., Feng, S.L. and 1994. Wood, J.F. Multivalent Fvs characterization of single chain Fv oligomers and preparation of a bispecific Fv. Protein Eng. 7: 1017–1026.
Shalaby, M.R., Shepard, H.M., Presta, L., Rodngues, M., Beverley, P.C.L., Feldmann, M. and Carter, P. 1992. Development of humanized bispecific antibodies reactive with cytotoxic lymphocytes and tumor cells overexpressing the HER2 protooncogene. J. Exp. Med. 175: 217–225.
Rodngues, M.L., Shalaby, M.R., Werther, W., Presta, L. and Carter, P. 1992. Engineering a humanized bispecific F(ab′)2 fragment for improved binding to T cells. Int. J. Cancer(Suppl.) 7: 45–50.
Shalaby, M.R., Carter, P., Maneval, D., Giltman, D. and Kotts, C. 1995. Bispecific HER2 x CD3 antibodies enhance T cell cytotoxicity in vitroand localize to HER2overexpressing xenografts in nude mice. Clin. Immunol. Immunopath. 74: 185–192.
Zhu, Z., Lewis, G.D. and Carter, P. 1995. Engineering high affinity humanized anti-pl85HHO/anti CD3 bispecific F(ab′)2 for efficient lysis of pl85Hoa overexpression tumor cells. Int. J. Cancer. 62: 319–324.
Carter, P., Kelley, R.F., Rodngues, M.L., Snedecor, B., Covarrubias, M., Velhgan, M.D., Wong, W.L.T., Rowland, A.M., Kotts, C.E., Carver, M.E., Yang, M., Bourell, J.H., Shepard, H.M. and Henner, D. 1992. High level Eschenchw coli expression and production of a bivalent humanized antibody fragment. Bio/Technology. 10: 163–167.
Bolivar, F., Rodnguez, R.L., Greene, P.J., Betlach, M.C., Heyneker, H.L., Boyer, H.W., Crosa, J.H. and Falkow, S. 1977. Construction and characten zation of new cloning vehicles II A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 2: 95–113.
Chang, C.N., Kuang, W.J. and Chen, E.Y. 1986. Nucleotide sequence of the alkaline phosphatase gene of Escherichia coli . Gene. 44: 121–125.
Picken, R.N., Mazaitis, A.J., Maas, W.K., Rey, M. and Heyneker, H. 1983. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for heat-stable enterotoxin II of Escherichia coli . Infect. Immun. 42: 269–275.
Rodngues, M.L., Presta, L., Kotts, C., Wirth, C., Moredenti, J., Osaka, G., Wong, W.L.T., Nuijens, A., Blackburn, B. and Carter, P., 1995. Development of a humanized disulfide stabilized anti-p185HER2 Fv-β-lactamase fusion pro tem for activation of a cephalosponn doxorubicin prodrug. Cancer. Res. 55: 63–70.
Rodngues, M.L., Snedecor, B., Chen, C., Wong, W.L.T., Garg, S., Blank, G.S., Maneval, D. and Carter, P. 1993. Engmeenng Fab′ fragments for efficient F(ab′)2 formation in Escherichia coli and for improved in vivo stability. J. Immunol. 151: 6954–6991.
Pensic, O., Webb, P.A., Holhger, P., Winter, G. and Williams, R.L. 1994. Crystal structure of a diabody, a bivalent antibody fragment. Structure. 2: 1217–1226.
Eigenbrot, C., Randal, M., Presta, L., Carter, P. and Kossiakoff, A. 1993. X-ray structures of the antigen binding domains from three vanants of humanized anti-pl85HER2 antibody 4D5 and comparison with molecular modeling. J. Mol. Biol. 229: 969–995.
Ulrich, H.D., Yang, P.Y., Patten, P.A., Romesberg, F.E. and Schultz, P.G. 1995. Expression studies of catalytic antibodies.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USAIn press.
Knappik, A. and Plückthun, A. 1995. Engineered turns of recombinant antibody improve its in vivo folding. Protein Engin. 8: 81–89.
Carter, P., Presta, L., Gorman, C.M., Ridgway, J.B.B., Henner, D., Wong, W.L.T., Rowland, A.M., Kotts, C., Carver, M.E. and Shepard, H.M. 1992. Humamzation of an anti-pl85HER2 antibody for human cancer therapy.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89: 4285–4289.
Sanger, F., Nicklen, S. and Coulson, A.R. 1977. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 74: 5463–5467.
Fendly, B.M., Kotts, C., Vetterlem, D., Lewis, G.D., Wuiget, M., Carver, M.E., Watson, S.R., Sarup, J., Saks, S., Ullnch, A. and Shepard, H.M. 1990. The extracellular domain of HER2/neu is a potential immunogen for active specific immunotherapy of breast cancer. J. Biol. Resp. Mod. 9: 449–455.
Zapata, G., Ridgway, J.B.B., Mordenti, J., Osaka, J., Wong, W.L.T., Bennett, G. and Carter, P. 1995. Engmeenng linear F(ab′)2 fragments. Protein Engineering.In press.
Kelley, R.F. and O'Connell, M.P. 1993. Thermodynamics of an antibody functional epitope. Biochemistry. 32: 6828–6835.
Zhu, Z. and Carter, P. 1995. Identification of heavy chain residues in a humanized anti CD3 antibody important for efficient antigen binding and T cell activation. J. Immunol. 155: 1903–1910.
Kabat, E.A., Wu, T.T., Perry, H.M., Gottesman, K.S. and Foeller, C. 1991. Sequences of Proteins of Immunological Interest, Ed 5 National Institutes of Health Bethesda, MD.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Z., Zapata, G., Shalaby, R. et al. High Level Secretion of a Humanized Bispecific Diabody from Escherichia coli. Nat Biotechnol 14, 192–196 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0296-192
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0296-192
This article is cited by
-
A semi high-throughput method for screening small bispecific antibodies with high cytotoxicity
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Disulfide-stabilized diabody antiCD19/antiCD3 exceeds its parental antibody in tumor-targeting activity
Cellular Oncology (2012)
-
Bispecific antibody and its clinical applications in cancer
Chinese Science Bulletin (2001)