Abstract
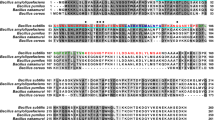
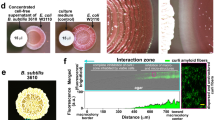
We report the construction and use of a new system for the direct screening of recombinant clones after transformation. The system uses a Bacillus subtilis-Escherichia coli shuttle vector that carries the B. subtilis structural gene for α-amylase. Insertion of foreign DNA into this gene results in a loss of amylolytic activity in the host cells that can be assayed using a simple and inexpensive staining procedure.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rüther, U. 1980. Construction and properties of a new cloning vehicle allowing direct screening for recombinant plasmids. Mol. Gen. Genet. 178: 475–477.
Balbás, P., Soberón, K., Merino, E., Zurita, M., Lomeli, H., Valle, F., Flores, N. and Bolivar, F. 1986. Plasmid pBR322 and its special purpose derivatives—a review. Gene 50: 3–40.
Souza, M.B.N.S. 1986. Clonagem molecular e expressão do gene de alfa-amilase de Bacillus sp. MSc Thesis, Brasília University, Brasília, DF, Brazil.
Maniatis, T., Fritsch, E.F. and Sambrook, J. 1982. Molecular Cloning, a Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York.
Briggs, M.S. and Gierasch, L.M. 1986. Molecular mechanisms of protein secretion: the role of the signal sequence. Adv. Prot. Chem. 38: 109–180.
Thomsen, K.K. 1983. Mouse α-amylase synthesized by Saccharomyces cerevisiae is released into the culture medium. Carlsberg Res. Commun. 48: 545–555.
Astolfi-Filho, S., Galembeck, E.V., Faria, J.B. and Schenberg-Frascino, A.C. 1986. Stable yeast transformants that secrete functional α-amylase encoded by cloned mouse pancreatic cDNA. Bio/Technology 4: 311–315.
Rothstein, S.J., Lazarus, C.M., Smith, W.E., Baulcombe, D.C. and Gatenby, A.A. 1984. Secretion of a wheat α-amylase expressed in yeast. Nature 308: 662–665.
Twigg, A.J. and Sherrat, D. 1980. Trans-complementable copy-number mutants of plasmid ColE1. Nature 283: 216–218.
Gryczan, T.J., Contente, S. and Dubnau, D. 1978. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus plasmids introduced by transformation into Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 134: 318–329.
Bolivar, F. and Bachman, K. 1979. Plasmids of Escherichia coli as cloning vectors. Meth. Enzymol. 68: 245–267.
Miller, J. 1972. Experiments in Molecular Genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York.
Birnboim, H.C. and Doly, J. 1979. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids. Res. 7: 1513–1523.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ikuta, N., Souza, M., Valencia, F. et al. The α-Amylase Gene as a Marker for Gene Cloning: Direct Screening of Recombinant Clones. Nat Biotechnol 8, 241–242 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0390-241
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0390-241
This article is cited by
-
Development of cloning vectors and transformation methods for Amycolatopsis
Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology (2003)