Abstract
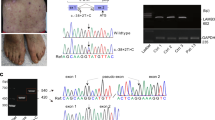
Junctional epidermolysis bullosa (JEB) is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by blister formation within the dermal–epidermal basement membrane. Genes for the lamina lucida protein, kalinin/laminin 5, have been proposed as candidates for some forms of JEB, based on immunofluorescence analysis recognizing kalinin epitopes. We studied the cDNA of laminin γ2 chain for mutations in JEB using heteroduplex analysis. One patient showed a homozygous splice site mutation while another was heterozygous for a deletion–insertion, resulting in a premature termination codon in one allele. Our data implicate mutations in the laminin γ2 chain gene (LAMC2) in some forms of JEB.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lin, A.N. & Carter, D.M. (eds) Epidermolysis bullosa. Basic and clinical aspects (Springer-Verlag, New York, 1992).
Fine, J.D. et al. Revised clinical and laboratory criteria for subtypes of inherited epidermolysis bullosa. A consensus report by the subcommittee on diagnosis and classification of the National Epidermolysis Bullosa Registry. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 24, 119–135 (1991).
Epstein, E.H., Jr. Molecular genetics of epidermolysis bullosa. Science 256, 799–804 (1992).
Uitto, J. & Christiano, A.M. Molecular genetics of the cutaneous basement membrane zone. Perspectives on epidermolysis bullosa and other blistering skin diseases. J. clin. Invest. 90, 687–692 (1992).
Bonifas, J.M., Rothman, A.-L. & Epstein, E. Epidermolysis bullosa simplex: evidence in two families for keratin gene abnormalities. Science 254, 1201–1205 (1991).
Coulombe, P.A. et al. Point mutations in human keratin 14 genes of epidermolysis bullosa simplex patients: genetic and functional analyses. Cell 66, 1301–1311 (1991).
Hovnanian, A. et al. A missense mutation in the rod domain of keratin 14 associated with recessive epidermolysis bullosa simplex. Nature Genet. 3, 327–332 (1993).
Humphries, M.M. et al. A mutation (Met->Arg) in the type I keratin (K14) gene responsible for autosomal dominant epidermolysis bullosa simplex. Hum. Mut. 2, 37–42 (1993).
Dong, W., Ryynänen, M. & Uitto, J. Identification of a leucine-to-proline mutation in the keratin 5 gene in a family with the generalized Köbner type of epidermolysis bullosa simplex. Hum. Mut. 2, 94–102 (1993).
Lane, E.B. et al. A mutation in the conserved helix termination peptide of keratin 5 in hereditary skin blistering. Nature 356, 244–246 (1992).
Fuchs, E. & Coulombe, P.A. Of mice and men: genetic skin diseases of keratin. Cell 69, 899–902 (1992).
Ryynänen, M. et al. Human type VII collagen: genetic linkage of the gene (COL7A1) on chromosome 3 to dominant dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Am. J. hum. Genet. 49, 797–803 (1991).
Ryynänen, M. et al. Genetic linkage of type VII collagen (COL7A1) to dominant dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa in families with abnormal anchoring fibrils. J. clin. Invest. 89, 974–980 (1992).
Al-Imara, L. et al. Linkage of autosomal dominant dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa in three British families to the marker D3S2 close to the COL7A1 locus. J. med. Genet. 29, 381–382 (1992).
Gruis, N.A. et al. Genetic linkage between the collagen VII (COL7A1) gene and the autosomal dominant form of dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa in two dutch kindreds. J. invest. Dermatol. 99, 528–530 (1992).
Christiano, A.M. et al. A missense mutation in type VII collagen in two affected siblings with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Nature Gentet. 4, 62–66 (1993).
Verrando, P., Pisani, A. & Ortonne, J.-P. The new basement membrane antigen recognized by the monoclonal antibody GB3 is a large size weight glycoprotein: modulation of its expression by retinoic acid. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 942, 45–56 (1988).
Rousselle, P., Lunstrum, G.P., Keene, D.R. & Burgeson, R.E. Kalinin: an epithelium-specific basement membrane adhesion molecule that is a component of anchoring filaments. J. Cell Biol. 114, 567–576 (1991).
Carter, W.G., Ryan, M.C. & Gahr, P.J. Epiligrin, a new cell adhesion ligand for integrin α3β1 in epithelial basement membranes. Cell 65, 599–610 (1991).
Marinkovich, M.P. et al. The basement membrane proteins kalinin and nicein are structurally and immunologically identical. Lab. Invest. 69, 295–299 (1993).
Verrando, P. et al. Monoclonal antibody GB3 defines a widespread defect of several basement membranes and a keratinocyte dysfunction in patients with lethal junctional epidermolysis bullosa. Lab. Invest. 64, 85–91 (1991).
Burgeson, R.E. et al. A new nomenclature for laminins. Matrix Biol. (in the press).
Timpl, R. & Dziadek, M. Structure, development and molecular pathology of basement membranes. Int. Rev. Exp. Pathol. 29, 1–112 (1986).
Kallunki, P. et al. A truncated laminin chain homologous to the B2 chain: structure, spatial expression, and chromosomal assignment. J. Cell Biol. 119, 679–693 (1992).
Marinkovich, M.P., Lunstrum, G.P., Keene, D.R. & Burgeson, R.E. The dermal-epidermal junction of human skin contains a novel laminin variant. J. Cell Biol. 119, 695–703 (1992).
Marinkovich, P. Genetics of basement membrane diseases. Arch. Derm. 219, 1557–1565 (1993).
Meneguzzi, G. et al. Kalinin is abnormally expressed in epithelial basement membranes of Herlitz's junctional epidermolysis bullosa patients. Exp. Dermatol. 1, 221–229 (1992).
Sanger, F., Nicklen, S. & Coulson, A.R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 5463–5467 (1977).
Green, M.R. Biochemical mechanisms of constitutive and regulated pre-mRNA splicing. Ann. Rev. Cell Biol. 7, 559–599 (1991).
Urlaub, G., Mitchell, P.J., Ciudad, C.J. & Chasin, L.A. Nonsense mutations in the dihydrofolate reductase gene affect RNA processing. Molec. Cell. Biol. 9, 2868–2880 (1989).
McIntosh, I., Hamosh, A. & Dietz, H.C. Nonsense mutations and diminished mRNA levels. Nature Genet. 4, 219 (1993).
Dietz, H.C. et al. The skipping of constitutive exons in vivo induced by nonsense mutations. Science 259, 680–683 (1993).
Mayer, L.I. et al. A single EGF-like motif of laminin is responsible for high affinity nidogen binding. EMBO J. 12, 1879–1885 (1993).
Aeschlimann, D., Paulsson, M. & Mann, K. Identification of GIn726 in nidogen as the amine acceptor in transglutaminase-catalyzed cross-linking of laminin-nidogen complexes. J. biol. Chem. 267, 11316–11321 (1992).
Marinkovich, M.P., Lunstrum, G.P. & Burgeson, R.E. The anchoring filament protein kalinin is synthesized and secreted as a high molecular weight precursor. J. biol. Chem. 267, 17900–17905 (1992).
Verrando, P. et al. A new laminin variant defined by the cDNA sequence of the 100 kDa subunit of the basement membrane protein nicein (BM-600)/ kalinin. Eur. J. Biochem. (in the press).
Olsen, D.R. et al. Human laminin: cloning and sequence analysis of cDNAs encoding A, B1 and B2 chains, and the expression of corresponding genes in human skin and cultured cells. Lab. Invest. 60, 772–782 (1989).
Olsen, D.R. et al. Human nidogen: cDNA cloning, cellular expression, and mapping of the gene to chromosome 1q43. Am. J. hum. Genet. 44, 876–885 (1989).
Olsen, D.R. & Uitto, J. Differential expression of type IV procollagen and laminin genes by fetal vs. adult skin fibroblasts in culture: determination of subunit mRNA steady-state levels. J. invest. Dermatol. 93, 127–131 (1989).
Chen, Y.Q., Mauviel, A., Ryynänen, J., Sollberg, S. & Uitto, J. Type VII collagen gene expression by human skin fibroblasts and keratinocytes in culture. Influence of donor age and cytokine responses. J. invest. Dermatol. 102, 205–209 (1994).
Christiano, A.M. & Uitto, J. DNA-based prenatal diagnosis of heritable skin diseases. Arch. Derm. 129, 1455–1459 (1993).
Verlinsky, Y. & Kuliev, A.M. (eds) Preimplantation diagnosis of genetic diseases. A new technique in assisted reproduction. (Wiley-Liss, New York, 1993).
Richards, B. et al. Multiplex PCR amplification from the CFTR gene using DNA prepared from buccal brushes/swabs. Hum. molec. Genet. 2, 159–163 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pulkkinen, L., Christiano, A., Airenne, T. et al. Mutations in the γ2 chain gene (LAMC2) of kalinin/laminin 5 in the junctional forms of epidermolysis bullosa. Nat Genet 6, 293–298 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0394-293
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0394-293
This article is cited by
-
Defective perlecan-associated basement membrane regeneration and altered modulation of transforming growth factor beta in corneal fibrosis
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2022)
-
Chemically defined and xenogeneic-free culture method for human epidermal keratinocytes on laminin-based matrices
Nature Protocols (2020)
-
Biologically relevant laminin as chemically defined and fully human platform for human epidermal keratinocyte culture
Nature Communications (2018)
-
Genome-wide meta-analysis implicates mediators of hair follicle development and morphogenesis in risk for severe acne
Nature Communications (2018)
-
Laminin: loss-of-function studies
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2017)