Abstract
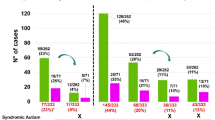
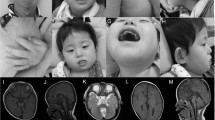
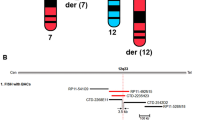
A major challenge for human genetics is to identify new causes of mental retardation, which, although present in about 3% of individuals, is unexplained in more than half of all cases. We have developed a strategy to screen for the abnormal inheritance of subtelomeric DMA polymorphisms in individuals with mental retardation and have detected three abnormalities in 99 patients with normal routine karyotypes. Pulsed–field gel electrophoresis and reverse chromosome painting showed that one case arose from an interstitial or terminal deletion and two from the de novo inheritance of derivative translocation chromosomes. At least 6% of unexplained mental retardation is accounted for by these relatively small chromosomal abnormalities, which will be an important resource in the characterization of the genetic basis of neurodevelopment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rutter, M., Tizard, J. & Whitmore, K. Education, Health and Behaviour (Longiman, London, 1970).
Birch, H.G., Richardson, S.A., Baird, D., Horabin, G. & Ilsley, R. Mental subnormality in the community:a clinical and epidemiological study. (Willams and Wilkins, Baltimore, 1970).
Drillien, C.M., Jameson, S. & Wilkinson, E.M. Studies in mental handicap. Part I: Prevalence and distribution by clinical type and severity of defects. Arch. Dis. Childh. 41, 529–538 (1966).
McDonald, A.D. Severely retarded children in Quebec: prevalence, causes and care. Am. J. Men. Defic. 78, 205–215 (1973).
Gustavson, K.-H., Hagberg, B., Hagberg, G. & Sars, K. Severe mental retardation in a Swedish county. II. Etiologic and pathogenetic aspects of children bom 1959–1970. Neuropäediatrie 8, 293–304 (1977).
Laxova, R., Ridler, M.A.C. & Bowen-Bravery, M. An etiological survey of the severely retarded Hertfordshire children who were born between January 1, 1965 and December 31, 1967. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1, 75–86 (1977).
Elwood, J.H. & Darragh, P.M. Severe mental handicap in Northern Ireland. J. men. Defic. Res. 25, 147–155 (1981).
McQueen, P.C., Spence, M.W., Winsor, E.J.T., Garner, J.B. & Pereira, L.H. Causal origins of major mental handicap In the Canadian maritime provinces. Dev. Med. and Child Neurol. 28, 697–707 (1986).
Hagberg, B., Hagberg, G., Lewerth, A. & Lindberg, U. Mild mental retardation in Swedish school children-1. Prevalence. Acta paediat scand. 70, 441–444 (1981).
Hagberg, B., Hagberg, G., Lewerth, A. & Lindberg, U. Mild mental retardation in Swedish school children-II. Etiologic and pathogenetic aspects. Acta paediat. scand. 70, 445–452 (1981).
Einfeld, S.L. Clinical assessment of 4500 developmentally delayed individuals. J. men. Defic. Res. 28, 129–142 (1984).
Broman, S., Nichols, P.L., Shaughnessy, P. & Kennedy, W. Retardation in Young Children: A Developmental Study of Cognitive Deficit (Erlbaum, New Jersey, 1987).
Lamont, M.A. & Dennis, N.R. Aetiology of mild mental retardation. Arch. Dis. Childh. 63, 1032–1038 (1988).
Bundey, S., Thake, A. & Todd, J. The recurrence risks for mild idiopathic mental retardation. J. med. Genet. 26, 260–266 (1989).
Gostason, R., Wahlstrom, J., Johannisson, T. & Holmqvist, D. Chromosomal aberrations in the mildly mentally retarded. J. men. Defic. Res. 35, 240–246 (1991).
Wllkie, A.O.M. Detection of cryptic chromosomal abnormalities in unexplained mental retardation: a general strategy using hypervariable subtelomeric DNA polymorphisms. Am. J. hum. Genet. 53, 688–701 (1993).
Lamb, J. et al. Detection of breakpoints in submicroscopic chromosomal translocation, illustrating an important mechanism for genetic disease. Lancet ii, 819–824 (1989).
Wilkie, A.O.M. et al. Clinical features and molecular analysis of the a thalassemia/mental retardation syndromes. I. Cases due to deletions involving chromosome band 16p13.3. Am. J. hum. Genet. 46, 1112–1126 (1990).
Altherr, M.R. et al. Molecular confirmation of Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome with a subtle translocation of chromosome 4. Am. J. hum. Genet. 49, 1235–1242 (1991).
Goodship, J. et al. A submicroscopic translocation, t(4;10), responsible for recurrent Wolf-Hirschhom syndrome identified by allele loss and fluorescent in situ hybridisation. J. med. Genet. 29, 451–454 (1992).
Kuwano, A., Ledbetter, S.A., Dobyns, W.B., Emanuel, B.S. and Ledbetter, D.H. Detection of deletions and cryptic translocations in Miller-Dieker syndrome by in situ hybridization. Am. J. hum. Genet. 49, 707–714 (1991).
Overhauser, J. et al. Prenatal diagnosis and carrier detection of a cryptic translocation by using DNA markers from the short arm of chromosome 5. Am. J. hum. Genet. 45, 296–303 (1989).
Lamb, J. et al. De novo truncation of chromosome 16p and healing with (TTAGGG)n in the α-thalassemia/mental retardation syndrome (ATR-16). Am. J. hum. Genet. 52, 668–676 (1993).
Nicholls, R.D. Genomic imprinting and uniparental disomy in Angelman and Prader Willi syndromes: a review. Am. J. med. Genet. 46, 16–25 (1993).
Henry, I. et. al. Somatic mosaicism for partial isodisomy in Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome: a postfertilization event. Eur. J. hum. Genet. 1, 19–29 (1993).
Armour, J.A.L., Povey, S., Jeremiah, S. & Jeffreys, A.J. Systematic cloning of human minisatellites from ordered array charomid libraries. Genomics 8, 501–512 (1990).
Vergnaud, G. et al. The use of synthetic tandem repeats to isolate new VNTR loci. Cloning of a human hypermutable sequence. Genomics 11, 135–144 (1991).
NIH/CEPH Collaborative Mapping Group. Acomprehensive genetic linkage map of the human genome. Science 258, 67–86 (1992).
Armour, J.A.L., Crosier, M. & Jeffreys, A.J. A highly polymorphic mlnisatellite (pMS626)on chromosome 13 (D13S103). Nucl. Acids Res. 19, 5447 (1991).
Cooke, H.J., Brown, W.R.A. & Rappold, G.A. Hypervariable telomeric sequences from the human sex chromosomes are pseudoautosomal. Nature 317, 687–692 (1985).
Armour, J.A.L., Crosier, M. & Jeffreys, A.J. Human minisatelllte alleles detectable only after PCR amplification. Genomics 12, 116–124 (1992).
Royle, N.J., Armour, J.A., Crosier, M. & Jeffreys, A.J. Abnormal segregation of alleles in CEPH pedigree DNAs arising from allele loss in lymphoblastoid DNA. Genomics 15, 119–122 (1993).
James, R.S. et al. A systematic search for uniparental disomy in carriers of chromosomal translocations. Eur. J. hum. Genet. 2, 83–95 (1994).
Hing, A.V., Helms, C. & Donis-Keller, H. VNTR and microsatellite polymorphisms within the subtelomeric region of 7q. Am. J. hum. Genet. 53, 509–517 (1993).
Ledbetter, D.H., Cryptic translocations and telomere integrity. Am. J . hum. Genet. 52, 451–456 (1992).
Reed, P.W. et al. Chromosome-specific mlcrosatellite sets for fluorescence-based, semi-automated genome mapping. Nature Genet. 7, 390–395 (1994).
Nakahori, Y. et al. Molecular heterogeneity of the fragile X syndrome. Nucl. Acids Res. 19, 4355–4359 (1991).
Wilkie, A.O.M. et al. Stable length polymorphism of up to 260 kb at the tip of the short arm of human chromosome 16. Cell 64, 595–606 (1991).
Bucan, M. et al. Physical maps of 4p16.3, the area expected to contain the Huntington disease mutation. Genomics 6, 1–15 (1990).
Bates, G.P. et al. Defined physical limits of the Huntington disease gene candidate region. Am. J. hum. Genet. 49, 7–16 (1991).
Henke, A., Fischer, C. & Rappold, G.A. Genetic map of the human pseudoautosomal region reveals a high rate of recombination in female meioses at the Xp telomere. Genomics 18, 478–485 (1993).
Takahashi, E.-i., YamaKawa, K., Nakamura, Y. & Hori, T. A high-resolution cytogenetic map of human chromosome 3: localization of 291 new cosmid markers by direct R-banding fluorescence in situ hybridization. Genomics 13, 1047–1055 (1992).
Nesslinger, N.J. et al. Clinical, cytogenetic, and molecular characterization of seven patients with deletions of chromosome 22q13. 3. Am. J. hum. Genet. 54, 464–472 (1994).
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F. & Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. (2nd edn., New York, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 1989).
Buckle, V.J. & Rack, K., Fluorescent in situ hybridisation. In Human Genetic Diseases: A Practical Approach 2nd edn (ed. Davies, K.E.) 59–80 (IRL Press, Oxford, 1993).
Rack, K.A. et al. Characterization of three de novo derivative chromosomes 16 by ‘reverse chromosome painting’ and molecular analysis. Am. J. hum. Genet. 52, 987–997 (1993).
Telenius, H. et al. Degenerate oligonucleotide-primed PCR: general amplification of target DNA by a single degenerate primer. Genomics 13, 718–725 (1992).
MacDonald, M.E. et al. Clustering of multiallele DNA markers near the Huntington's disease gene. J. clin. Invest. 84, 1013–1016 (1989).
Wong, Z., Wilson, V., Patel, I., Povey, S. & Jeffreys, A.J. Characterisation of a panel of highly variable minisatellites cloned from human DNA. Ann. hum. Genet. 51, 269–288 (1987).
Crosier, M., Armour, J.A.L. & Jeffreys, A.J. A highly polymorphic minisatellite (pMS627) on chromosome 14 (D14S44). Nucl. Acids Res. 19, 5446 (1991).
Jarman, A.P., Nicholls, R.D., Weatherall, D.J., Clegg, J.B. & Higgs, D.R. Molecular characterization of a hypervariable region downstream of the human α-globin gene cluster. EMBO J. 5, 1857–1863 (1986).
Armour, J.A.L., Wong, Z., Wilson, V., Royle, N.J. & Jeffreys, A.J. Sequences flanking the repeat arrays of human minisatellites: Association with tandem and dispersed repeat elements. Nucl. Acids Res. 17, 4925–4935 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Flint, J., Wilkie, A., Buckle, V. et al. The detection of subtelomeric chromosomal rearrangements in idiopathic mental retardation. Nat Genet 9, 132–140 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0295-132
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0295-132
This article is cited by
-
Phelan-McDermid syndrome: a classification system after 30 years of experience
Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases (2022)
-
An ethical analysis of divergent clinical approaches to the application of genetic testing for autism and schizophrenia
Human Genetics (2022)
-
Association of SHANK Family with Neuropsychiatric Disorders: An Update on Genetic and Animal Model Discoveries
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2022)
-
Prenatal diagnosis of a 4.5-Mb deletion at chromosome 4q35.1q35.2: Case report and literature review
Molecular Cytogenetics (2021)
-
Strukturelle Chromosomenstörungen bei Intelligenzminderung
Medizinische Genetik (2018)