Abstract
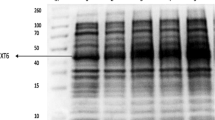
A gene encoding bovine acidic fibroblast growth factor has been chemically synthesized, cloned and expressed as a biologically active protein in Escherichia coli. The 440 base pair gene was assembled by enzymatic ligation of 16 oligonucleotides and cloned into a pBR322–derived expression plasmid downstream of the hybrid tac promoter. Expressed recombinant mitogen comigrated with the native bovine brain–derived protein as detected by Western blot immunological analysis. The expression product of the synthetic gene has been purified to apparent homogeneity and demonstrates a mitogenic activity for Balb/c 3T3 cells in the presence of heparin equivalent to the brain–derived mitogen. These results demonstrate the feasibility of expressing large amounts of functional acidic fibroblast growth factor in bacteria and provide a system for site–specific mutagenesis of the protein.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Esch, F., Baird, A., Ling, N., Ueno, N., Hill, F., Denoroy, L., Klepper, R., Gospodarowicz, D., Bohlen, P., and Guillemin, R. 1985. Primary structure of bovine pituitary basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and comparison with the amino-terminal sequence of bovine brain acidic FGF. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82: 6507–6511.
Huang, J.S., Huang, S.S., and Kuo, M.-D. 1986. Bovine brain derived growth factor, purification and characterization of its interaction with the responsive cells. J. Biol. Chem. 261: 11600–11607.
Walicke, P., Cowan, W. M., Ueno, N., Baird, A., and Guillemin, R. 1986. Fibroblast growth factor promotes survival of dissociated hippocampal neurons and enhances neurite extension. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83: 3012–3016.
Morrison, R.S., Sharma, A., de Vellis, J., and Bradshaw, R.A. 1986. Basic fibroblast growth factor supports the survival of cerebral cortical neurons in primary culture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83: 7537–7541.
Thomas, K.A., Rios-Candelore, M., Gimenez-Gallego, G., DiSalvo, J., Bennett, C., Rodkey, J., and Fitzpatrick, S. 1985. Pure brain-derived acidic fibroblast growth factor is a potent angiogenic vascular endothelial cell mitogen with sequence homology to interleukin 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82: 6409–6413.
Lobb, R.R., Alderman, E.M., and Fett, J.W. 1985. Induction of angiogenesis by bovine class 1 heparin-binding growth factor. Biochemistry 24: 4969–4973.
Thomas, K.A., Rios-Candelore, M., and Fitzpatrick, S. 1984. Purification and characterization of acidic fibroblast growth factor from bovine brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81: 357–361.
Lemmon, S.K. and Bradshaw, R.A. 1983. Purification and partial characterization of bovine fibroblast growth factor. J. Cell Biochem. 21: 195–208.
Bohlen, P., Baird, A., Esch, F., Ling, N., and Gospodarowicz, D. 1984. Isolation and partial molecular characterization of pituitary fibroblast growth factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81: 5364–5368.
Lobb, R.R. and Fett, J.W. 1984. Purification of two distinct growth factors from bovine neural tissue by heparin affinity chromatography. Biochemistry 23: 6295–6299.
Gospodarowicz, D., Cheng, J., Ge-Ming, L., Baird, A., and Bohlen, P. 1984. Isolation of brain fibroblast growth factor by heparin-sepharose affinity chromatography: identity with pituitary fibroblast growth factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81: 6963–6967.
Maciag, T., Mehlman, T., Freisel, R., and Schreiber, A. 1984. Heparin binds endothelial cell growth factor, the principal endothelial cell mitogen in bovine brain. Science 225: 932–935.
Gimenez-Gallego, G., Conn, G., Hatcher, V.B., and Thomas, K.A. 1986. Human brain-derived acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors: Amino terminal sequences and specific mitogenic activities. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 135: 541–548.
Schreiber, A.B., Kenney, J., Kowalski, J., Thomas, K.A., Gimenez-Gallego, G., Rios-Candelore, M., DiSalvo, J., Barritault, D., Courty, J., Courtois, Y., Moenner, M., Loret, C., Burgess, W. H., Mehlman, T., Friesel, R., Johnson, W., and Maciag, T. 1985. A unique family of endothelial cell polypeptide mitogens: The antigenic and receptor cross-reactivity of bovine endothelial cell growth factor, brain-derived acidic fibroblast growth factor and eye-derived growth factor II. J. Cell Biol. 101: 1623–1626.
Baird, A., Esch, F., Gospodarowicz, D., and Guillemin, R. 1985. Retina- and eye-derived endothelial cell growth factors: Partial molecular characterization and identity with acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors. Biochemistry 24: 7855–7860.
D'Amore, P.A. and Klagsbrun, M. 1984. Endothelial cell mitogens derived from retina and hypothalamus: Biochemical and biological similarities. J. Cell Biol. 99: 1545–1549.
Lobb, R., Sasse, J., Sullivan, R., Shing, Y., D'Amore, P., Jacobs, J., and Klagsbrun, M. 1986. Purification and characterization of heparin-binding endothelial cell growth factors. J. Biol. Chem. 261: 1924–1928.
Pettmann, B., Weibel, M., Sensenbrenner, M., and Labourdette, G. 1985. Purification of two astroglial growth factors from bovine brain. FEBS Lett. 189: 102–108.
Crabb, J.W., Armes, L.G., Carr, S.A., Johnson, C.M., Roberts, G.D., Bordali, R.S., and McKeehan, W.L. 1986. Complete primary structure of prostatropin, a prostate epithelial cell growth factor. Biochemistry 25: 4988–4993.
Gimenez-Gallego, G., Rodkey, J., Bennett, C., Rios-Candelore, M., DiSalvo, J., and Thomas, K.A. 1985. Brain-derived acidic fibroblast growth factor: Complete amino acid sequence and homologies. Science 230: 1385–1388.
Esch, F., Ueno, N., Baird, A., Hill, F., Denoroy, L., Ling, N., Gospodarowicz, D., and Guillemin, R. 1985. Primary structure of bovine brain acidic fibroblast growth factor (FGF). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 133: 544–562.
Strydom, D.J., Harper, J.W., and Lobb, R.R. 1986. Amino acid sequence of bovine brain-derived class 1 heparin-binding growth factor. Biochemistry 25: 945–951.
Thomas, K.A. and Gimenez-Gallego, G. 1986. Fibroblast growth factors: broad spectrum mitogens with potent angiogenic activity. Trends. Biochem. Sci. 11: 81–84.
Bohlen, P., Esch, F., Baird, A., Jones, K.L., and Gospodarowicz, D. 1985. Human brain fibroblast growth factor, isolation and partial chemical characterization. FEBS Lett. 185: 177–181.
Gimenez-Gallego, G., Conn, G., Hatcher, V.B., and Thomas, K.A. 1986. The complete amino acid sequence of human brain-derived acidic fibroblast growth factor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 138: 611–617.
Jaye, M., Howk, R., Burgess, G.A., Ricca, W., Chiu, I.-M., Ravera, M.W., O'Brien, S.J., Modi, W.S., Maciag, T., and Drohan, W.N. 1986. Human endothelial cell growth factor: Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and chromosome localization. Science 233: 541–l545.
Abraham, J.A., Mergia, A., Whang, J.L., Tumolo, A., Friedman, J., Hjerrild, K.A., Gospodarowicz, D., and Fiddes, J.C. 1986. Nucleotide sequence of a bovine clone encoding the angiogenic protein, basic fibroblast growth factor. Science 233: 545–548.
Grantham, R., Gautier, C., Gouy, M., Jacobzone, M., and Mercier, R. 1981. Codon catalog usage is a genome strategy modulated for gene expressivity. Nucl. Acids Res. 9: r43–r75.
Maxam, A.M. and Gilbert, W. 1980. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol 65: 499–560.
deBoer, H.A., Comstock, L.J., and Vasser, M. 1983. The tac promoter: A functional hybrid derived from the trp and lac promoters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80: 21–25.
Amman, E., Brosius, J., and Ptashne, M. 1983. Vectors bearing a hybrid trp-lac promoter useful for regulated expression of cloned genes in Escherichia coli . Gene 25: 167–178.
Roberts, D.M., Crea, R., Malecha, M., Alvarado-Urbina, G., Chiarello, R.H., and Watterson, D.M. 1985. Chemical synthesis and expression of a calmodulin gene designed for site-specific mutagenesis. Biochemistry 24: 5090–5098.
Vieira, J. and Messing, J. 1982. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7- derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene 19: 259–268.
Shine, J. and Dalgarno, L. 1974. The 3′ terminal sequence of the Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 71: 1342–1346.
Thornton, S.C., Mueller, S.N., and Levine, E.M. 1983. Human endothelial cells: use of heparin in cloning and long-term serial cultivation. Science 222: 623–625.
Schreiber, A.B., Kenney, J., Kowalski, W.J., Friesel, R., Mehlman, T., and Maciag, T. 1985. Interaction of endothelial cell growth factor with heparin: Characterization by receptor and antibody recognition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82: 6138–6142.
Terranova, V.P., DiFlorio, R., Lyall, R.M., Hic, S., Friesel, R., and Maciag, T. 1985. Human endothelial cells are chemotactic to endothelial cell growth factor and heparin. J. Cell Biol. 101: 2330–2334.
Thomas, K., Gimenez-Gallego, G., DiSalvo, J., Linemeyer, D., Kelly, L., Menke, J., Mellin, T., and Busch, R. 1987. Structure and Activities of Acidic Fibroblast Growth Factor, p. 9–12. In: Angiogenesis, Mechanisms and Pathobiology (Current Communications in Molecular Biology). Rifkin, D. B. and Klagsbrun, M. (eds.). Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
Bolivar, F., Rodriguez, R.L., Greene, P.J., Betlach, M.C., Heynecker, H.L., Boyer, H.W., Crosa, J.H., and Falkow, S. 1977. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene 2: 95–113.
Yanisch-Perron, C., Vieira, J., and Messing, J. 1985. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mpl8 and pUC19 vectors. Gene 33: 103–119.
Low, B. 1968. Formation of merodiploids in matings with a class of Rec recipient strains of Escherichia coli . Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 60: 160–167.
Matteucci, M.D. and Caruthers, M.H. 1981. Synthesis of deoxyoligonucleotides on a polymer support. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 103: 3185–3191.
Beaucage, S.L. and Caruthers, M.H. 1981. Deoxynucleoside phosphoramidites—A new class of key intermediates for deoxypolynucleotide synthesis. Tetrahedron Lett. 22: 1859–1862.
Maniatis, T., Fritsch, E.F., and Sambrook, J. 1982. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
Towbin, H., Staehelin, T., and Gordon, J. 1979. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76: 4350–4354.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Linemeyer, D., Kelly, L., Menke, J. et al. Expression in Escherichia coli of a Chemically Synthesized Gene for Biologically Active Bovine Acidic Fibroblast Growth Factor. Nat Biotechnol 5, 960–965 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0987-960
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0987-960
This article is cited by
-
The heparan sulfate co-receptor and the concentration of fibroblast growth factor-2 independently elicit different signalling patterns from the fibroblast growth factor receptor
Cell Communication and Signaling (2010)
-
Microprojectile bombardment of Laminaria japonica gametophytes and rapid propagation of transgenic lines within a bubble-column bioreactor
Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture (PCTOC) (2009)